 Posted by Paul Ruiz – Senior Developer Relations Engineer, and Kris Tonthat – Technical Writer
Posted by Paul Ruiz – Senior Developer Relations Engineer, and Kris Tonthat – Technical Writer

Earlier this year, we previewed on-device text-to-image generation with diffusion models for Android via MediaPipe Solutions. Today we’re happy to announce that this is available as an early, experimental solution, Image Generator, for developers to try out on Android devices, allowing you to easily generate images entirely on-device in as quickly as ~15 seconds on higher end devices. We can’t wait to see what you create!
There are three primary ways that you can use the new MediaPipe Image Generator task:
- Text-to-image generation based on text prompts using standard diffusion models.
- Controllable text-to-image generation based on text prompts and conditioning images using diffusion plugins.
- Customized text-to-image generation based on text prompts using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) weights that allow you to create images of specific concepts that you pre-define for your unique use-cases.
Models
Before we get into all of the fun and exciting parts of this new MediaPipe task, it’s important to know that our Image Generation API supports any models that exactly match the Stable Diffusion v1.5 architecture. You can use a pretrained model or your fine-tuned models by converting it to a model format supported by MediaPipe Image Generator using our conversion script.
You can also customize a foundation model via MediaPipe Diffusion LoRA fine-tuning on Vertex AI, injecting new concepts into a foundation model without having to fine-tune the whole model. You can find more information about this process in our official documentation.
If you want to try this task out today without any customization, we also provide links to a few verified working models in that same documentation.
Image Generation through Diffusion Models
The most straightforward way to try the Image Generator task is to give it a text prompt, and then receive a result image using a diffusion model.
Like MediaPipe’s other tasks, you will start by creating an options object. In this case you will only need to define the path to your foundation model files on the device. Once you have that options object, you can create the ImageGenerator.
val options = ImageGeneratorOptions.builder().setImageGeneratorModelDirectory(MODEL_PATH).build()
imageGenerator = ImageGenerator.createFromOptions(context, options)
|
|
After creating your new ImageGenerator, you can create a new image by passing in the prompt, the number of iterations the generator should go through for generating, and a seed value. This will run a blocking operation to create a new image, so you will want to run it in a background thread before returning your new Bitmap result object.
val result = imageGenerator.generate(prompt_string, iterations, seed)
val bitmap = BitmapExtractor.extract(result?.generatedImage())
|
|
In addition to this simple input in/result out format, we also support a way for you to step through each iteration manually through the execute() function, receiving the intermediate result images back at different stages to show the generative progress. While getting intermediate results back isn’t recommended for most apps due to performance and complexity, it is a nice way to demonstrate what’s happening under the hood. This is a little more of an in-depth process, but you can find this demo, as well as the other examples shown in this post, in our official example app on GitHub.
Image Generation with Plugins
While being able to create new images from only a prompt on a device is already a huge step, we’ve taken it a little further by implementing a new plugin system which enables the diffusion model to accept a condition image along with a text prompt as its inputs.
We currently support three different ways that you can provide a foundation for your generations: facial structures, edge detection, and depth awareness. The plugins give you the ability to provide an image, extract specific structures from it, and then create new images using those structures.
LoRA Weights
The third major feature we’re rolling out today is the ability to customize the Image Generator task with LoRA to teach a foundation model about a new concept, such as specific objects, people, or styles presented during training. With the new LoRA weights, the Image Generator becomes a specialized generator that is able to inject specific concepts into generated images.
LoRA weights are useful for cases where you may want every image to be in the style of an oil painting, or a particular teapot to appear in any created setting. You can find more information about LoRA weights on Vertex AI in the MediaPipe Stable Diffusion LoRA model card, and create them using this notebook. Once generated, you can deploy the LoRA weights on-device using the MediaPipe Tasks Image Generator API, or for optimized server inference through Vertex AI’s one-click deployment.
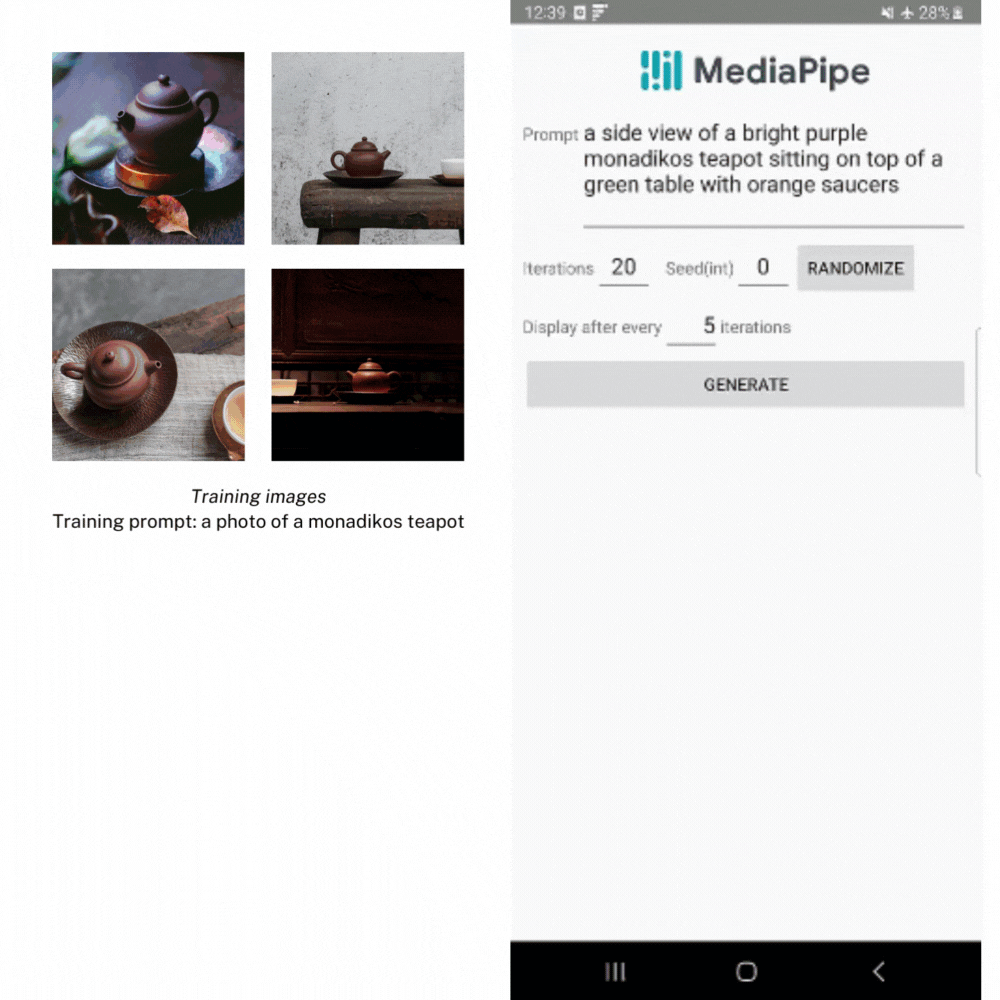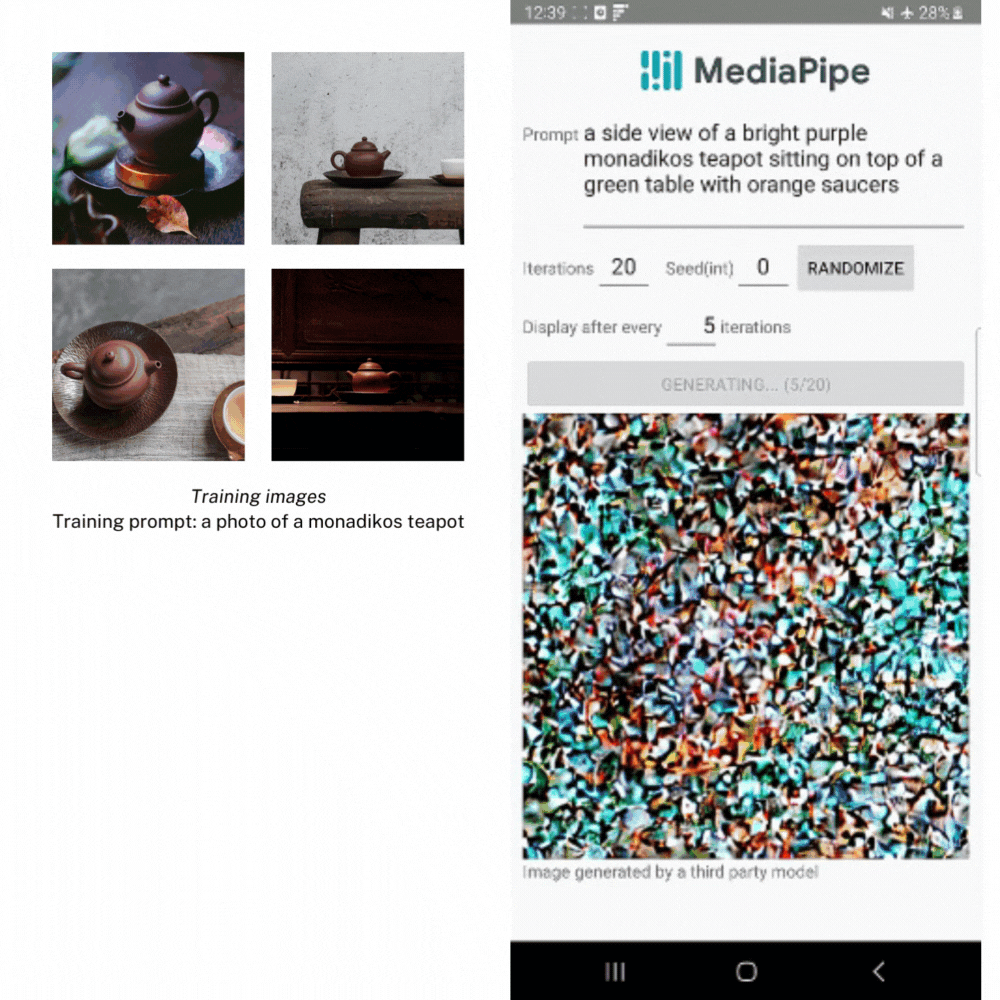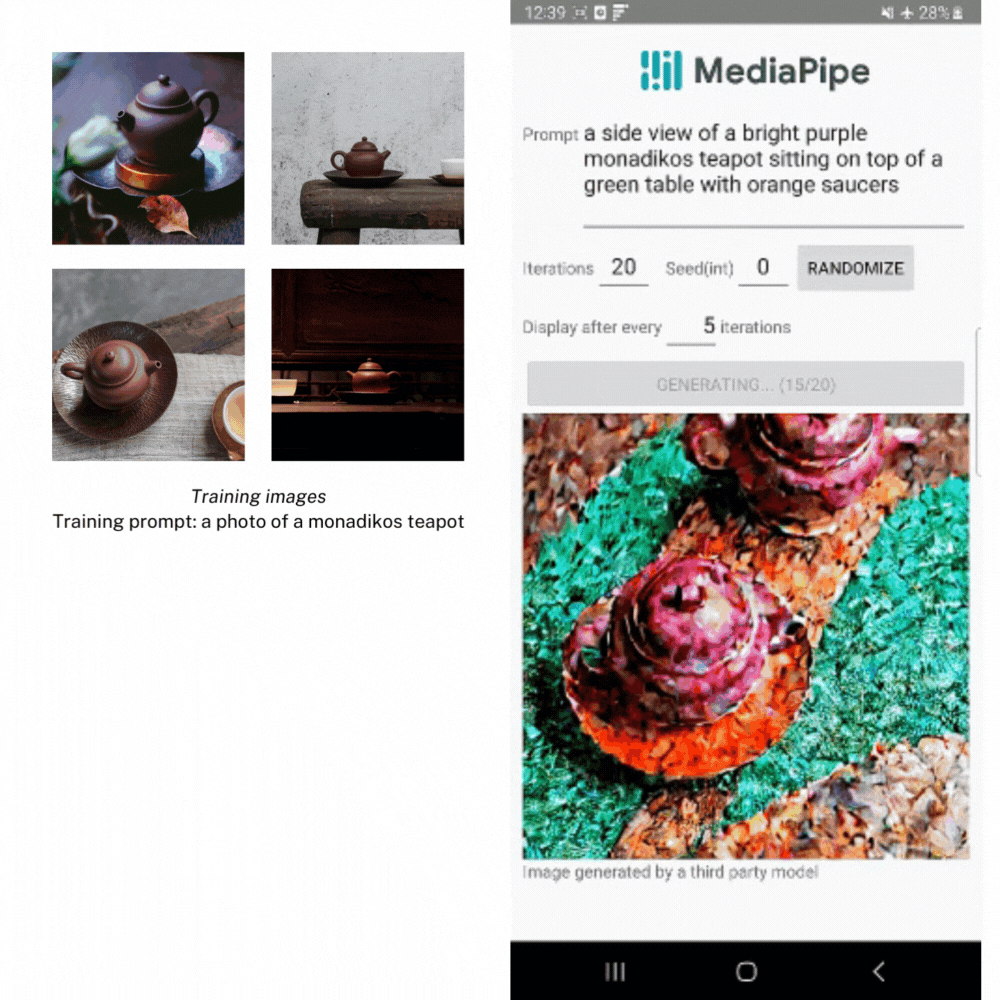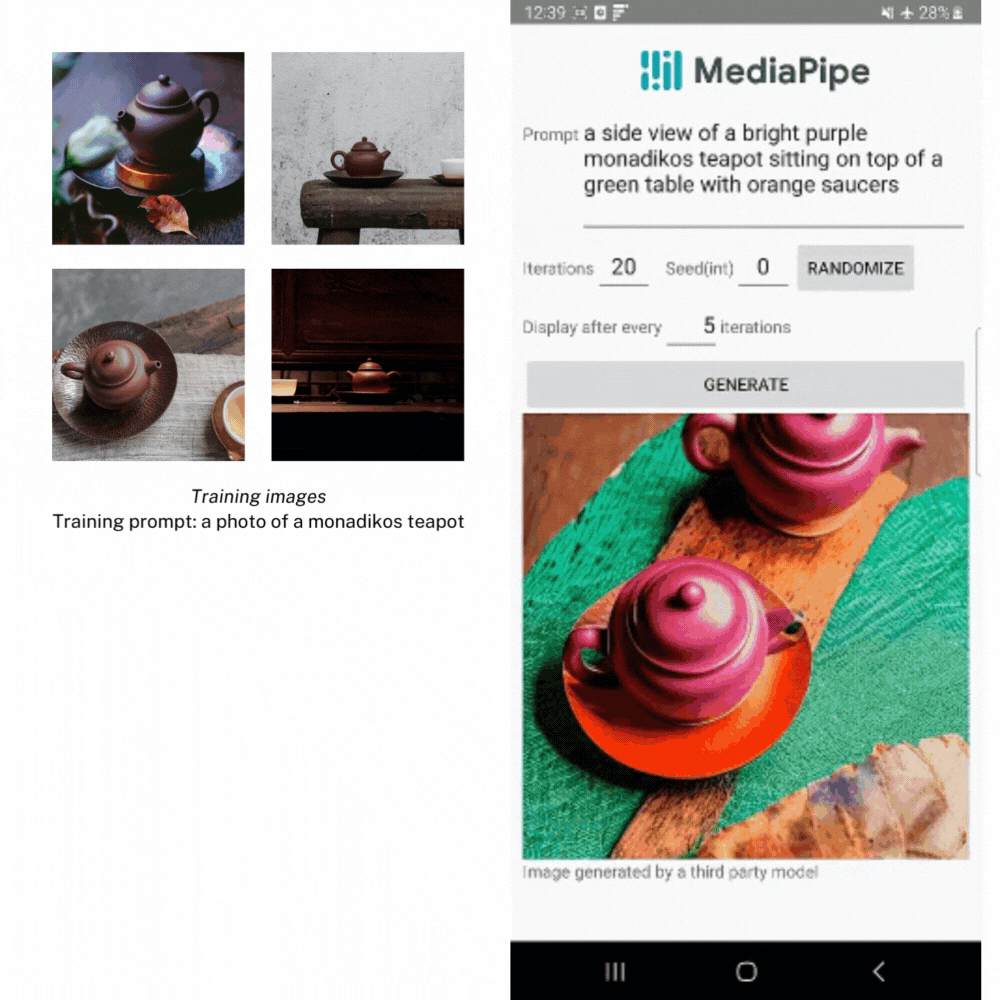
In the example below, we created LoRA weights using several images of a teapot from the Dreambooth teapot training image set. Then we use the weights to generate a new image of the teapot in different settings.
Image generation with the LoRA weights
Next Steps
This is just the beginning of what we plan to support with on-device image generation. We’re looking forward to seeing all of the great things the developer community builds, so be sure to post them on X (formally Twitter) with the hashtag #MediaPipeImageGen and tag @GoogleDevs. You can check out the official sample on GitHub demonstrating everything you’ve just learned about, read through our official documentation for even more details, and keep an eye on the Google for Developers YouTube channel for updates and tutorials as they’re released by the MediaPipe team.
Acknowledgements
We’d like to thank all team members who contributed to this work: Lu Wang, Yi-Chun Kuo, Sebastian Schmidt, Kris Tonthat, Jiuqiang Tang, Khanh LeViet, Paul Ruiz, Qifei Wang, Yang Zhao, Yuqi Li, Lawrence Chan, Tingbo Hou, Joe Zou, Raman Sarokin, Juhyun Lee, Geng Yan, Ekaterina Ignasheva, Shanthal Vasanth, Glenn Cameron, Mark Sherwood, Andrei Kulik, Chuo-Ling Chang, and Matthias Grundmann from the Core ML team, as well as Changyu Zhu, Genquan Duan, Bo Wu, Ting Yu, and Shengyang Dai from Google Cloud.

 Posted by Annum Munir, Product Marketing Manager
Posted by Annum Munir, Product Marketing Manager
 Posted by Paul Ruiz – Senior Developer Relations Engineer, and Kris Tonthat – Technical Writer
Posted by Paul Ruiz – Senior Developer Relations Engineer, and Kris Tonthat – Technical Writer



 Posted by Joe Fernandez, AI Developer Relations, and Jaimie Hwang, AI Developer Marketing
Posted by Joe Fernandez, AI Developer Relations, and Jaimie Hwang, AI Developer Marketing
 Posted by Isabella Fiterman – Product Marketing Manager, and Sandhya Mohan – Product Manager
Posted by Isabella Fiterman – Product Marketing Manager, and Sandhya Mohan – Product Manager

 Posted by Yariv Adan, Director of Cloud Conversational AI and Pati Jurek, Google for startups Accelerator Regional Lead
Posted by Yariv Adan, Director of Cloud Conversational AI and Pati Jurek, Google for startups Accelerator Regional Lead
 Posted by Rob Simpson, Product Manager - Google Play & Joe Davis, Manager - Google Play Academy
Posted by Rob Simpson, Product Manager - Google Play & Joe Davis, Manager - Google Play Academy




 Posted by Chanel Greco, Developer Advocate
Posted by Chanel Greco, Developer Advocate


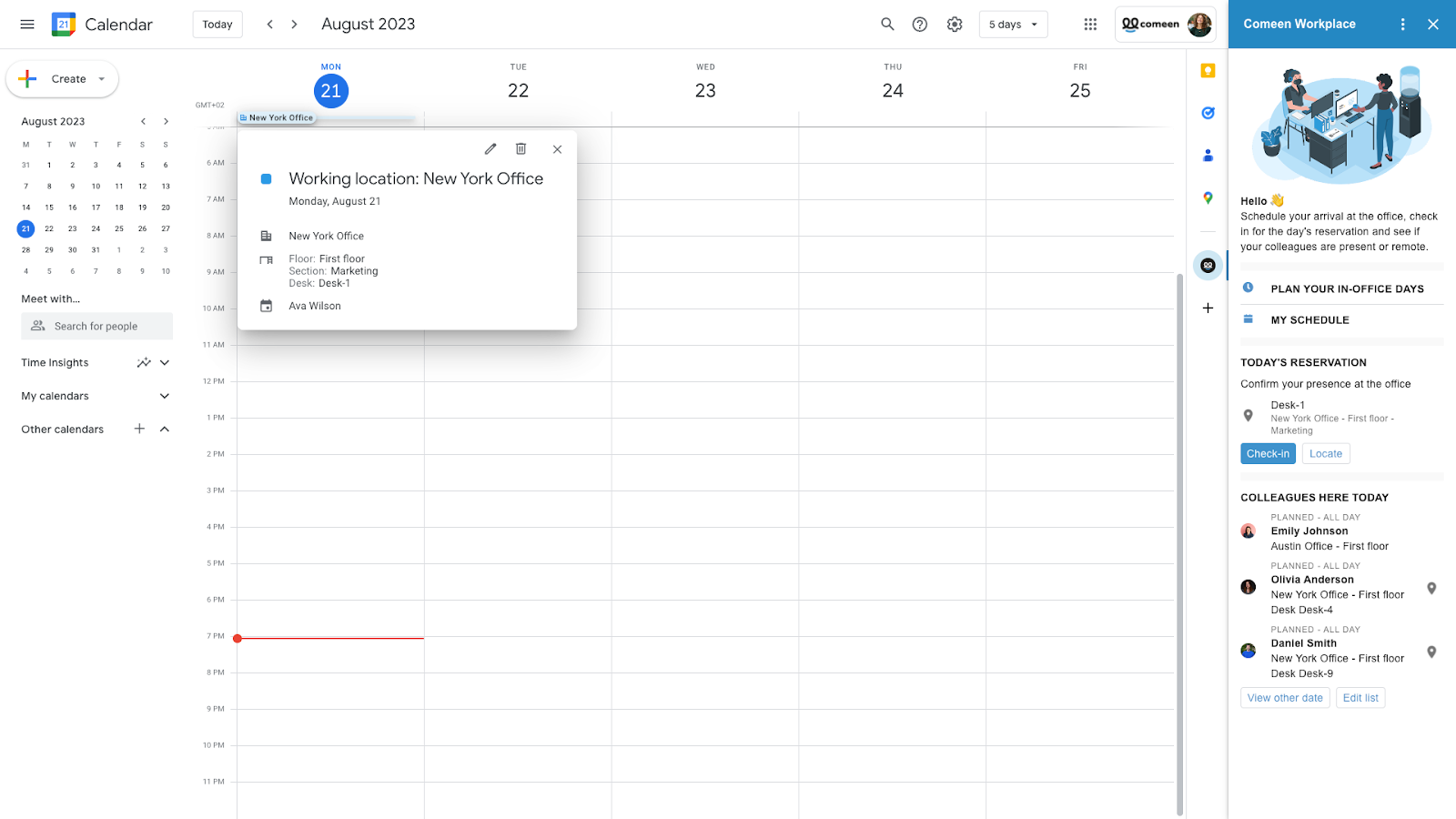
 Posted by
Posted by 


 Posted by Iran Karimian, Startup Developer Ecosystem Lead, Canada
Posted by Iran Karimian, Startup Developer Ecosystem Lead, Canada

 Posted by Harsh Dattani - Program Manager, Developer Ecosystem
Posted by Harsh Dattani - Program Manager, Developer Ecosystem
