Posted by Ehsan Amid, Research Scientist, and Rohan Anil, Principal Engineer, Google Research, Brain Team While model design and training data are key ingredients in a deep neural network’s (DNN’s) success, less-often discussed is the specific optimization method used for updating the model parameters (weights). Training DNNs involves minimizing a loss function that measures the discrepancy between the ground truth labels and the model’s predictions. Training is carried out by backpropagation, which adjusts the model weights via gradient descent steps. Gradient descent, in turn, updates the weights by using the gradient (i.e., derivative) of the loss with respect to the weights.
The simplest weight update corresponds to stochastic gradient descent, which, in every step, moves the weights in the negative direction with respect to the gradients (with an appropriate step size, a.k.a. the learning rate). More advanced optimization methods modify the direction of the negative gradient before updating the weights by using information from the past steps and/or the local properties (such as the curvature information) of the loss function around the current weights. For instance, a momentum optimizer encourages moving along the average direction of past updates, and the AdaGrad optimizer scales each coordinate based on the past gradients. These optimizers are commonly known as first-order methods since they generally modify the update direction using only information from the first-order derivative (i.e., gradient). More importantly, the components of the weight parameters are treated independently from each other.
More advanced optimization, such as Shampoo and K-FAC, capture the correlations between gradients of parameters and have been shown to improve convergence, reducing the number of iterations and improving the quality of the solution. These methods capture information about the local changes of the derivatives of the loss, i.e., changes in gradients. Using this additional information, higher-order optimizers can discover much more efficient update directions for training models by taking into account the correlations between different groups of parameters. On the downside, calculating higher-order update directions is computationally more expensive than first-order updates. The operation uses more memory for storing statistics and involves matrix inversion, thus hindering the applicability of higher-order optimizers in practice.
In “LocoProp: Enhancing BackProp via Local Loss Optimization”, we introduce a new framework for training DNN models. Our new framework, LocoProp, conceives neural networks as a modular composition of layers. Generally, each layer in a neural network applies a linear transformation on its inputs, followed by a non-linear activation function. In the new construction, each layer is allotted its own weight regularizer, output target, and loss function. The loss function of each layer is designed to match the activation function of the layer. Using this formulation, training minimizes the local losses for a given mini-batch of examples, iteratively and in parallel across layers. Our method performs multiple local updates per batch of examples using a first-order optimizer (like RMSProp), which avoids computationally expensive operations such as the matrix inversions required for higher-order optimizers. However, we show that the combined local updates look rather like a higher-order update. Empirically, we show that LocoProp outperforms first-order methods on a deep autoencoder benchmark and performs comparably to higher-order optimizers, such as Shampoo and K-FAC, without the high memory and computation requirements.
Method
Neural networks are generally viewed as composite functions that transform model inputs into output representations, layer by layer. LocoProp adopts this view while decomposing the network into layers. In particular, instead of updating the weights of the layer to minimize the loss function at the output, LocoProp applies pre-defined local loss functions specific to each layer. For a given layer, the loss function is selected to match the activation function, e.g., a tanh loss would be selected for a layer with a tanh activation. Each layerwise loss measures the discrepancy between the layer's output (for a given mini-batch of examples) and a notion of a target output for that layer. Additionally, a regularizer term ensures that the updated weights do not drift too far from the current values. The combined layerwise loss function (with a local target) plus regularizer is used as the new objective function for each layer.
 |
| Similar to backpropagation, LocoProp applies a forward pass to compute the activations. In the backward pass, LocoProp sets per neuron "targets" for each layer. Finally, LocoProp splits model training into independent problems across layers where several local updates can be applied to each layer's weights in parallel. |
Perhaps the simplest loss function one can think of for a layer is the squared loss. While the squared loss is a valid choice of a loss function, LocoProp takes into account the possible non-linearity of the activation functions of the layers and applies layerwise losses tailored to the activation function of each layer. This enables the model to emphasize regions at the input that are more important for the model prediction while deemphasizing the regions that do not affect the output as much. Below we show examples of tailored losses for the tanh and ReLU activation functions.
 |
| Loss functions induced by the (left) tanh and (right) ReLU activation functions. Each loss is more sensitive to the regions affecting the output prediction. For instance, ReLU loss is zero as long as both the prediction (â) and the target (a) are negative. This is because the ReLU function applied to any negative number equals zero. |
After forming the objective in each layer, LocoProp updates the layer weights by repeatedly applying gradient descent steps on its objective. The update typically uses a first-order optimizer (like RMSProp). However, we show that the overall behavior of the combined updates closely resembles higher-order updates (shown below). Thus, LocoProp provides training performance close to what higher-order optimizers achieve without the high memory or computation needed for higher-order methods, such as matrix inverse operations. We show that LocoProp is a flexible framework that allows the recovery of well-known algorithms and enables the construction of new algorithms via different choices of losses, targets, and regularizers. LocoProp’s layerwise view of neural networks also allows updating the weights in parallel across layers.
Experiments
In our paper, we describe experiments on the deep autoencoder model, which is a commonly used baseline for evaluating the performance of optimization algorithms. We perform extensive tuning on multiple commonly used first-order optimizers, including SGD, SGD with momentum, AdaGrad, RMSProp, and Adam, as well as the higher-order Shampoo and K-FAC optimizers, and compare the results with LocoProp. Our findings indicate that the LocoProp method performs significantly better than first-order optimizers and is comparable to those of higher-order, while being significantly faster when run on a single GPU.
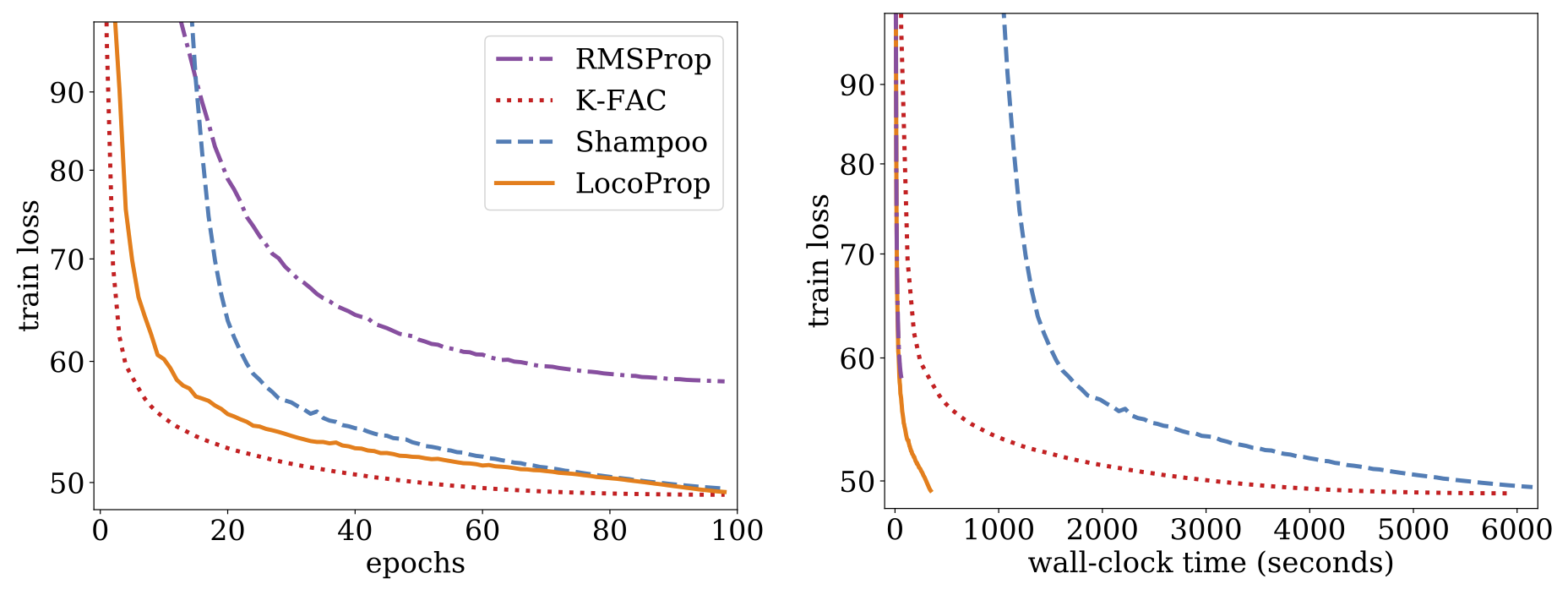 |
| Train loss vs. number of epochs (left) and wall-clock time, i.e., the real time that passes during training, (right) for RMSProp, Shampoo, K-FAC, and LocoProp on the deep autoencoder model. |
Summary and Future Directions
We introduced a new framework, called LocoProp, for optimizing deep neural networks more efficiently. LocoProp decomposes neural networks into separate layers with their own regularizer, output target, and loss function and applies local updates in parallel to minimize the local objectives. While using first-order updates for the local optimization problems, the combined updates closely resemble higher-order update directions, both theoretically and empirically.
LocoProp provides flexibility to choose the layerwise regularizers, targets, and loss functions. Thus, it allows the development of new update rules based on these choices. Our code for LocoProp is available online on GitHub. We are currently working on scaling up ideas induced by LocoProp to much larger scale models; stay tuned!
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank our co-author, Manfred K. Warmuth, for his critical contributions and inspiring vision. We would like to thank Sameer Agarwal for discussions looking at this work from a composite functions perspective, Vineet Gupta for discussions and development of Shampoo, Zachary Nado on K-FAC, Tom Small for development of the animation used in this blogpost and finally, Yonghui Wu and Zoubin Ghahramani for providing us with a nurturing research environment in the Google Brain Team.