Posted by Melvin Johnson, Senior Software Engineer, Google Research and Sebastian Ruder, Research Scientist, DeepMind One of the key challenges in natural language processing (NLP) is building systems that not only work in English but in
all of the world’s ~6,900 languages. Luckily, while most of the world’s languages are
data sparse and do not have enough data available to train robust models on their own, many languages do share a considerable amount of underlying structure. On the vocabulary level, languages often have words that stem from the same origin — for instance, “
desk” in English and “
Tisch” in German both come from the Latin “
discus”. Similarly, many languages also mark semantic roles in similar ways, such as the use of
postpositions to mark temporal and spatial relations in both Chinese and Turkish.
In NLP, there are a number of methods that leverage the shared structure of multiple languages in training in order to overcome the data sparsity problem. Historically, most of these methods focused on performing a specific task in multiple languages. Over the last few years, driven by advances in deep learning, there has been an increase in the number of approaches that attempt to learn
general-purpose multilingual representations (e.g.,
mBERT,
XLM,
XLM-R), which aim to capture knowledge that is shared across languages and that is useful for many tasks. In practice, however, the evaluation of such methods has mostly focused on a small set of tasks and for linguistically similar languages.
To encourage more research on multilingual learning, we introduce “
XTREME: A Massively Multilingual Multi-task Benchmark for Evaluating Cross-lingual Generalization”, which covers 40 typologically diverse languages (spanning 12 language families) and includes nine tasks that collectively require reasoning about different levels of syntax or semantics. The languages in XTREME are selected to maximize language diversity, coverage in existing tasks, and availability of training data. Among these are many under-studied languages, such as the
Dravidian languages Tamil (spoken in southern India, Sri Lanka, and Singapore), Telugu and Malayalam (spoken mainly in southern India), and the
Niger-Congo languages Swahili and Yoruba, spoken in Africa. The code and data, including examples for running various baselines, is available
here.
XTREME Tasks and LanguagesThe tasks included in XTREME cover a range of paradigms, including
sentence classification,
structured prediction,
sentence retrieval and
question answering. Consequently, in order for models to be successful on the XTREME benchmarks, they must learn representations that generalize to many standard cross-lingual transfer settings.
 |
| Tasks supported in the XTREME benchmark. |
Each of the tasks covers a subset of the 40 languages. To obtain additional data in the low-resource languages used for analyses in XTREME, the test sets of two representative tasks, natural language inference (
XNLI) and question answering (
XQuAD), were automatically translated from English to the remaining languages. We show that models using the translated test sets for these tasks exhibited performance comparable to that achieved using human-labelled test sets.
Zero-shot EvaluationTo evaluate performance using XTREME, models must first be pre-trained on multilingual text using objectives that encourage cross-lingual learning. Then, they are fine-tuned on task-specific English data, since English is the most likely language where labelled data is available. XTREME then evaluates these models on
zero-shot cross-lingual transfer performance, i.e., on other languages for which no task-specific data was seen. The three-step process, from pre-training to fine-tuning to zero-shot transfer, is shown in the figure below.
 |
| The cross-lingual transfer learning process for a given model: pre-training on multilingual text, followed by fine-tuning in English on downstream tasks, and finally zero-shot evaluation with XTREME. |
In practice, one of the benefits of this zero-shot setting is computational efficiency — a pre-trained model only needs to be fine-tuned on English data for each task and can then be evaluated directly on other languages. Nevertheless, for tasks where labelled data is available in other languages, we also compare against fine-tuning on in-language data. Finally, we provide a combined score by obtaining the zero-shot scores on all nine XTREME tasks.
A Testbed for Transfer LearningWe conduct experiments with several state-of-the-art pre-trained multilingual models, including:
multilingual BERT, a multilingual extension of the popular BERT model;
XLM and
XLM-R, two larger versions of multilingual BERT that have been trained on even more data; and a massively multilingual machine translation model,
M4. A common feature of these models is that they have been pre-trained on large amounts of data from multiple languages. For our experiments, we choose variants of these models that are pre-trained on around 100 languages, including the 40 languages of our benchmark.
We find that while models achieve close to human performance on most existing tasks in English, performance is significantly lower for many of the other languages. Across all models, the gap between English performance and performance for the remaining languages is largest for the structured prediction and question answering tasks, while the spread of results across languages is largest for the structured prediction and sentence retrieval tasks.
For illustration, in the figure below we show the performance of the best-performing model in the zero-shot setting, XLM-R, by task and language, across all language families. The scores across tasks are not comparable, so the main focus should be the relative ranking of languages across tasks. As we can see, many high-resource languages, particularly from the Indo-European language family, are consistently ranked higher. In contrast, the model achieves lower performance on many languages from other language families such as Sino-Tibetan, Japonic, Koreanic, and Niger-Congo languages.
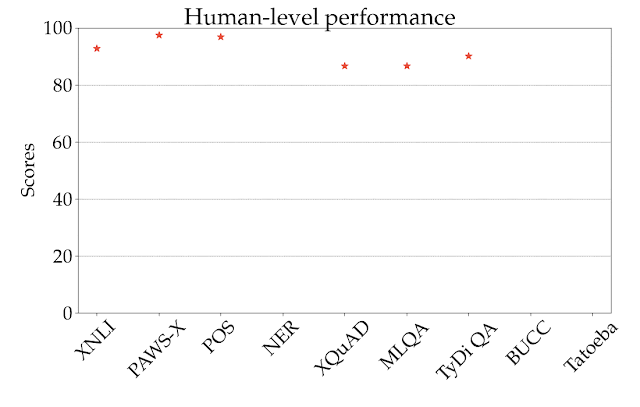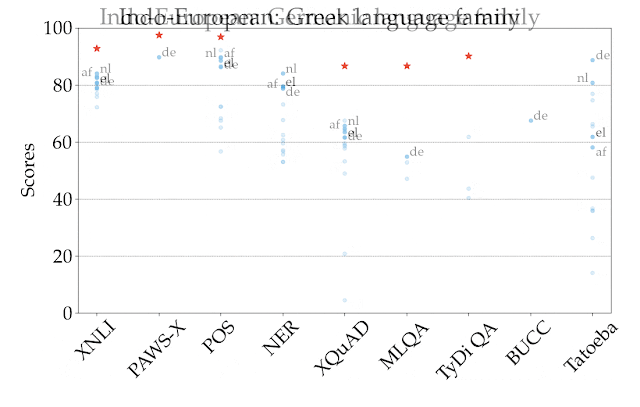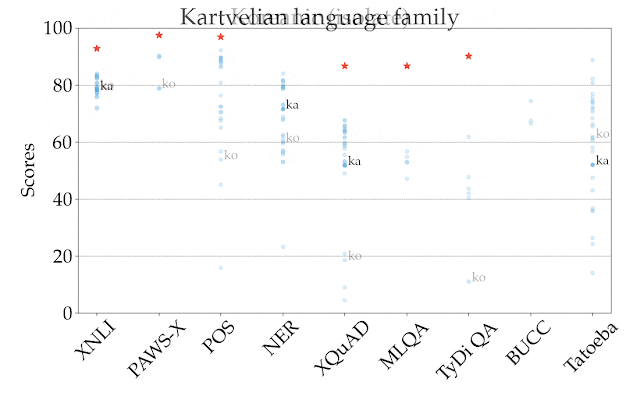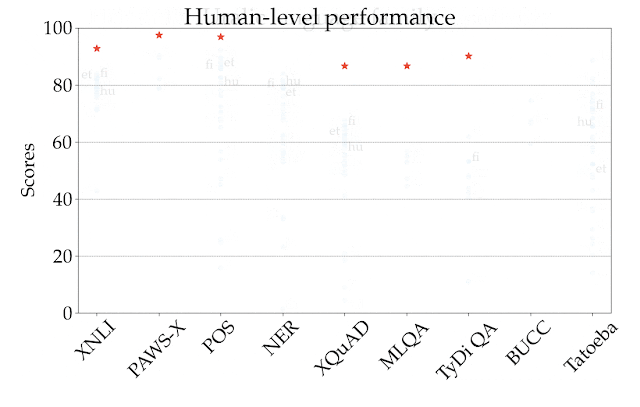 |
| Performance of the best-performing model (XLM-R) across all tasks and languages in XTREME in the zero-shot setting. The reported scores are percentages based on task-specific metrics and are not directly comparable across tasks. Human performance (if available) is represented by a red star. Specific examples from each language family are represented with their ISO 639-1 codes. |
In general we made a number of interesting observations.
- In the zero-shot setting, M4 and mBERT are competitive with XLM-R for most tasks, while the latter outperforms them in the particularly challenging question answering tasks. For example, on XQuAD, XLM-R scored 76.6 compared to 64.5 for mBERT and 64.6 for M4, with similar spreads on MLQA and TyDi QA.
- We find that baselines utilizing machine translation, which translate either the training data or test data, are very competitive. On the XNLI task, mBERT scored 65.4 in the zero shot transfer setting, and 74.0 when using translated training data.
- We observe that the few-shot setting (i.e., using limited amounts of in-language labelled data, when available) is particularly competitive for simpler tasks, such as NER, but less useful for the more complex question answering tasks. This can be seen in the performance of mBERT, which improves by 42% on the NER task from 62.2 to 88.3 in the few-shot setting, but for the question answering task (TyDi QA), only improves by 25% (59.7 to 74.5).
- Overall, a large gap between performance in English and other languages remains across all models and settings, which indicates that there is much potential for research on cross-lingual transfer.
Cross-lingual Transfer Analysis Similar to previous observations regarding the generalisation ability of deep models, we observe that results improve if more pre-training data is available for a language, e.g., mBERT compared to XLM-R, which has more pre-training data. However, we find that this correlation does not hold for the structured prediction tasks,
part-of-speech tagging (POS) and
named entity recognition (NER), which indicates that current deep pre-trained models are not able to fully exploit the pre-training data to transfer to such syntactic tasks. We also find that models have difficulties transferring to non-Latin scripts. This is evident on the POS task, where mBERT achieves a zero-shot accuracy of 86.9 on Spanish compared to just 49.2 on Japanese.
For the natural language inference task, XNLI, we find that a model makes the same prediction on a test example in English and on the same example in another language about 70% of the time.
Semi-supervised methods might be helpful in encouraging improved consistency between the predictions on examples and their translations in different languages. We also find that models struggle to predict POS tag sequences that were not seen in the English training data on which they were fine-tuned, highlighting that these models struggle to learn the syntax of other languages from the large amounts of unlabelled data used for pre-training. For named entity recognition, models have the most difficulty predicting entities that were not seen in the English training data for distant languages — accuracies on Indonesian and Swahili are 58.0 and 66.6, respectively, compared to 82.3 and 80.1 for Portguese and French.
Making Progress on Multilingual Transfer Learning English has been the focal point of most recent advances in NLP despite being spoken by only around 15% of the world’s population. We believe that building on deep contextual representations, we now have the tools to make substantial progress on systems that serve the remainder of the world’s languages. We hope that XTREME will catalyze research in multilingual transfer learning, similar to how benchmarks such as
GLUE and
SuperGLUE have spurred the development of deep monolingual models, including
BERT,
RoBERTa,
XLNet,
AlBERT, and others. Stay tuned to our
Twitter account for information on our upcoming website launch with a submission portal and leaderboard.
Acknowledgements: This effort has been successful thanks to the hard work of a lot of people including, but not limited to the following (in alphabetical order of last name): Jon Clark, Orhan Firat, Dan Garrette, Junjie Hu, Graham Neubig, and Aditya Siddhant. 









