Posted by Hector Parra, Jaime Martínez, Miguel Fernandes, Julia Hernández
Merchant Center lets merchants manage how their in-store and online product inventory appears on Google. It allows them to reach hundreds of millions of people looking to buy products like yours each day.
To upload their products, merchants can make use of feeds, that is, files with a list of products in a specific format. These can be shared with Merchant Center in different ways: using Google Sheets, SFTP or FTP shares, Google Cloud Storage or manually through the user interface. These methods work great for the majority of cases. But, if a merchant's product list grows over time, they might reach the usage limits of the feeds. Depending on the case, quota extensions could be granted, but if the list continues to grow, it might reach a point where feeds no longer support that scale, and the Content API for Shopping would become the recommended way to go forward.
The main issue is, if a merchant is recommended to stop using feeds and start using the Content API due to scale problems, it means that the number of products is massive, and trying to use the Content API directly will give them usage and quota errors, as the QPS and products per call limits will be exceeded.
For this specific use case, Centimani becomes critical in helping merchants handle the upload process through the Content API in a controlled manner, avoiding any overload of the API.
Centimani is a configurable massive file processor able to split text files in chunks, process them following a strategic pattern and store the results in BigQuery for reporting. It provides configurable options for chunk size and number of retries, and takes care of exponential backoff to ensure all requests have enough retries to overcome potential temporary issues or errors. Centimani comes with two operators: Google Ads Offline Conversions Uploader, and Merchant Center Products Uploader, but it can be extended to other uses easily.
Centimani uses Google Cloud as its platform, and makes use of Cloud Storage for storing the data, Cloud Functions to do the data processing and the API calls, Cloud Tasks to coordinate the execution of each call, and BigQuery to store the audit information for reporting. 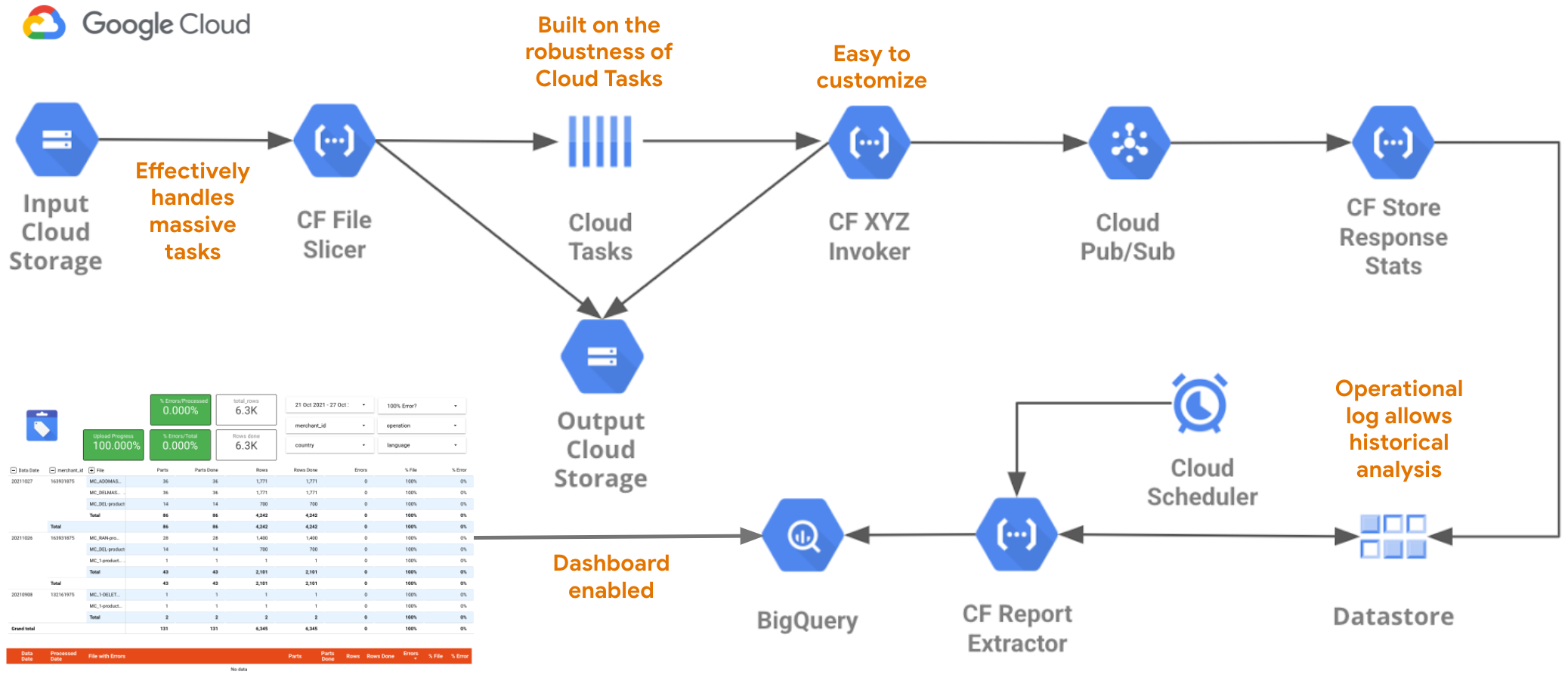
Centimani Architecture
To start using Centimani, a couple of configuration files need to be prepared with information about the Google Cloud Project to be used (including the element names), the credentials to access the Merchant Center accounts and how the load will be distributed (e.g., parallel executions, number of products per call). Then, the deployment is done automatically using a deployment script provided by the tool.
After the tool is deployed, a cloud function will be monitoring the input bucket in Cloud Storage, and every time a file is uploaded there, it will be processed. The tool uses the name of the file to select the operator that is going to be used (“MC” indicates Merchant Center Products Uploader), and the particular configuration to use (multiple configurations can be used to connect to Merchant Center accounts with different access credentials).
Whenever a file is uploaded, it will be sliced in parts if it is greater than the number of products allowed per call, they will be stored in the output bucket in Cloud Storage, and Cloud Tasks will start launching the API calls until all files are processed. Any file with errors will be stored in a folder called “slices_failed” to help troubleshoot any issues found in the process. Also, all the information about the executions will be stored temporarily in Datastore and then moved to BigQuery, where it can be used for monitoring the whole process from a centralized place.
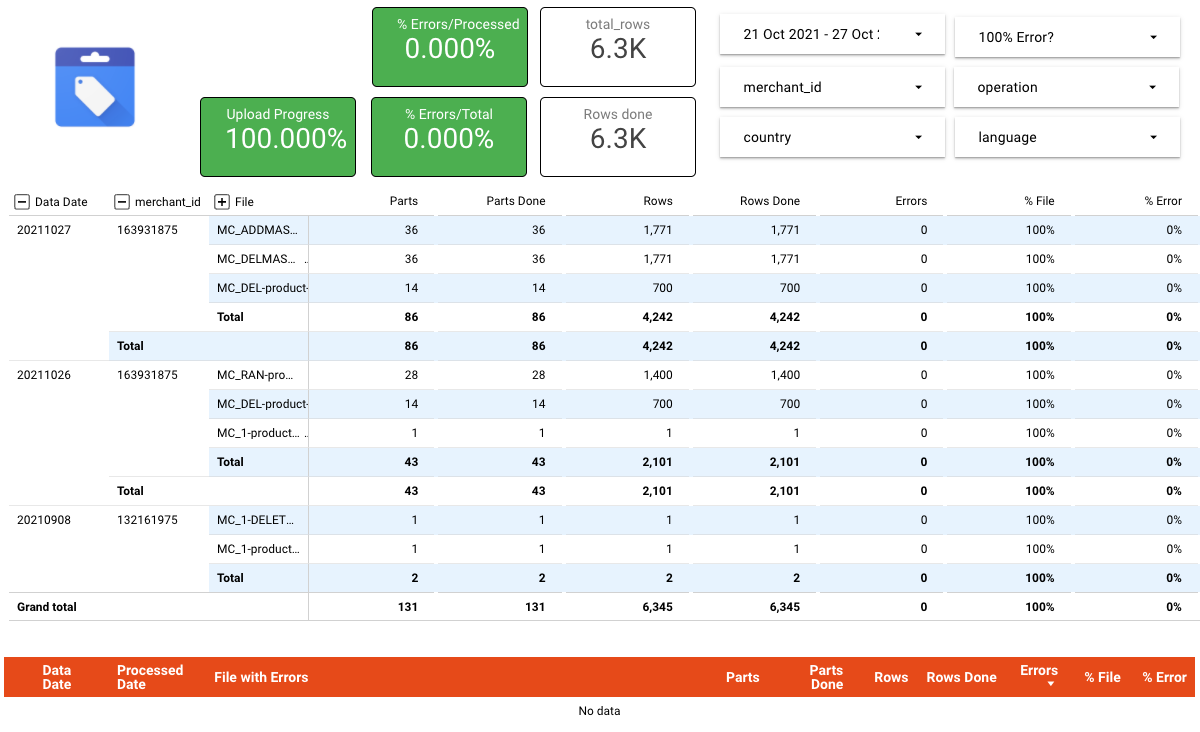
Centimani Status Dashboard Architecture
Centimani provides an easy way for merchants to start using the Content API for Shopping to manage their products, without having to deal with the complexity of keeping the system under the limits.
For more information you can visit the Centimani repository on Github.