

AMD, Arm, AWS, Google, NVIDIA, Intel, Tesla, SambaNova, and more come together to crack the code for colossal AI workloads
As AI models grow increasingly complex and compute-intensive, the need for efficient, scalable, and hardware-agnostic infrastructure has never been greater. OpenXLA is a deep learning compiler framework that makes it easy to speed up and massively scale AI models on a wide range of hardware types—from GPUs and CPUs to specialized chips like Google TPUs and AWS Trainium. It is compatible with popular modeling frameworks—JAX, PyTorch, and TensorFlow—and delivers leading performance. OpenXLA is the acceleration infrastructure of choice for global-scale AI-powered products like Amazon.com Search, Google Gemini, Waymo self-driving vehicles, and x.AI's Grok.
The OpenXLA Dev Lab
On April 25th, the OpenXLA Dev Lab played host to over 100 expert ML practitioners from 10 countries, representing industry leaders like AMD, Arm, AWS, ByteDance, Cerebras, Cruise, Google, NVIDIA, Intel, Tesla, SambaNova, and more. The full-day event, tailored to AI hardware vendors and infrastructure engineers, broke the mold of previous OpenXLA Summits by focusing purely on “Lab Sessions”, akin to office hours for developers, and hands-on Tutorials. The energy of the event was palpable as developers worked side-by-side, learning and collaborating on both practical challenges and exciting possibilities for AI infrastructure.
 |
| Figure 1: Developers from around the world congregated at the OpenXLA Dev Lab. |
The Dev Lab was all about three key things:
- Educate and Empower: Teach developers how to implement OpenXLA's essential workflows and advanced features through hands-on tutorials.
- Offer Expert Guidance: Provide personalized office hours led by OpenXLA experts to help developers refine their ideas and contributions.
- Foster Community: Encourage collaboration, knowledge-sharing, and lasting connections among the brilliant minds in the OpenXLA community.
Tutorials
The Tutorials included:
Integrating an AI Compiler & Runtime into PJRT
- Learn how PJRT connects ML frameworks to AI accelerators, standardizing their interaction for easy model deployment on diverse hardware.
- Explore the PJRT C API for framework-hardware communication.
- Implement a PJRT Plugin, a Python package that implements the C API.
- Discover plugin examples for Apple Metal, CUDA, Intel GPU, and TPU.
Led by Jieying Luo and Skye Wanderman-Milne
Extracting StableHLO Graphs + Intro to StableHLO Quantizer
- Learn to export StableHLO from JAX, PyTorch, and TensorFlow using static/dynamic shapes and SavedModel format.
- Hack along with the tutorial using the JAX, PyTorch, and TensorFlow Colab notebooks provided on OpenXLA.org.
- Simplify quantization with StableHLO Quantizer; a framework and device-agnostic tool.
- Explore streamlined parameter selection and model rewriting for lower precision.
Led by Kevin Gleason Jen Ha, and Xing Liu
Optimizing PyTorch/XLA Auto-sharding for Your Hardware
- Discover this experimental feature that automates distributing large-scale PyTorch models across XLA devices.
- Learn how it partitions and distributes for out-of-the-box performance without manual intervention
- Explore future directions such as customizable cost models for different hardware
Led by Yeounoh Chung and Pratik Fegade
Optimizing Compute and Communication Scheduling with XLA
- Scale ML models on multi-GPUs with SPMD partitioning, collective communication, HLO optimizations.
- Explore tensor parallelism, latency hiding scheduler, pipeline parallelism.
- Learn collective optimizations, pipeline parallelism for efficient large-scale training.
Led by Frederik Gossen, TJ Xu, and Abhinav Goel
Lab Sessions
Lab Sessions featured use case-specific office hours for AMD, Arm, AWS, ByteDance, Intel, NVIDIA, SambaNova, Tesla, and more. OpenXLA engineers were on hand to provide development teams with dedicated support and walkthrough specific pain points and designs. In addition, Informational Roundtables that covered broader topics like GPU ML Performance Optimization, JAX, and PyTorch-XLA GPU were available for those without specific use cases. This approach led to productive exchanges and fine-grained exploration of critical contribution areas for ML hardware vendors.
Don’t just take our word for it – here’s some of the feedback we received from developers:
"PJRT is awesome, we're looking forward to building with it. We are very grateful for the support we are getting."
— Mark Gottscho, Senior Manager and Technical Lead at SambaNova
"Today I learned a lot about Shardonnay and about some of the bugs I found in the GSPMD partitioner, and I got to learn a lot of cool stuff."
— Patrick Toulme, Machine Learning Engineer at AWS
“I learned a lot, a lot about how XLA is making tremendous progress in building their community.”
— Tejash Shah, Product Manager at NVIDIA
“Loved the format this year - please continue … lots of learning, lots of interactive sessions. It was great!”
— Om Thakkar, AI Software Engineer at Intel
Technical Innovations and The Bold Road Ahead
The event kicked off with a keynote by Robert Hundt, Distinguished Engineer at Google, who outlined OpenXLA's ambitious plans for 2024, particularly three major areas of focus:,/p>
- Large-scale training
- GPU and PyTorch compute performance
- Modularity and extensibility
Empowering Large-Scale Training
OpenXLA is introducing powerful features to enable model training at record-breaking scales. One of the most notable additions is Shardonnay, a tool coming soon to OpenXLA that automates and optimizes how large AI workloads are divided across multiple processing units, ensuring efficient use of resources and faster time to solution. Building on the success of its predecessor, SPMD, Shardonnay empowers developers with even more fine-grained control over partitioning decisions, all while maintaining the productivity benefits that SPMD is known for.
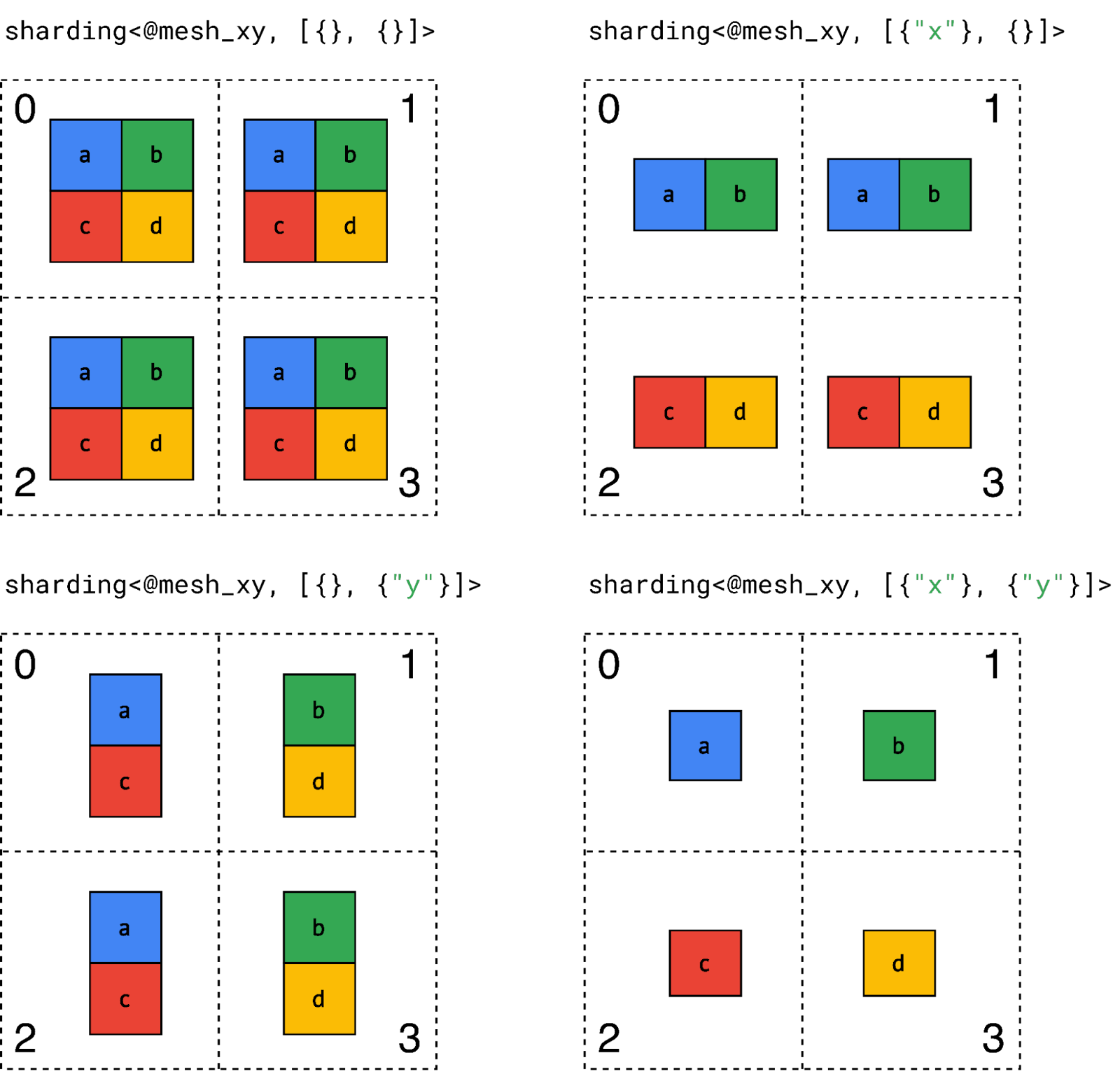 |
| Figure 2: Sharding representation example with a simple rank 2 tensor and 4 devices. |
In addition to Shardonnay, developers can expect a suite of features designed to optimize computation and communication overlap, including:
- Automatic profile-guided latency estimation
- Collective pipelining
- Heuristics-based collective combiners
These innovations will enable developers to push the boundaries of large-scale training and achieve unprecedented performance and efficiency.
OpenXLA Delivers on TorchBench Performance
OpenXLA has also made significant strides in enhancing performance, particularly on GPUs with key PyTorch-based generative AI models. PyTorch-XLA GPU is now neck and neck with TorchInductor for TorchBench Full Graph Models and has a TorchBench pass rate within 5% of TorchInductor.
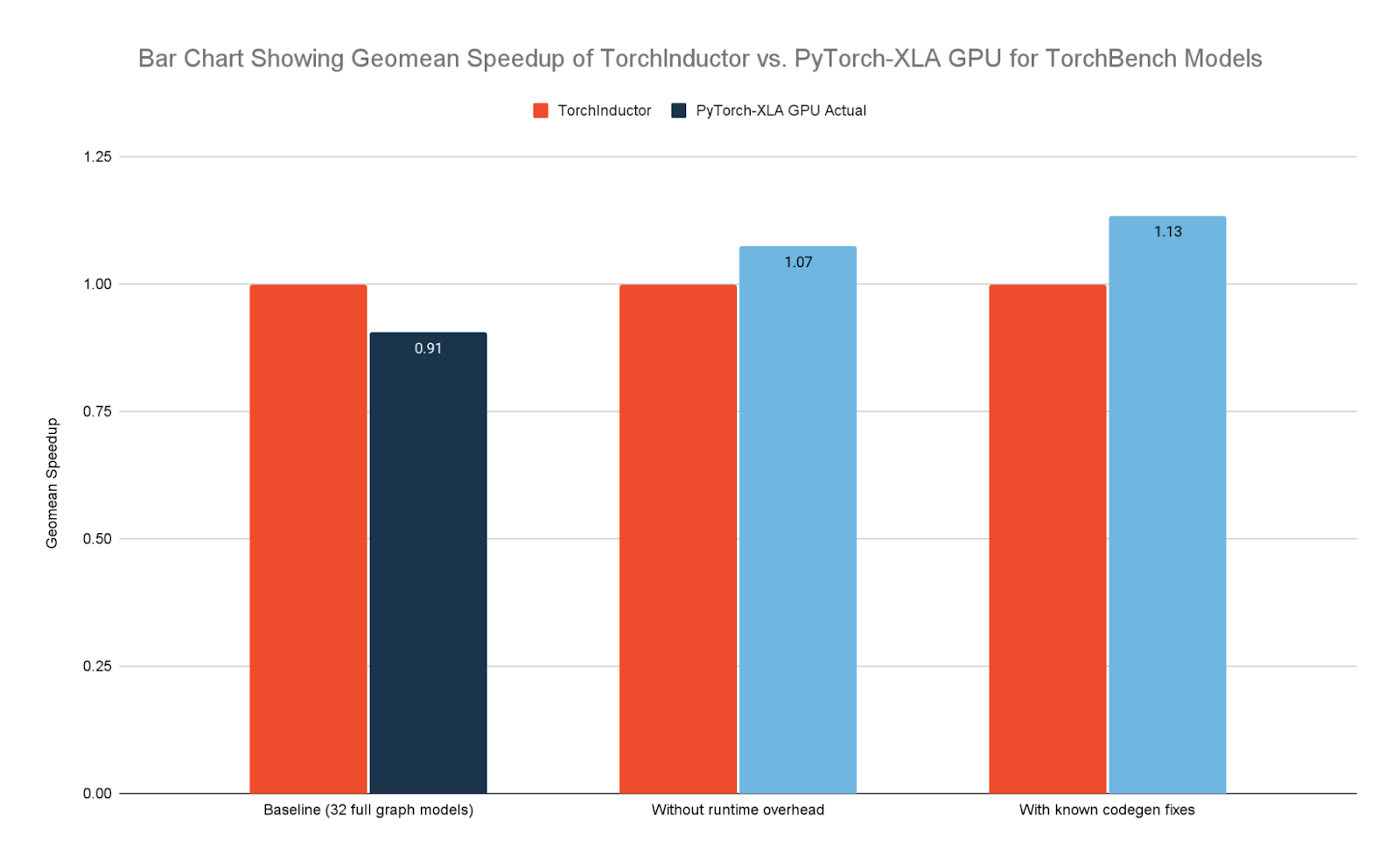 |
| Figure 3: Performance comparison of TorchInductor vs. PyTorch-XLA GPU on Google Cloud NVIDIA H100 GPUs. “Full graph models” represent all TorchBench models that can be fully represented by StableHLO |
Behind these impressive gains lies XLA GPU's global cost model, a game-changer for developers. In essence, this cost model acts as a sophisticated decision-making system, intelligently determining how to best optimize computations for specific hardware. The cost model delivers state-of-the-art performance through a priority-based queue for fusion decisions and is highly extensible, allowing third-party developers to seamlessly integrate their backend infrastructure for both general-purpose and specialized accelerators. The cost model's adaptability ensures that computation optimizations are tailored to specific accelerator architectures, while less suitable computations can be offloaded to the host or other accelerators.
OpenXLA is also breaking new ground with novel kernel programming languages, Pallas and Mosaic, which empower developers to write highly optimized code for specialized hardware. Mosaic demonstrates remarkable efficiency in programming key AI accelerators, surpassing widely used libraries in GPU code generation efficiency for models with 64, 128, and 256 Q head sizes, as evidenced by its enhanced utilization of TensorCores.
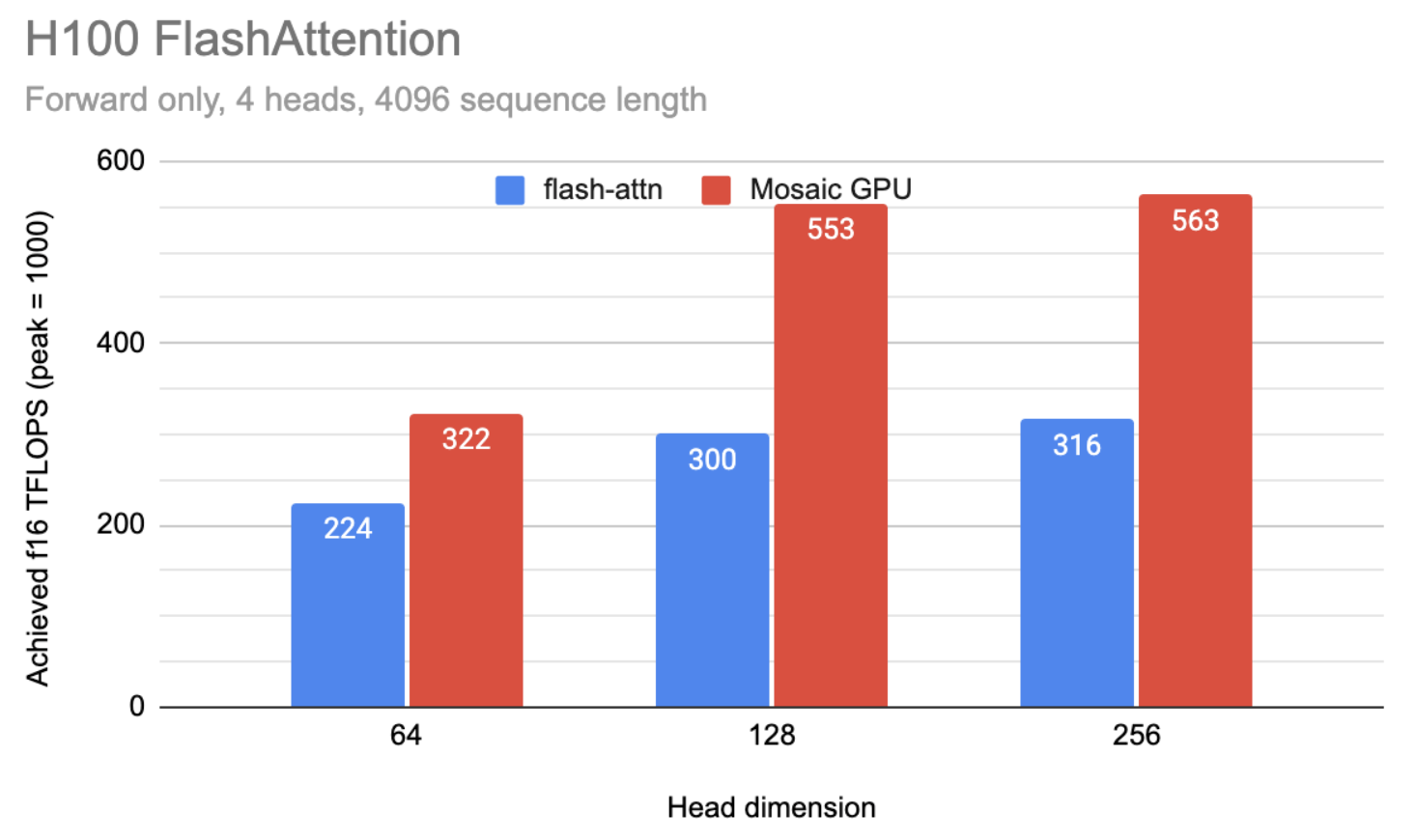 |
| Figure 4: Performance comparison of Flash Attention vs. Mosaic GPU on NVIDIA H100 GPUs. |
Modular and Extensible AI Development
In addition to performance enhancements, OpenXLA is committed to making the entire stack more modular and extensible. Several initiatives planned for 2024 include:
- Strengthening module interface contracts
- Enhancing code sharing between platforms
- Enabling a shared high-level compiler flow through runtime configuration and component registries
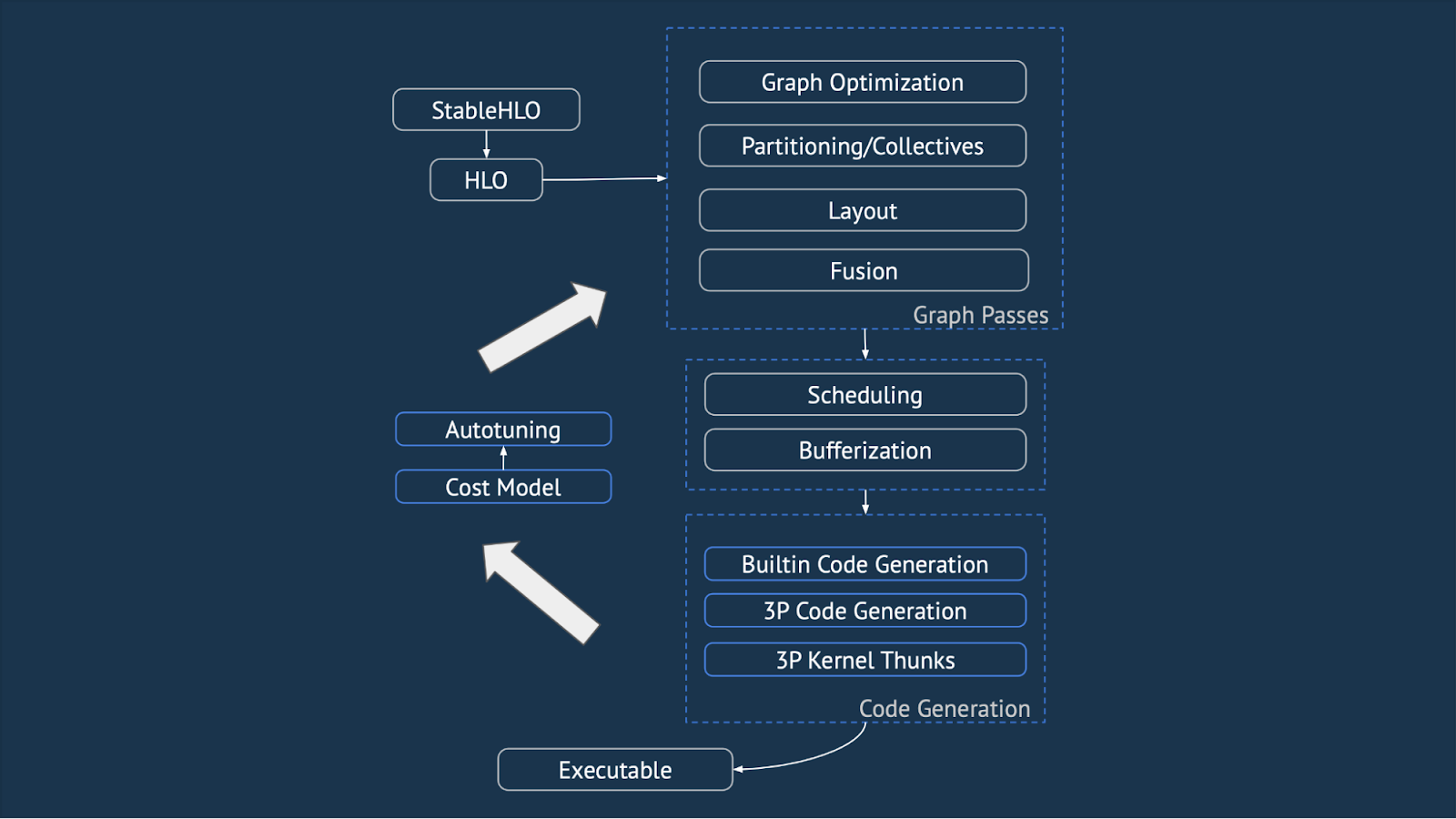 |
| Figure 5: Modules and subcomponents of the OpenXLA stack. |
These improvements will make it easier for developers to build upon and extend OpenXLA.
Alibaba's success with PyTorch XLA FSDP within their TorchAcc framework is a prime example of the benefits of OpenXLA's modularity and extensibility. By leveraging these features, Alibaba achieved state-of-the-art performance for the LLaMa 2 13B model, surpassing the previous benchmark set by Megatron. This demonstrates the power of the developer community in extending OpenXLA to push the boundaries of AI development.
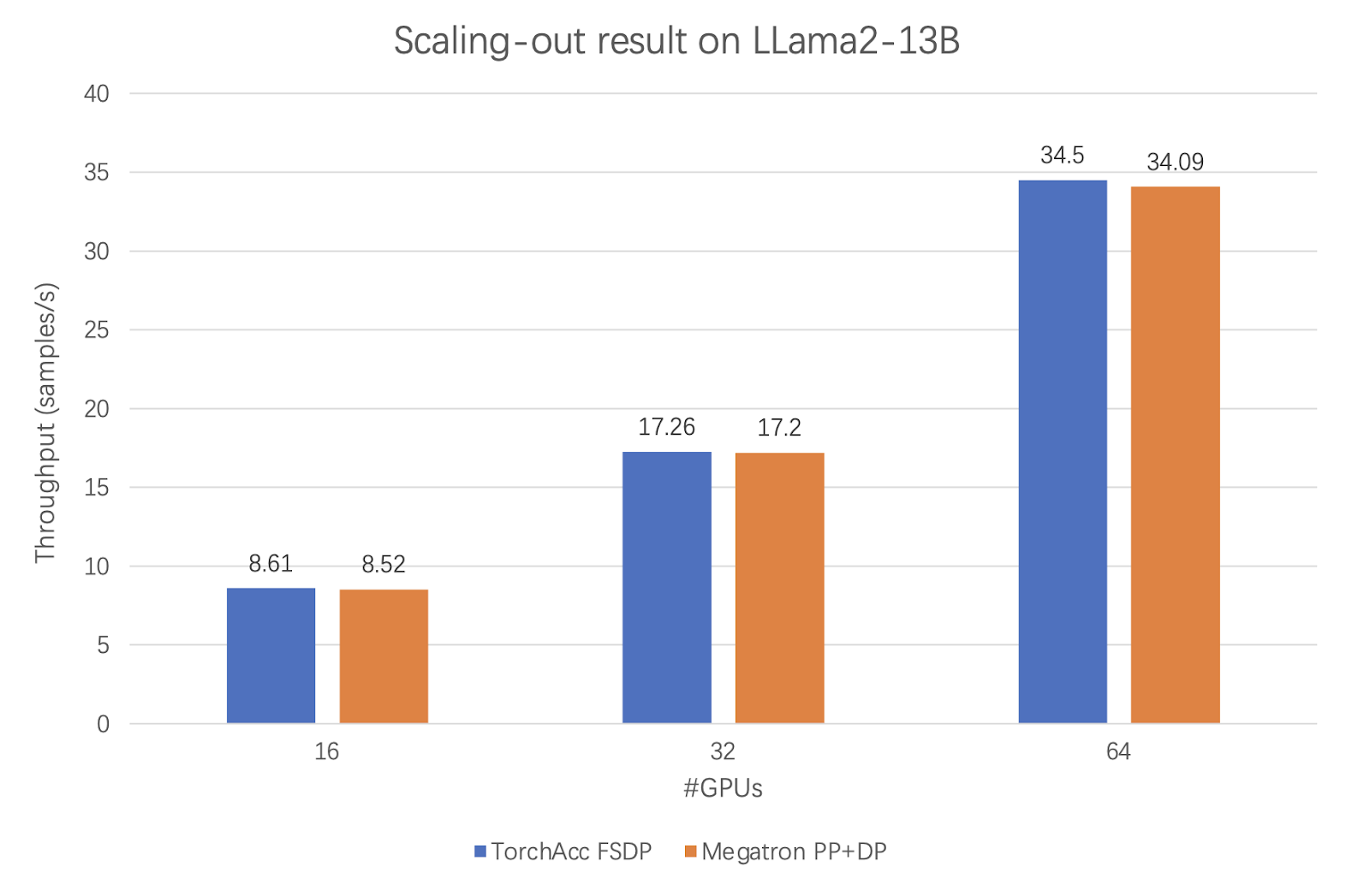 |
| Figure 6: Performance comparison of TorchAcc and Megatron for LLaMa 2 13B at different numbers of GPUs. |
Join the OpenXLA Community
If you missed the Dev Lab, don't worry! You can still access StableHLO walkthroughs on openxla.org, as well as the GitHub Gist for the PJRT session. Additionally, the recorded keynote and tutorials are available on our YouTube channel. Explore these resources and join our global community – whether you're an AI systems expert, model developer, student, or just starting out, there's a place for you in our innovative ecosystem.
Acknowledgements
Adam Paske, Allen Hutchison, Amin Vahdat, Andrew Leaver, Andy Davis, Artem Belevich, Abhinav Goel, Benjamin Kramer, Berkin Illbeyi, Bill Jia, Eugene Zhulenev, Florian Reichl, Frederik Gossen, George Karpenkov, Gunhyun Park, Han Qi, Jack Cao, Jaesung Chung, Jen Ha, Jianting Cao, Jieying Luo, Jiewin Tan, Jini Khetan, Kevin Gleason, Kyle Lucke, Kuy Mainwaring, Lauren Clemens, Manfei Bai, Marisa Miranda, Michael Levesque-Dion, Milad Mohammadi, Nisha Miriam Johnson, Penporn Koanantakool, Robert Hundt, Sandeep Dasgupta, Sayce Falk, Shauheen Zahirazami, Skye Wanderman-milne, Yeounoh Chung, Pratik Fegade, Peter Hawkins, Vaibhav Singh, Tamás Danyluk, Thomas Jeorg, Adam Paszke and TJ Xu.
By James Rubin, Aditi Joshi, and Elliot English on behalf of the OpenXLA Project





.png)

 Google researchers and Harvard neuroscientists have worked together to reveal incredible images of the human brain.
Google researchers and Harvard neuroscientists have worked together to reveal incredible images of the human brain.










 Learn about America’s Chinatowns in this new hub from Google Arts and Culture and the National Trust for Historic Preservation.
Learn about America’s Chinatowns in this new hub from Google Arts and Culture and the National Trust for Historic Preservation.
 Learn more about how the new generative AI tools for Chrome browser were developed.
Learn more about how the new generative AI tools for Chrome browser were developed.