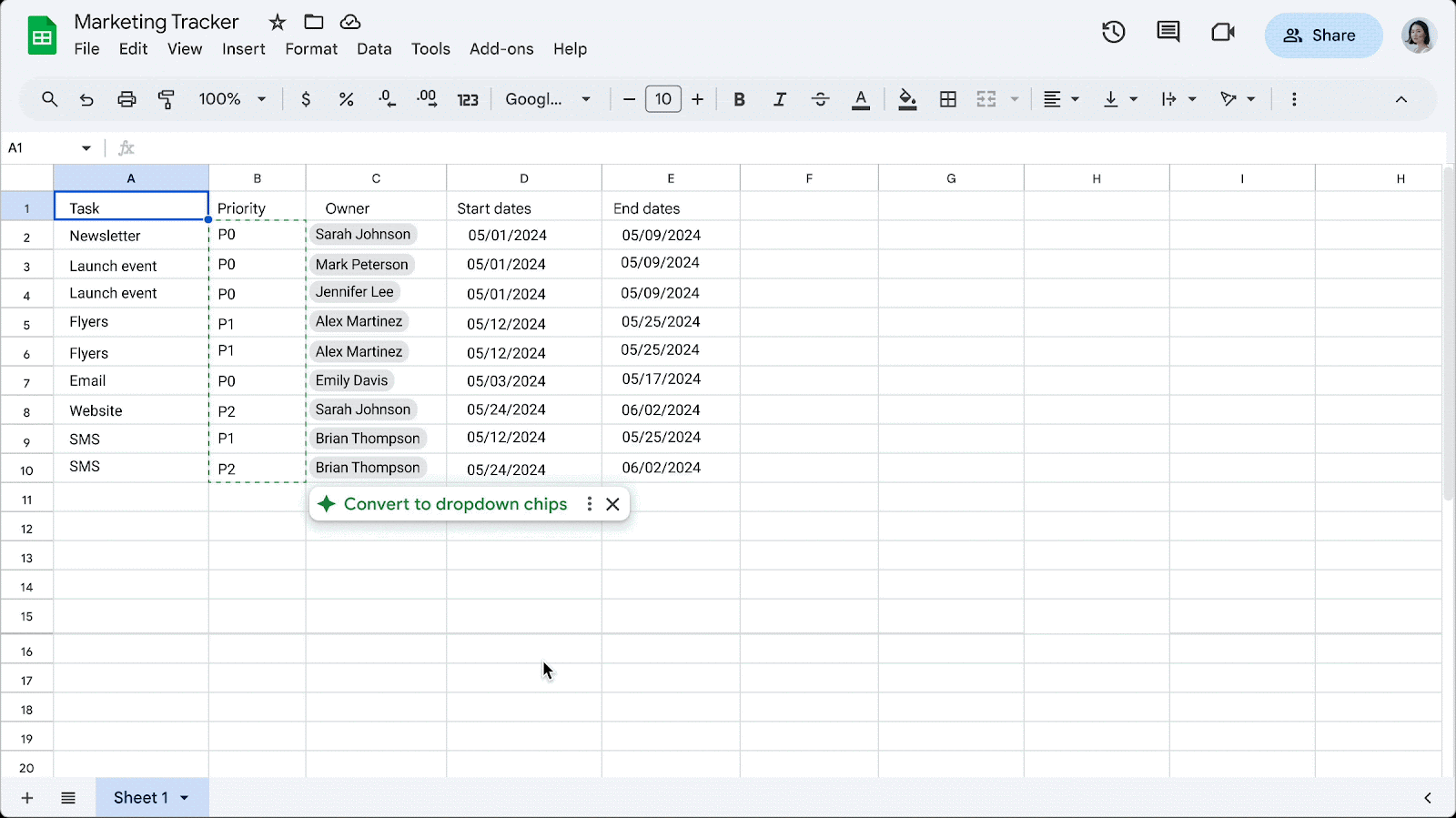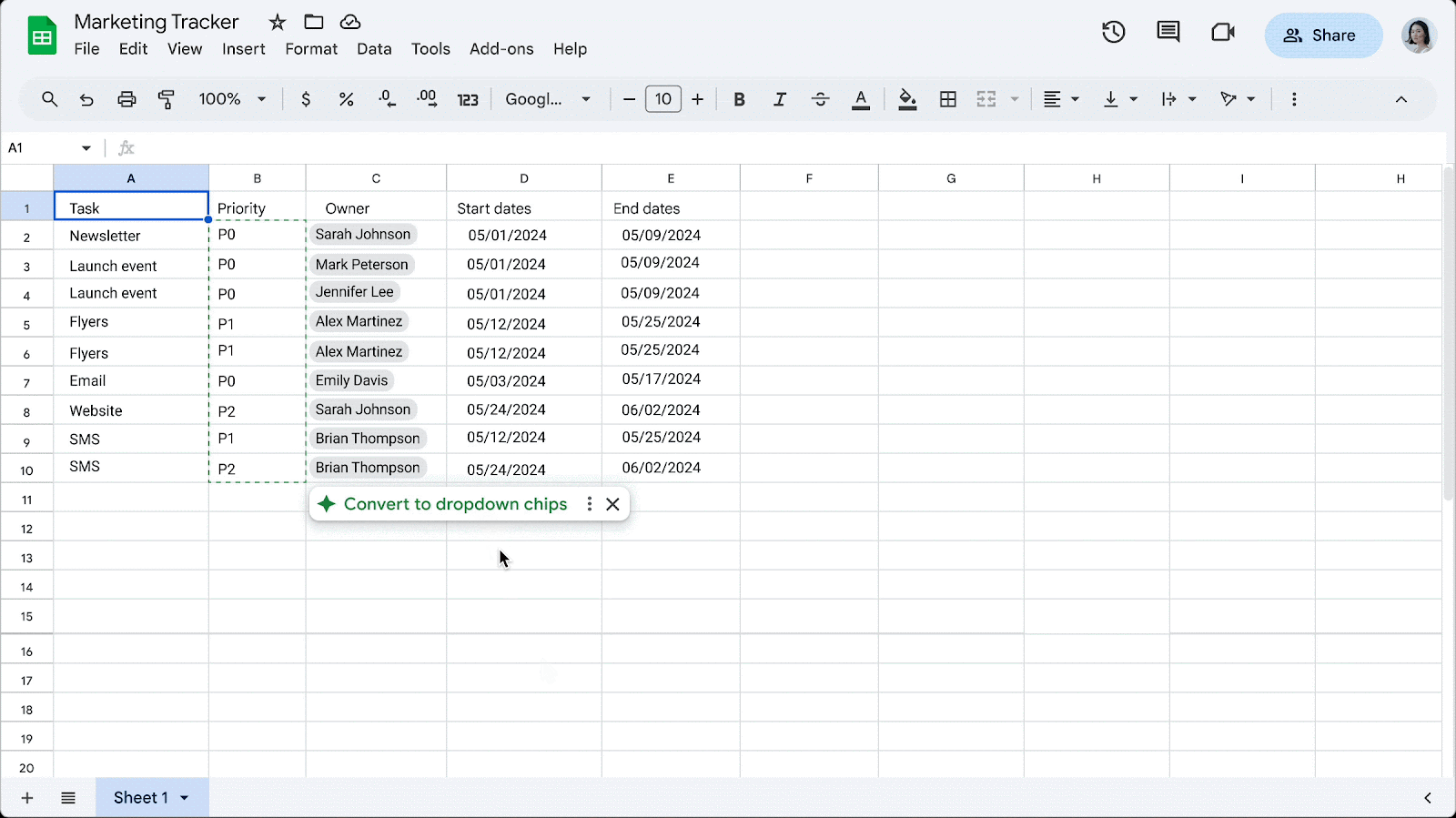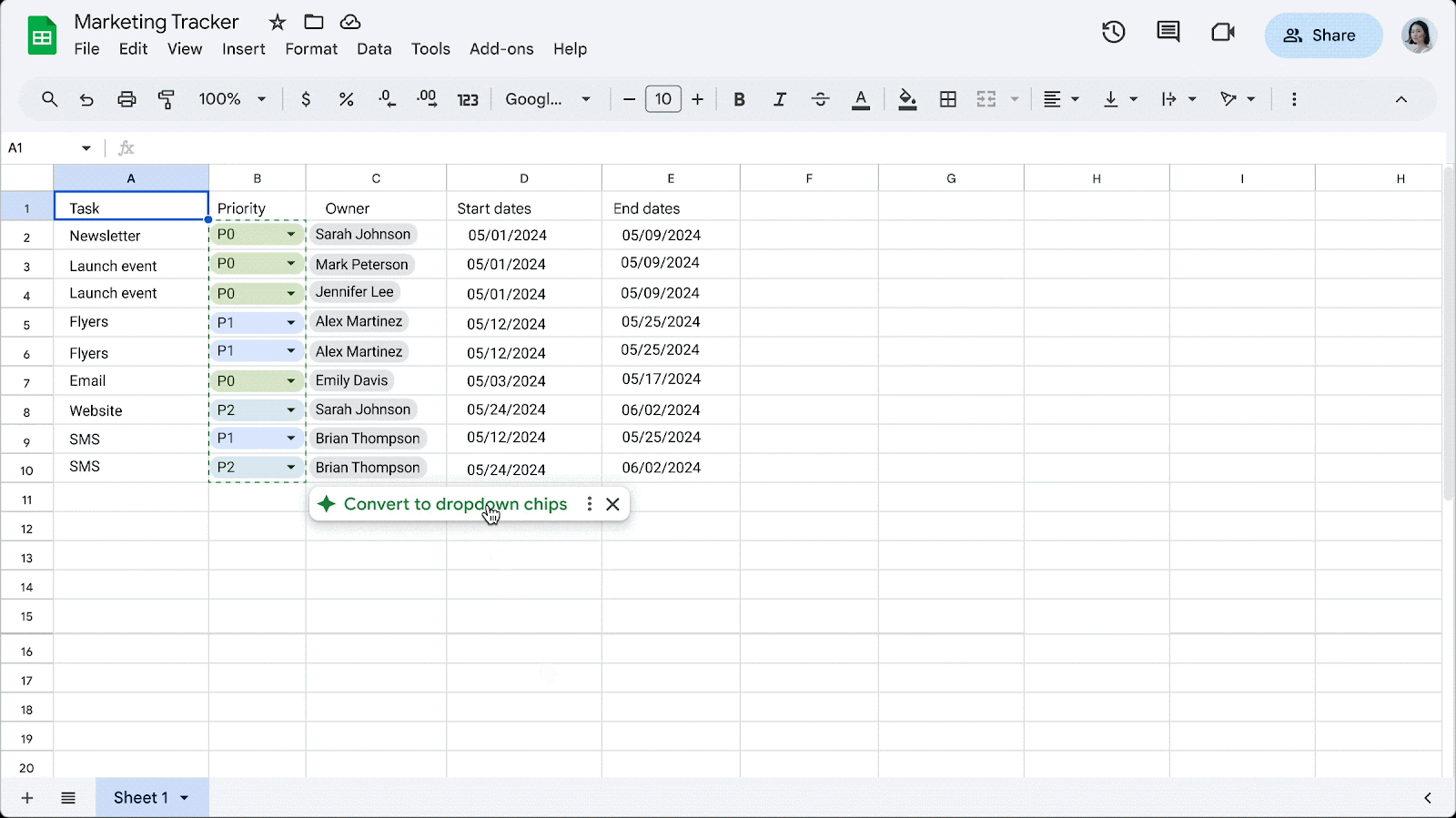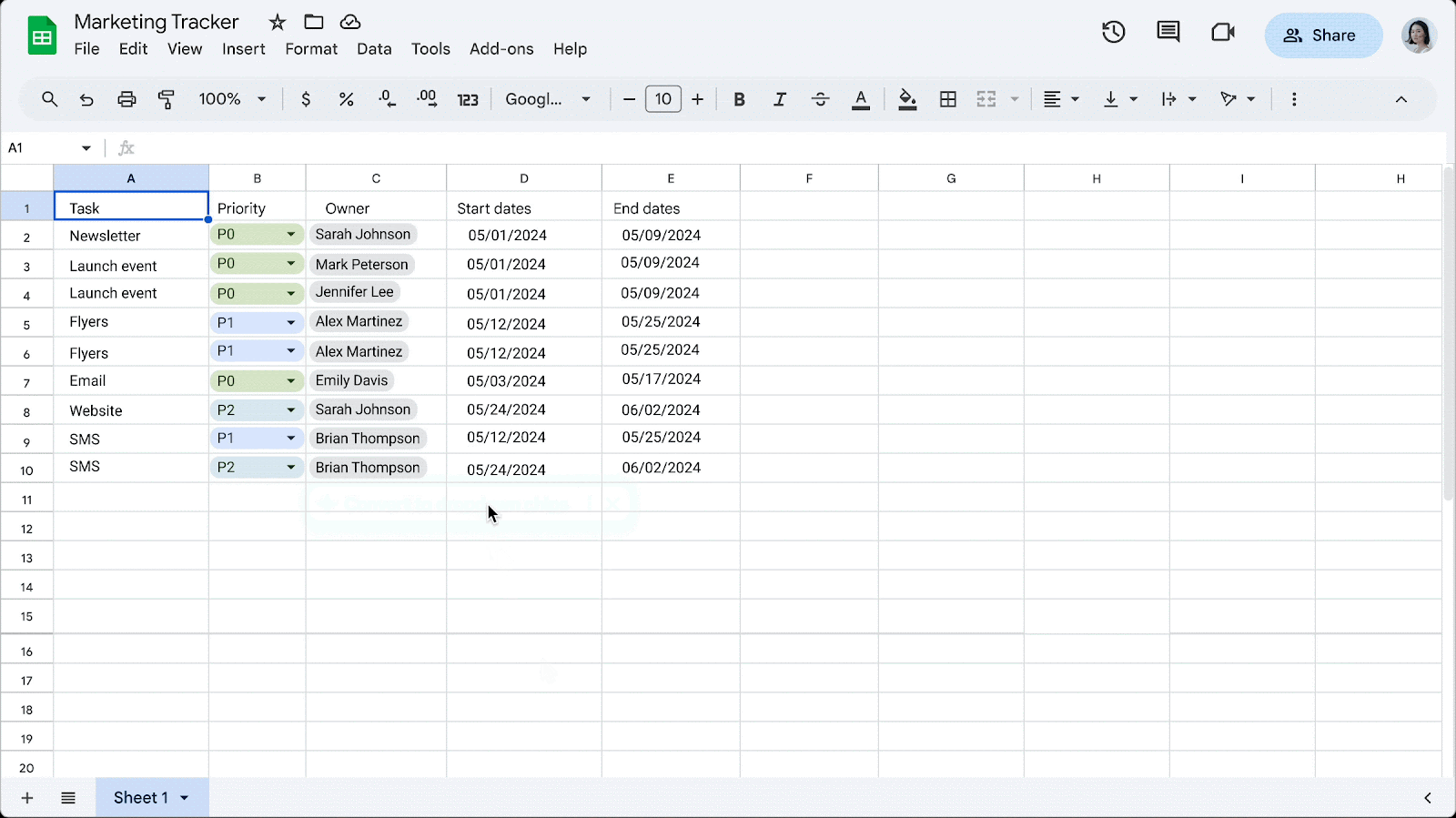
Easily convert data to dropdown chips in Google Sheets
What’s changing
Getting started
- Admins: There is no admin control for this feature.
- End users:
- To insert dropdown chips on your own, type “@” followed by “dropdown.
- To turn off this feature, go to Tools > Suggestion controls > (deselect) Enable dropdown chip suggestions.
- Visit the Help Center to learn more about inserting smart chips in your Google Sheets.
Rollout pace
- Rapid Release domains: Extended rollout (potentially longer than 15 days for feature visibility) starting on May 7, 2024, with expected completion by May 30, 2024
- Scheduled Release domains: Gradual rollout (up to 15 days for feature visibility) starting on May 30, 2024
Availability
- Available to all Google Workspace customers, Google Workspace Individual subscribers, and users with personal Google accounts
Resources
Source: Google Workspace Updates
Improving suspension alerting for Google Meet hardware devices
What’s changing
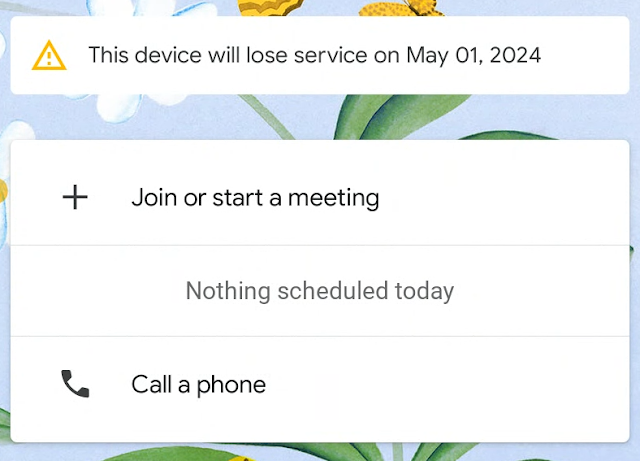
To ensure customers with Google Meet hardware devices have sufficient notice about canceled or expired device subscriptions, we’re adding notifications in the Admin console. Depending on your subscription details and timeline, you will see:- A warning banner in the Google Meet hardware section of Admin console when your Google Meet hardware subscription has expired and suspension is imminent. It will include the suspension date.
%20(1).png)
- A warning banner in the Google Meet hardware section of Admin console when your Google Meet hardware subscription has been suspended.
- An on-device suspension warning.
- The on-device warning will be ON by default and will begin to appear for customers with imminent suspensions starting May 29, 2024.
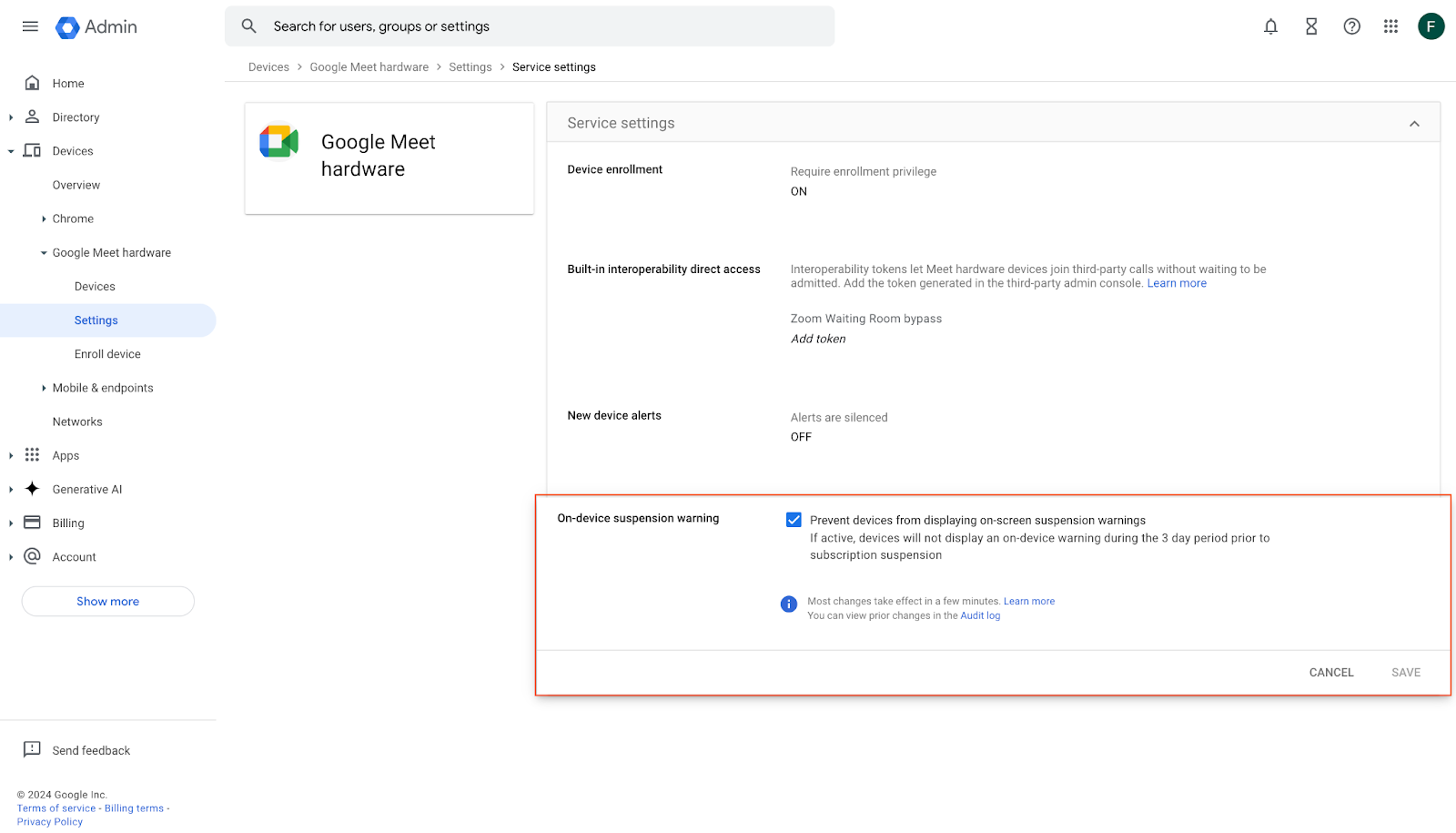
- To turn the on-device warning OFF, go to Admin console > Google Meet hardware > Settings > On-device suspension warning > Prevent devices from displaying on-screen suspension warnings.
- If this box is checked, devices will not display an on-device warning during the 3-day period prior to subscription suspension.
 |
Who’s impacted
Why it’s important
Additional details
Getting started
- Admins: For each Google Meet hardware device you purchase, you also purchase and assign a software license to that device. Licenses allow your device to work with the Google Meet service and gain access to device management tools in the Google Admin console. Visit the Help Center to learn more about licensing.
- End users: If a on-device suspension warning occurs, people in the room will see a warning when the device is 3 days away from suspension.
Rollout pace
- Rapid Release and Scheduled Release domains: Gradual rollout (up to 15 days for feature visibility) starting on May 15, 2024.
Availability
- This update impacts all Google Workspace customers with Meet hardware devices.
Resources
Source: Google Workspace Updates
More frequent, focused updates for Android Studio

Three years ago, we changed how we named and versioned Android Studio to make it easier to follow updates – we changed how we numbered the versions of the IDE to more closely map to versioning of the IntelliJ IDEA platform, on which Android Studio is built. We also introduced animal codenames to signify each major release, starting with Arctic Fox. Our most recent release, Koala (2024.1.1), will soon be available in the Beta channel and is built on top of IntelliJ IDEA 2024.1. All Studio releases use a version number that maps to the following schema:
<Year of IntelliJ Version>.<IntelliJ major version>.<Studio major version>
Soon, we are launching the Koala Feature Drop to the Canary channel as version 2024.1.2 — our second release based on IntelliJ IDEA 2024.1. This signals the start of an improved release cycle, where each animal codename includes two major Studio releases: a platform update followed by a feature drop.
The initial animal releases will have the ‘.1’ Android Studio major version and introduce the updated IntelliJ platform version, while subsequent Feature Drops will increase the Android major version to ‘.2’ and focus on introducing Android-specific features that help you be more productive for Android app development.
Versioning system
Year of IntelliJ Version
IntelliJ major version
Studio major version
Jellyfish
2023
.3
.1
Koala
2024
.1
.1
Koala Feature Drop
2024
.1
.2
Leading with IDE platform updates
Going forward, each new “animal” of Android Studio will prioritize updates to the underlying IntelliJ platform. This focus on foundational elements lets developers benefit from usability, performance, and stability improvements to the underlying IntelliJ IDEA platform.
The base version of Android Studio Koala, numbered 2024.1.1 and launched to Canary in March, focuses on adopting updates from IntelliJ IDEA 2024.1. Some benefits of this platform update include:
- Sticky lines in the editor to simplify working with large files and exploring new codebases
- Overhauled terminal featuring both visual and functional enhancements
- Basic IDE functionalities available for Java and Kotlin during indexing
- Language injections in string templates
- (Alpha) K2 Kotlin mode for enhanced Kotlin code analysis
- Inline breakpoints for multiple statements
- New inspections and quick-fixes
- And much much more…
See What’s New in IntelliJ IDEA 2024.1 for more details on all the platform updates included in this release.
By focusing a whole release cycle on updating to the latest IntelliJ IDEA platform version, we’re able to get those changes into the Stable channel faster than with the previous release process — ensuring developers have access to the latest upstream features and improvements.
Android-specific functionality with Feature Drops
Android Studio is a tailored environment for Android developers. You will continue to receive new and updated features specifically designed for Android development. These will arrive through Feature Drops that share the same animal codename as the base release, and will follow soon after the base animal release hits the Stable channel. Our first such release is Android Studio Koala Feature Drop, and numbered 2024.1.2.
When the Android Studio Koala Feature Drop is available, you can benefit from these new features:
- A new sign-in flow that makes onboarding with multiple Google services, such as Firebase and Gemini in Android Studio, much easier
- Device UI Setting Shortcuts in the Running Device Window to quickly test your app against different device UI settings
- A new Gemini API template to help build Generative AI into your app
- And more
Feature Drops will leverage the stabilized IDE platform from the previous Android Studio update and focus on new features geared towards Android development. By doing so, we hope to bring these features to the stable channel faster and with higher quality. To learn about even more new features coming to Koala Feature Drop, make sure to tune in to Google I/O 2024.
To sum it up: 2X more frequent updates

Our primary goal with these changes is to ensure that important updates to the IntelliJ IDEA platform reach the Android Studio Stable channel more frequently, and new Android-specific features ship with higher quality and polish. Expect the first animal release to introduce a number of updates from the latest IntelliJ IDEA platform, with a Feature Drop update to follow soon after with more Android-specific features and tools.
By separating IDE platform updates from Feature Drops, we can deliver both types of enhancements in a more streamlined manner, resulting in much more frequent updates to the stable channel that are each focused on improving your productivity.
Similarly, versions of the Android Gradle plugin will also see updates to the stable channel more frequently. Each new animal version and Feature Drop of Android Studio will be accompanied by a new version of the Android Gradle plugin. For example, Android Studio Koala was released alongside AGP 8.5 and Android Studio Koala Feature Drop will be released alongside AGP 8.6.
As always, if you want to be on the cutting edge, we encourage you to join the Canary channel by downloading and installing Android Studio Koala Feature Drop for early access to the latest and greatest. Also you can be part of our vibrant Android developer community on LinkedIn, Medium, YouTube, or X.
Source: Android Developers Blog
Meet Pixel 8a: The Google AI phone at an unbeatable value
 Pixel 8a is the latest A-series phone, bringing you a phone packed with Google AI at an affordable price.
Pixel 8a is the latest A-series phone, bringing you a phone packed with Google AI at an affordable price.
Source: The Official Google Blog
Block compromised mobile devices using context-aware access
What’s changing
Getting started
- Admins: Visit the Help Center to learn more about how to create context conditions and apply rules with compromised device signals, and our Developer documentation regarding custom access level specification. Compromised device events reports can be viewed in the security center by going to Security > Security center > dashboard > compromised device events.
Rollout pace
- Block access to Google Workspace data: available immediately for both Android and iOS.
- Remediation message: available immediately for Android, available on May 9, 2024 for iOS.
Availability
- Enterprise Standard and Plus
- Education Standard and Plus
- Frontline Standard
- Enterprise Essentials Plus
- Cloud Identity Premium
Resources
Source: Google Workspace Updates
Unimos a los educadores esta Semana de Agradecimiento a los Maestros
 La Profesora Estadounidense del Año 2024 Missy Testerman, de Tennessee, comparte más sobre su historia y el compromiso de Google con el futuro de la educación.
La Profesora Estadounidense del Año 2024 Missy Testerman, de Tennessee, comparte más sobre su historia y el compromiso de Google con el futuro de la educación.
Source: The Official Google Blog
Bringing educators together this Teacher Appreciation Week
 Google shares ongoing commitment to education with an essay from 2024 Teacher of the Year, Missy Testerman.
Google shares ongoing commitment to education with an essay from 2024 Teacher of the Year, Missy Testerman.
Source: The Official Google Blog
Test Failures Should Be Actionable
There are a lot of rules and best practices around unit testing. There are many posts on this blog; there is deeper material in the Software Engineering at Google book; there is specific guidance for every major language; there is guidance on test frameworks, test naming, and dozens of other test-related topics. Isn’t this excessive?
Good unit tests contain several important properties, but you could focus on a key principle: Test failures should be actionable.
When a test fails, you should be able to begin investigation with nothing more than the test’s name and its failure messages—no need to add more information and rerun the test.
Effective use of unit test frameworks and assertion libraries (JUnit, Truth, pytest, GoogleTest, etc.) serves two important purposes. Firstly, the more precisely we express the invariants we are testing, the more informative and less brittle our tests will be. Secondly, when those invariants don’t hold and the tests fail, the failure info should be immediately actionable. This meshes well with Site Reliability Engineering guidance on alerting.
Consider this example of a C++ unit test of a function returning an absl::Status (an Abseil type that returns either an “OK” status or one of a number of different error codes):
If the test on the left fails, you have to investigate why the test failed; the test on the right immediately gives you all the available detail, in this case because of a more precise GoogleTest matcher.
Here are some other posts on this blog that emphasize making test failures actionable:
Writing Descriptive Test Names - If our tests are narrow and sufficiently descriptive, the test name itself may give us enough information to start debugging.
Keep Tests Focused - If we test multiple scenarios in a single test, it’s hard to identify exactly what went wrong.
Prefer Narrow Assertions in Unit Tests - If we have overly wide assertions (such as depending on every field of a complex output proto), the test may fail for many unimportant reasons. False positives are the opposite of actionable.
Keep Cause and Effect Clear - Refrain from using large global test data structures shared across multiple unit tests, allowing for clear identification of each test’s setup.
Source: Google Testing Blog
A simplified experience for Workspace users to add 2-Step Verification (2SV) methods
What’s changing
We’re simplifying how users turn on 2-Step Verification (2SV), which will streamline the process, and make it easier for admins to enforce 2SV policies in their organizations.
Here are some of the important changes with this change:
- Users may add “second step methods” (such as Google Authenticator, or a hardware security key) before turning on 2SV. This is particularly helpful for organizations using Google Authenticator (or other equivalent time-based one-time password (TOTP) apps). Previously, users had to enable 2SV with a phone number before being able to add Authenticator.
- Users with hardware security keys will have two options to add them to their account on the “Passkeys and security keys” page:
- ‘Use security key”: this registers a FIDO1 credential on the security key even if the key itself is FIDO2 capable.
- ‘Create passkey and follow instructions to “use another device”: this registers a FIDO2 credential on the security key, and will require users to use the key’s PIN for local verification (this creates a passkey on the security key).
- Note: users will continue to be asked for their password along with their passkey if the admin policy for “Allow users to skip passwords at sign-in by using passkeys” remains turned OFF (this is the default configuration).
- If an enrolled 2SV user turns 2SV OFF from their account settings, their enrolled second steps (such as backup codes, Google Authenticator, or second factor phone) are not automatically removed from their account. Before this change all second factors would be removed when the user turned 2SV off. Note: When an administrator turns off 2SV for a user from the Admin console or via the Admin SDK, the second factors will be removed as before, to ensure user off-boarding workflows remain unaffected
Getting started
- Admins: Visit the Help Center to learn more about how to protect your business with 2-step verification.
- End users: Visit the Help Center to learn more about turning on 2-step verification.
Rollout pace
- Rapid Release and Scheduled Release domains: Full rollout (1–3 days for feature visibility) starting on May 6, 2024
Availability
- Available to all Google Workspace customers and users with personal Google accounts