Posted by Gurupreet Singh, Developer Advocate; Android
Today marks the first stable release of Compose Material 3. The library allows you to build Jetpack Compose UIs with Material Design 3, the next evolution of Material Design. You can start using Material Design 3 in your apps today!
Note: The terms "Material Design 3", "Material 3", and "M3" are used interchangeably.
Material 3 includes updated theming and components, exclusive features like dynamic color, and is designed to be aligned with the latest Android visual style and system UI.
 |
| Multiple apps using Material Design 3 theming |
You can start using Material Design 3 in your apps by adding the Compose Material 3 dependency to your build.gradle files:
// Add dependency in module build.gradle
implementation "androidx.compose.material3:material3:$material3_version" |
Note: See the latest M3 versions on the
Compose Material 3 releases page.
Color schemes
Material 3 brings extensive, finer grained color customisation, and comes with both light and dark color scheme support out of the box. The
Material Theme Builder allows you to generate a custom color scheme using core colors, and optionally export Compose theming code. You can
read more about color schemes and color roles.
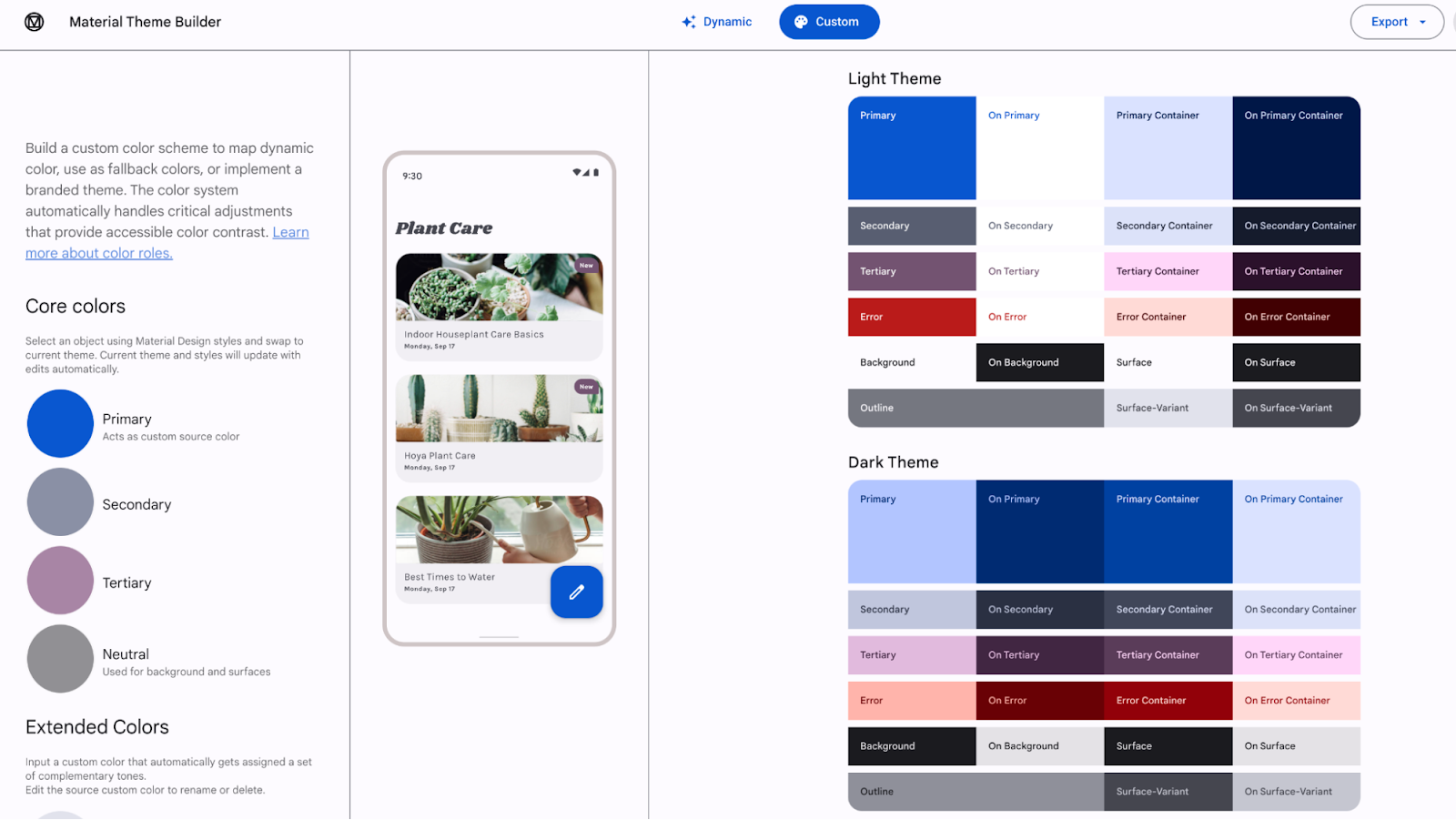 |
| Material Theme Builder to export Material 3 color schemes |
Dynamic color
Dynamic color derives from the user’s wallpaper. The colors can be applied to apps and the system UI.
Dynamic color is available on Android 12 (API level 31) and above. If dynamic color is available, you can set up a dynamic ColorScheme. If not, you should fall back to using a custom light or dark ColorScheme.
  |
| Reply Dynamic theming from wallpaper(Left) and Default app theming (Right) |
The ColorScheme class provides builder functions to create both dynamic and custom light and dark color schemes:
Theme.kt
// Dynamic color is available on Android 12+
val dynamicColor = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S
val colorScheme = when {
dynamicColor && darkTheme -> dynamicDarkColorScheme(LocalContext.current)
dynamicColor && !darkTheme -> dynamicLightColorScheme(LocalContext.current)
darkTheme -> darkColorScheme(...)
else -> lightColorScheme(...)
}
MaterialTheme(
colorScheme = colorScheme,
typography = typography,
shapes = shapes
) {
// M3 App content
} |
Material components
The Compose Material 3 APIs contain a wide range of both new and evolved Material components, with more planned for future versions. Many of the Material components, like
Card,
RadioButton and
CheckBox, are no longer considered experimental; their APIs are stable and they can be used without the
ExperimentalMaterial3Api annotation.
The M3
Switch component has a brand new UI refresh with accessibility-compliant minimum touch target size support, color mappings, and optional icon support in the switch thumb. The touch target is bigger, and the thumb size increases on user interaction, providing feedback to the user that the thumb is being interacted with.
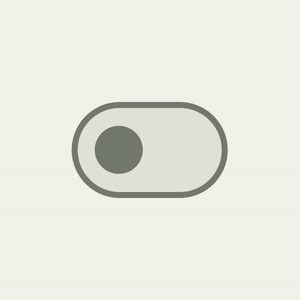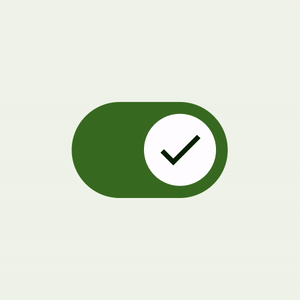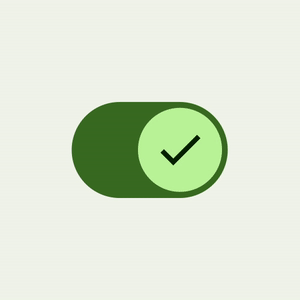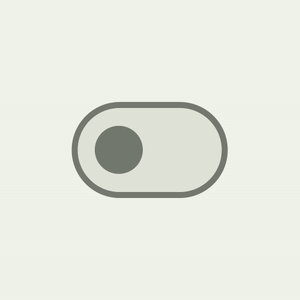 |
| Material 3 Switch thumb interaction |
Switch(
checked = isChecked,
onCheckedChange = { /*...*/ },
thumbContent = {
Icon(
imageVector = Icons.Default.Check,
contentDescription = stringResource(id = R.string.switch_check)
)
},
) |
Navigation drawer components now provide wrapper sheets for content to change colors, shapes, and elevation independently.
| Navigation drawer component | Content |
| ModalNavigationDrawer | ModalDrawerSheet |
PermanentNavigationDrawer
| PermanentDrawerSheet |
| DismissableNavigationDrawer | DismissableDrawerSheet |
 |
| ModalNavigationDrawer with content wrapped in ModalDrawerSheet |
ModalNavigationDrawer {
ModalDrawerSheet(
drawerShape = MaterialTheme.shapes.small,
drawerContainerColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primaryContainer,
drawerContentColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onPrimaryContainer,
drawerTonalElevation = 4.dp,
) {
DESTINATIONS.forEach { destination ->
NavigationDrawerItem(
selected = selectedDestination == destination.route,
onClick = { ... },
icon = { ... },
label = { ... }
)
}
}
} |
We have a brand new
CenterAlignedTopAppBar in addition to already existing app bars. This can be used for the main root page in an app: you can display the app name or page headline with home and action icons.
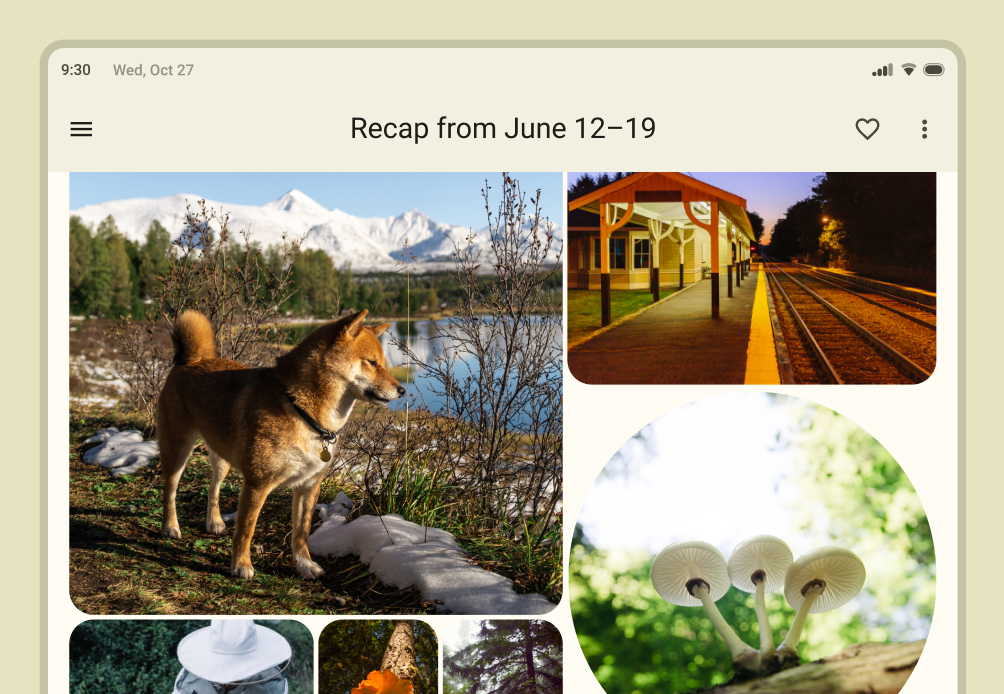 |
| Material CenterAlignedTopAppBar with home and action items. |
CenterAlignedTopAppBar(
title = {
Text(stringResources(R.string.top_stories))
},
scrollBehavior = scrollBehavior,
navigationIcon = { /* Navigation Icon */},
actions = { /* App bar actions */}
) |
Typography
Material 3 simplified the naming and grouping of typography to:
- Display
- Headline
- Title
- Body
- Label
There are large, medium, and small sizes for each, providing a total of 15 text style variations.
The Typography constructor offers defaults for each style, so you can omit any parameters that you don’t want to customize:val typography = Typography(
titleLarge = TextStyle(
fontWeight = FontWeight.SemiBold,
fontSize = 22.sp,
lineHeight = 28.sp,
letterSpacing = 0.sp
),
titleMedium = TextStyle(
fontWeight = FontWeight.SemiBold,
fontSize = 16.sp,
lineHeight = 24.sp,
letterSpacing = 0.15.sp
),
...
} |
You can customize your typography by changing default values of
TextStyle and
font-related properties like
fontFamily and
letterSpacing.
bodyLarge = TextStyle(
fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal,
fontFamily = FontFamily.SansSerif,
fontStyle = FontStyle.Italic,
fontSize = 16.sp,
lineHeight = 24.sp,
letterSpacing = 0.15.sp,
baselineShift = BaselineShift.Subscript
) |
Shapes
The Material 3 shape scale defines the style of container corners, offering a range of roundedness from square to fully circular.
There are different sizes of shapes:
- Extra small
- Small
- Medium
- Large
- Extra large
 |
| Material Design 3 shapes used in various components as default value. |
Each shape has a default value but you can override it:
val shapes = Shapes(
extraSmall = RoundedCornerShape(4.dp),
small = RoundedCornerShape(8.dp),
medium = RoundedCornerShape(12.dp),
large = RoundedCornerShape(16.dp),
extraLarge = RoundedCornerShape(28.dp)
) |
You can
read more about applying shape.
Window size classes
Jetpack Compose and Material 3 provide window size artifacts that can help make your apps adaptive. You can start by adding the Compose Material 3 window size class dependency to your build.gradle files:
// Add dependency in module build.gradle
implementation "androidx.compose.material3:material3-window-size-class:$material3_version" |
Window size classes group sizes into standard size buckets, which are breakpoints that are designed to optimize your app for most unique cases.
 |
| WindowWidthSize Class for grouping devices in different size buckets |
See the Reply Compose sample to learn more about adaptive apps and the window size classes implementation.
Window insets support
M3 components, like top app bars, navigation drawers, bar, and rail, include built-in support for window insets. These components, when used independently or with Scaffold, will automatically handle insets determined by the status bar, navigation bar, and other parts of the system UI.
Scaffold now supports the contentWindowInsets parameter which can help to specify insets for the scaffold content.
Scaffold insets are only taken into consideration when a topBar or bottomBar is not present in Scaffold, as these components handle insets at the component level.
Scaffold(
contentWindowInsets = WindowInsets(16.dp)
) {
// Scaffold content
} |
Resources
With Compose Material 3 reaching stable, it’s a great time to start learning all about it and get ready to adopt it in your apps. Check out the resources below to get started.

.jpg)
















