
Posted by Bessie Jiang – Software Engineer and Chris Schneider – Security Engineer
Contributors: Maciej Szawłowski – Security Engineer, Hannah Barnes – Technical Program Manager, Dirk Göhmann – Technical Writer, Patrick Mutchler – Software Engineer

Security is tricky, but vital to protecting your users and their data. We’re here to help you build secure Android apps with fewer vulnerabilities for an even safer Android ecosystem for everybody.
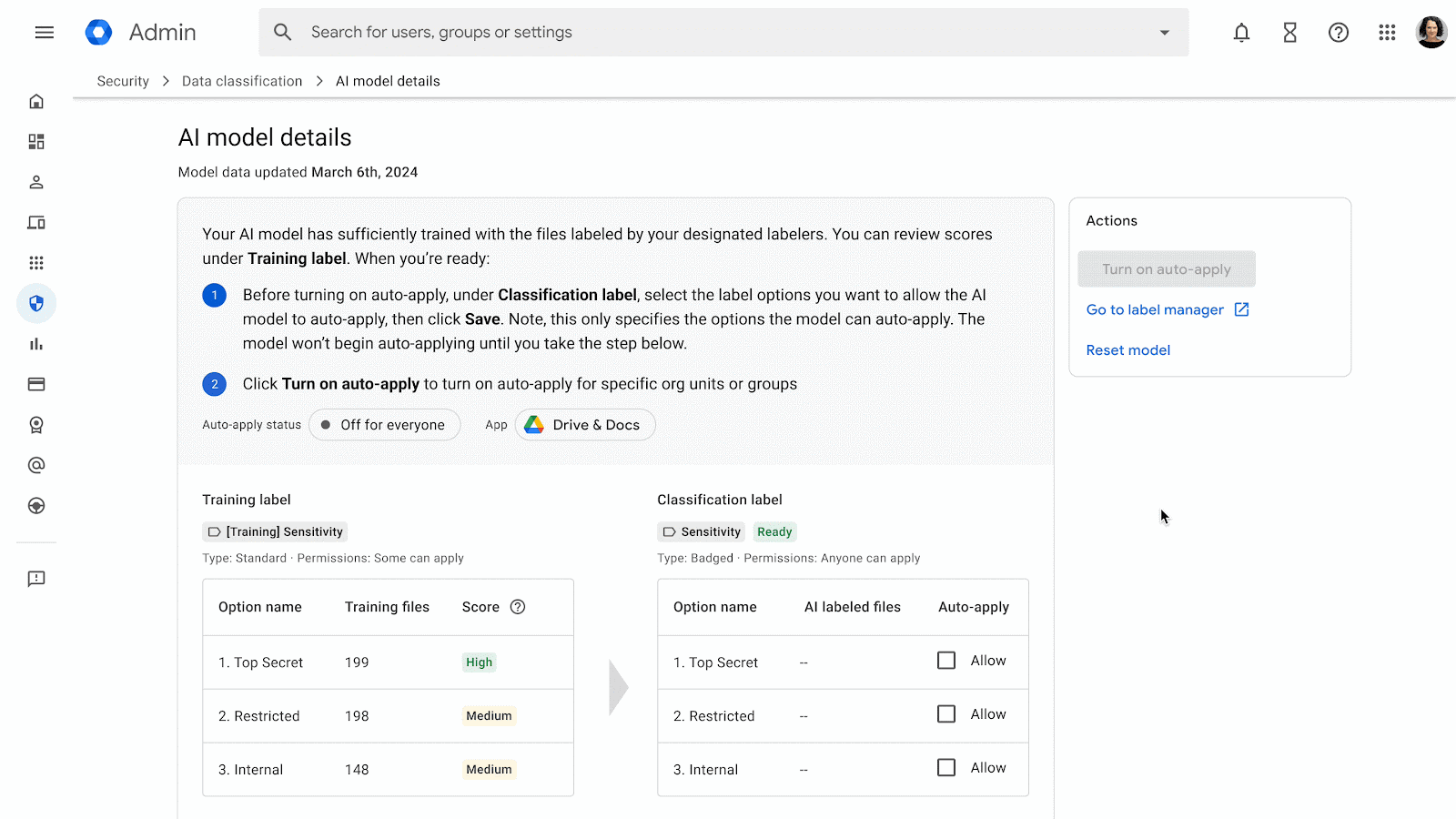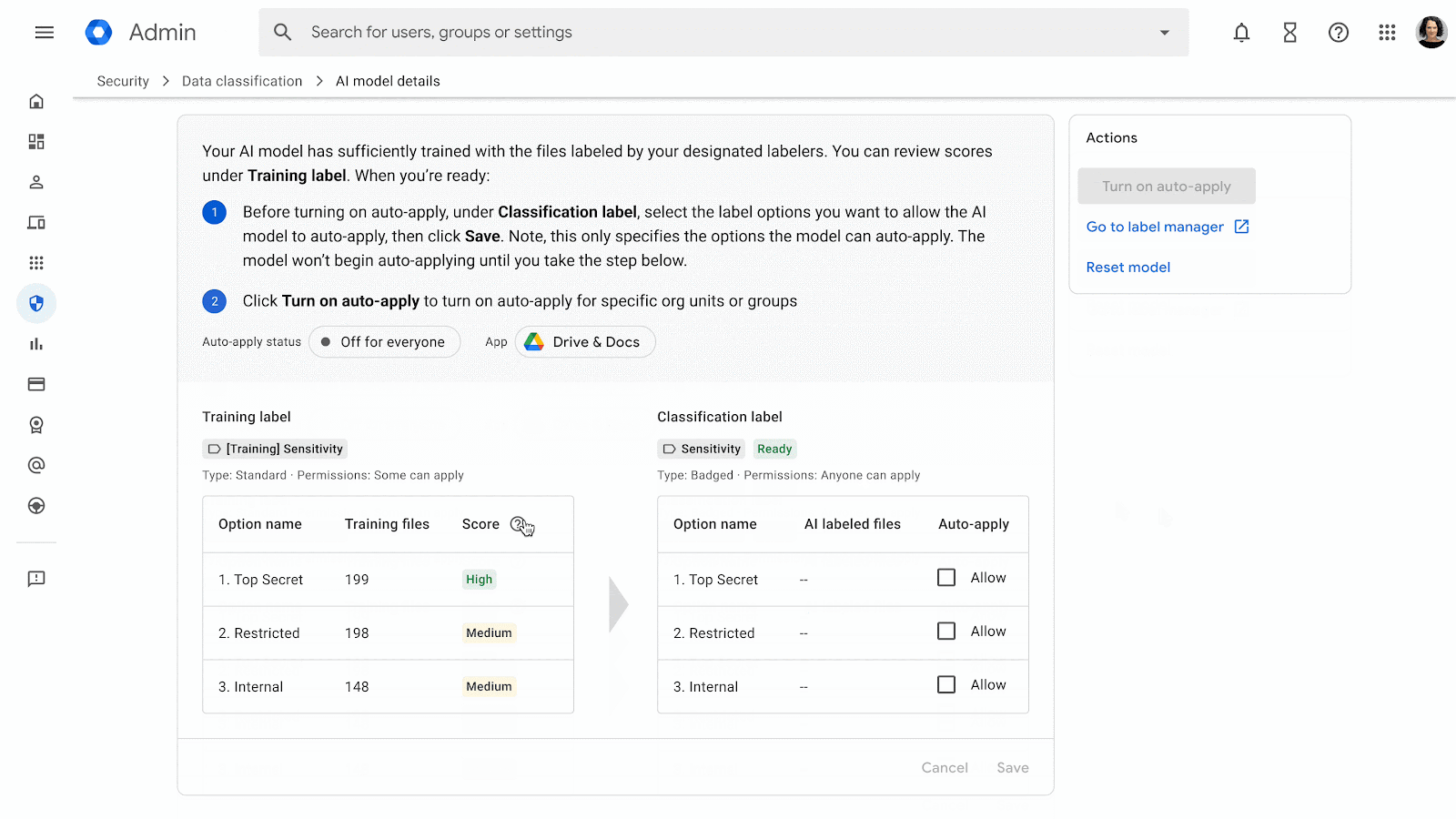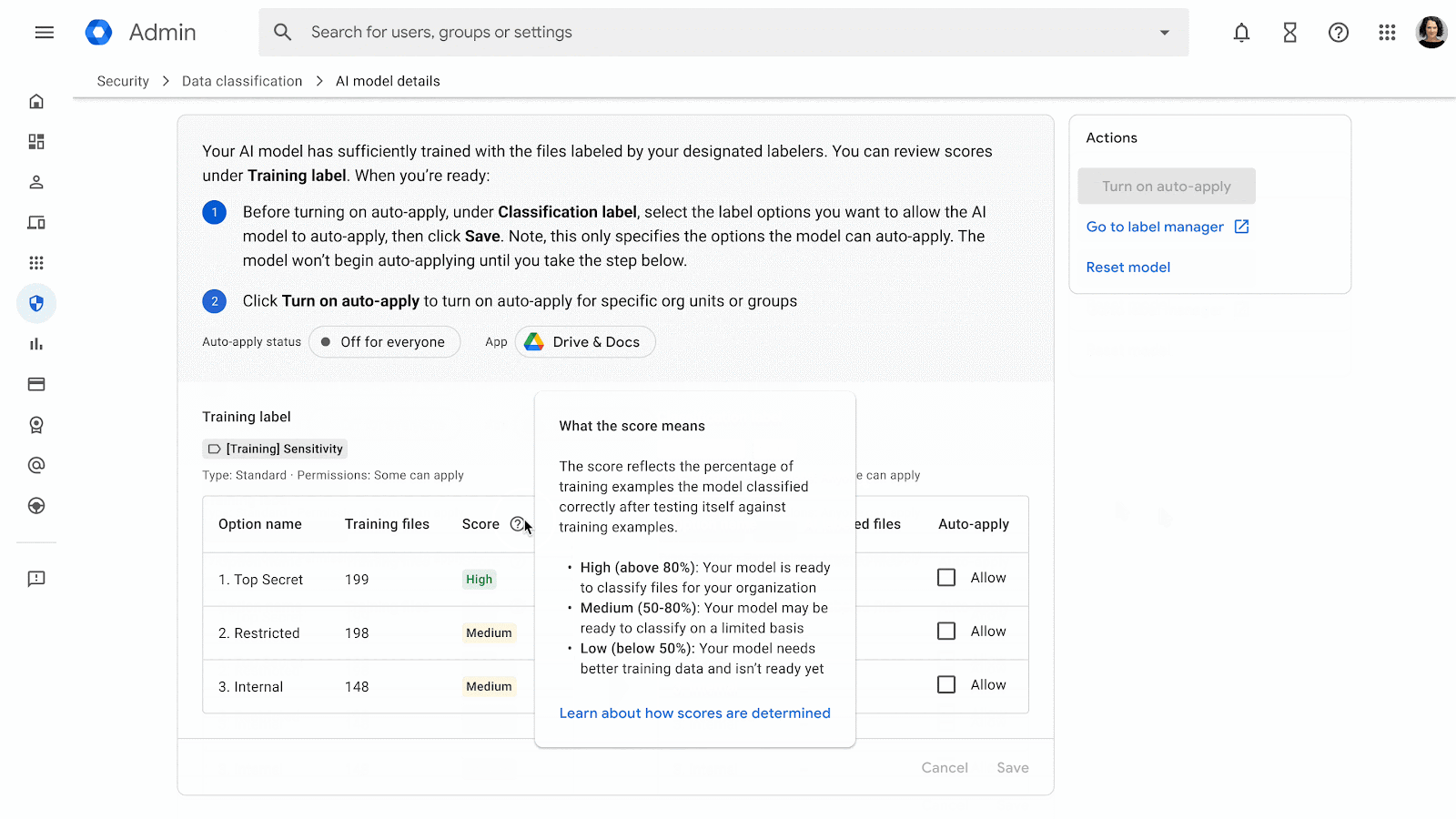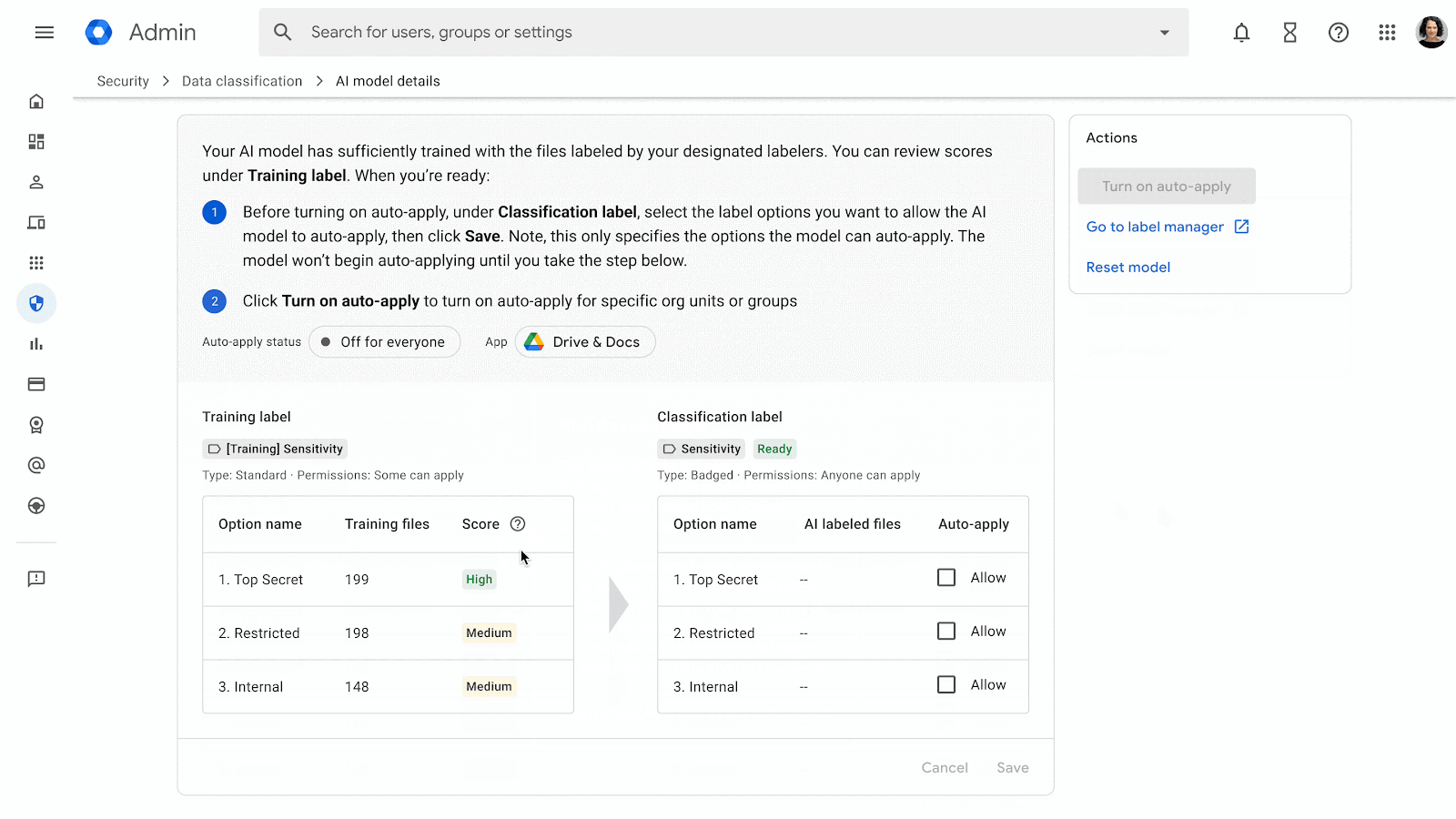
Vulnerability Detection – How it Works
Google currently scans every app on Google Play for dozens of common security vulnerability classes. If we spot something, we let you know so you can fix the problem. Imagine a pentesting team hunting for bugs in each of the millions of apps published on Play, rooting out issues like bad TLS configurations that expose network traffic or directory traversal vulnerabilities that let adversaries read from or write to an app’s private files.
We are committed to keeping our joint users protected. In serious cases, if a security vulnerability doesn't get fixed, Google may remove the app from Google Play to keep users safe.
Android Application Security Knowledge Base
We know that it isn’t always enough to just tell you about a vulnerability in your app; you need to know how to fix the issue and how to prevent similar issues from cropping up in the future. To this end, we are introducing our security guidance and recommendations under a new program: the Android Application Security Knowledge Base (AAKB).
AAKB aims to establish guidelines for writing secure Android software. It is a repository of common code issues, with remediation examples and explanations for implementing specific code patterns. Organic in nature, new issues are identified automatically for review with experts across the industry – ensuring broad but well-tested approaches and guidance.
Data collected from your engagement with AAKB is used to improve guidance, and to identify how to make the Android ecosystem more secure by default.
How Does it Work?
AAKB establishes clear, vetted guidance with code examples. Guidance is aligned to OWASP MASVS standards, and content is vetted in partnership with technical peers, such as Microsoft. This helps ensure the content is not biased to one party and represents state-of-the-art standards. This also provides an educational place for you to proactively remediate security risks in your applications using industry-wide standards, with direct access to knowledge from subject-matter experts.
The guidance is available through two mechanisms:
The AAKB homepage lists each article independently, aligned to the relevant OWASP MASVS category (e.g. MASVS-STORAGE). Anyone can view or provide direct feedback to this content. Security is an ever-changing field, and being able to update guidance on the fly means software development lifecycles can be updated dynamically with as little friction as possible.
Android Studio triggers remediation guidance from lint checks by pointing directly to AAKB articles. You can fix problems as you're building the app and before they ever reach users.
There are two methods to view remediation guidance with Android Studio:
Existing security lint checks within Android Studio Giraffe+ have had their descriptions updated to include a link to the relevant AAKB article, allowing you get more context as to why a particular code snippet might be potentially “at-risk”.
Figure 1. Example of a finding with a link to a relevant AAKB article in the Android Studio IDE
Meanwhile, the open-source Android Security lint checks give you access to our most recent guidance and experiments to further protect your mobile applications and get ahead of future security concerns.
Add the open source checks to your project by following the README. These lint checks all contain click-to-fix functionality that make it easy for you to write safer code with minimal effort, as well as links to the relevant AAKB articles like the built-in IDE checks.
Figure 2. Example of an open-source security lint finding, highlighting a vulnerable code snippet and click-to-fix solution
All built-in IDE lint checks can be found in this list, with many under the Security category containing links to relevant AAKB articles. We would love to hear your feedback and suggestions for new lint checks and other improvements to the open-source lint library.










 We’re bringing 1.5 Flash to Gemini, launching a new related content feature and expanding our Gemini for Teens experience.
We’re bringing 1.5 Flash to Gemini, launching a new related content feature and expanding our Gemini for Teens experience.