Android 13 is rolling out to Pixel devices starting today. Later this year, Android 13 will also roll out to more of your favorite devices from Samsung Galaxy, Asus, HMD (Nokia phones), iQOO, Motorola, OnePlus, Oppo, Realme, Sharp, Sony, Tecno, vivo, Xiaomi and more.
As always, we thank you for the feedback you’ve shared, and we appreciate the work you’ve done to make your apps compatible with today’s release. Your support and contributions are what make Android a great platform for everyone!
What’s in Android 13 for developers?
Here’s a look at some of what’s new in Android 13 - make sure to check out the
Android 13 developer site for details on all of the new features.
Developer productivity and tools
Themed app icons - Android 13 extends Material You dynamic color to all app icons, letting users opt-in to icons that inherit the tint of their wallpaper and other theme preferences. All your app needs to supply is a
monochromatic app icon and a tweak to the adaptive icon XML.
More here.
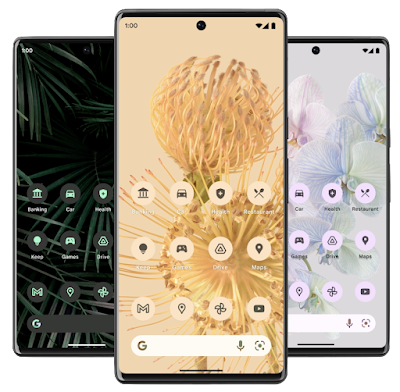 |
| Themed app icons adapting to wallpapers colors and dark theme (left). |
Per-app language preferences - Android 13 makes it easier to support multilingual users who want to use your apps in a language that’s different from the system language. Android now provides a standard “App language” Settings panel for apps that have
opted-in, and you can call
a new platform API to get or set the user’s preferred locale at runtime, helping to reduce boilerplate code and improve compatibility.
More here.
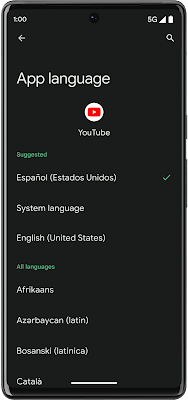 |
| Per-app languages in Settings |
Improved text support - Android 13 includes text and language improvements that help you deliver a more polished experience.
Faster hyphenation optimizes hyphenation performance by as much as 200% so you can now enable it in your TextViews with almost no impact on rendering performance.
Text conversion APIs make searching and autocompletion faster when using phonetic lettering input for languages like Japanese, Chinese, and others. Android 13 also
improves line heights for non-latin scripts (such as Tamil, Burmese, Telugu, and Tibetan), eliminating clipping and making them easier to read.
More here.
 |
Improved line height for non-Latin scripts in apps targeting Android 13 (bottom).
|
Color vector fonts - Android 13 adds rendering support for COLR version 1 (
spec,
intro video) fonts and updates the system emoji to the COLRv1 format. COLRv1 is a new, highly compact, font format that renders quickly and crisply at any size. For most apps this will just work, and the system handles everything.
More here.
 |
COLRv1 vector emoji (left) and bitmap emoji.
|
Quick Settings Placement API - For apps that provide
custom Quick Settings tiles, Android 13 makes it easier for users to discover and add your tiles. Using a new
tile placement API, your app can now prompt the user to directly add your custom Quick Settings tile in a single step, without leaving your app.
More here.
Programmable shaders - Android 13 introduces programmable
RuntimeShader objects, with behavior defined using the
Android Graphics Shading Language (AGSL). You can use these shaders to create
ripple,
blur,
stretch, and similar advanced effects in your apps.
More here.
Media controls derived from PlaybackState - For apps targeting Android 13, the system now derives media controls from
PlaybackState actions, providing a richer set of controls that are consistent across phones and tablet devices and align with other Android platforms such as Android Auto and Android TV.
More here.
 |
Android 13 media controls are consistent on phones and tablets. |
Bluetooth LE Audio - Low Energy (LE) Audio is the next-generation wireless audio built to enable new use cases like sharing and broadcasting audio to friends and family, or subscribing to public broadcasts for information, entertainment, or accessibility. It’s designed to ensure that users can receive high fidelity audio without sacrificing battery life, and lets them seamlessly switch between different use cases. Android 13 adds built-in support for LE Audio, so developers can use the new capabilities on compatible devices. More here.
MIDI 2.0 - Android 13 adds support for the new MIDI 2.0 standard, including the ability to connect MIDI 2.0 hardware through USB. This updated standard offers features such as increased resolution for controllers, better support for non-Western intonation, and more expressive performance using per-note controllers. More here.
OpenJDK 11 updates - Android 13 Core Libraries now align with the OpenJDK 11 LTS release, with both library updates and Java 11 programming language support for app and platform developers. We plan to bring these Core Library changes to more devices through Google Play system updates, as part of an ART module update for devices running Android 12 and higher. More here.
Predictive back gesture - Android 13 introduces new APIs that let your app tell the system that it will handle back events in advance, a practice we call the "ahead-of-time" model. This new approach is part of a multi-year effort to help you prepare your app to support the predictive back gesture, which is available for testing in this release through a developer option. More here.
Built for tablets
Android 13 extends the 12L update that we released earlier this year, and it delivers an even better experience on tablets. You’ll find features like an enhanced multitasking taskbar, more large-screen layouts and optimizations in system UI and apps, improved compatibility modes for apps, and more. We’re continuing to invest to give you the tools you need to build great experiences for tablets as well as Chromebooks and foldables. You can learn more about how to get started optimizing for large screens, and be sure to check out our large screens developer resources.
 |
| Multitasking on tablets with Android 13. |
Privacy and security
Photo picker and APIs - A new system photo picker now gives users a standard, privacy-protecting way to share local and cloud-based photos. Photo picker extends Android’s long-standing document picker and makes it easy for users to share specific photos and videos with an app, without giving the app permission to view all media files on the device. Photo picker provides a dedicated experience for photos and videos and includes APIs for apps to access the shared media files. The photo picker experience is now available to users who receive Google Play system updates, on devices (excepting Go devices) running Android 11 and higher.
More here.
 |
Photo picker lets users share specific photos and videos with an app. |
Notification permission - To help users focus on the notifications that are most important to them, Android 13 introduces a new notifications runtime permission. Apps now need to request the notification permission from the user before posting notifications. For apps targeting Android 12 or lower, the system will handle the upgrade flow on your behalf. More here.Notification permission dialog in Android 13.
|
Nearby device permission for Wi-Fi - Android 13 introduces the NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES runtime permission for apps that manage a device's connections to nearby access points over Wi-Fi. The new permission is required for many commonly-used Wi-Fi APIs and enables apps to discover and connect to nearby devices over Wi-Fi without also needing to acquire the location permission. More here.
Granular permissions for media file access - Photo picker is our recommended solution for user-friendly, permissionless sharing of photos and videos, but for apps that haven’t moved to photo picker yet or for audio use cases, Android 13 adds new granular media permissions. These new permissions replace the READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE permission and provide access to specific types of media files, including images, video, or audio. We highly recommend moving your app to photo picker if possible; otherwise, use the granular media permissions when targeting Android 13. More here.
 |
Requesting permission to access audio files.
|
Developer downgradable permissions - Starting in Android 13, apps that no longer require permissions previously granted by the user can use a
new API to downgrade the permissions. By removing unused permissions, your app can show that it’s using the minimum permissions needed, which can improve user trust.
More here.
Safer exported Intent filters - Android 13 applies stricter rules when delivering explicit intents to exported intent filters in another app that’s targeting Android 13. For intents that specify actions, the system now delivers the intents to the exported component only if the intent matches the receiver’s declared
<intent-filter> elements.
More here.
Performance for apps
Android 13 improves performance and efficiency for all apps through updates to the ART runtime. We plan to bring these improvements to more Android users through Google Play system updates, as part of our ongoing ART module updates for devices running Android 12 and higher.
Improved garbage collection - A new garbage collector based on the Linux kernel feature
userfaultfd is coming to ART on Android 13 devices in an upcoming Google Play system update. The new garbage collector eliminates the read barrier and its fixed overhead per object loaded, reducing memory pressure and leading to as much as ~10% reduction in compiled code size. It’s more efficient at GC-time as well, since pages are freed as compaction progresses. Overall, the new garbage collector helps to save battery, avoid jank during GC operations, and protect apps from low-memory kills.
Optimizations throughout ART - In Android 13, ART makes switching to and from native code much faster, with JNI calls now up to 2.5x faster. We’ve also reworked the runtime’s reference processing to make it mostly non-blocking, which further reduces jank. We’ve exposed a new public API,
Reference.refersTo(), which is useful in reclaiming unreachable objects sooner, and we’ve made the interpreter faster by optimizing class/method lookups. Lastly, ART now performs more byte-code verification at install time, avoiding the expense of verification at runtime and keeping app startup times fast.
More here.
Get your apps ready!
Now with today’s public release of Android 13 to AOSP, we’re asking all Android developers to
finish your compatibility testing and
publish your updates as soon as possible, to give your users a smooth transition to Android 13.
To test your app for compatibility, just install it on a
device running Android 13 and work through the app flows looking for any functional or UI issues. Review the Android 13
behavior changes for all apps first, to focus on areas where your current app could be affected. Here are some of the top changes to test:
- Notifications runtime permission - Make sure you understand how this new permission works with your app’s notifications, and plan on targeting Android 13 (API 33) as soon as possible to help support users. More here.
- Clipboard preview - Make sure your app hides sensitive data in Android 13’s new clipboard preview, such as passwords or credit card information. More here.
- JobScheduler prefetch - JobScheduler now tries to anticipate the next time your app will be launched and will run any associated prefetch jobs ahead of that time. If you use prefetch jobs, test that they are working as expected. More here.
Remember to test the libraries and SDKs in your app for compatibility. If you find any SDK issues, try updating to the latest version of the SDK or reaching out to the developer for help.
Once you’ve published the compatible version of your current app, you can start the
process to
update your app's targetSdkVersion. Review the
behavior changes for apps targeting Android 13 for this, and use the
compatibility framework to help detect issues quickly.
Tablet and large-screens support
With Android 13 bringing a better experience to tablets, make sure your apps look their best. You can test large-screen features by
setting up an Android emulator in Android Studio, or you can use a large screen device from our
Android 13 Beta partners. Here are some areas to watch for:
- Taskbar interaction - Check how your app responds when viewed with the new taskbar on large screens. Make sure your app's UI isn't cut off or blocked by the taskbar. More here.
- Multi-window mode - Multi-window mode is now enabled by default for all apps, regardless of app configuration, so make sure the app handles split-screen appropriately. You can test by dragging and dropping your app into split-screen mode and adjusting the window size. More here.
- Improved compatibility experience - if your app isn’t optimized for tablets yet, such as using a fixed orientation or not being resizable, check how your app responds to compatibility mode adjustments such as letterboxing. More here.
- Media projection - If your app uses media projection, check how your app responds while playing back, streaming, or casting media on large screens. Be sure to account for device posture changes on foldable devices as well. More here.
- Camera preview - For camera apps, check how your camera preview UI responds on large screens when your app is constrained to a portion of the screen in multi-window or split-screen mode. Also check how your app responds when a foldable device's posture changes. More here.
You can read more about the tablet features in Android 13 and what to test
here.
What’s next?
Android 13 is rolling out to Pixel devices starting today.
If you’re currently enrolled in the Android Beta program, you’ll get the Android 13 final release and remain enrolled to receive ongoing Beta updates for Android 13 feature drops, starting later this year. If you’d like to opt out of ongoing Beta updates without needing to wipe your device, just visit the
Android Beta site and opt out after you get the Android 13 final release and before taking the first beta for Android 13 feature drops.
System images for Pixel devices are
available here for manual download and flash, and you can get the latest Android Emulator system images via the SDK Manager in Android Studio. If you're looking for the Android 13 source, you'll find it
here in the
Android Open Source Project repository under the Android 13 branches.
Thanks again for participating in our program of early previews and Betas! We're looking forward to seeing your apps on Android 13!
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.













.gif)
