Six months ago, we launched Project IDX, an experimental, cloud-based workspace for full-stack, multiplatform software development. We built Project IDX to simplify and streamline the developer workflow, aiming to reduce the sea of complexities traditionally associated with app development. It certainly seems like we've piqued your interest, and we love seeing what IDX has helped you build.
For example, we recently learned about Tanaki, an AI-enhanced content creation app built using Project IDX:
 |
Pasquale D’Silva one of the developers that built Tanaki, said:
"Using the IDX shared workspace to build Tanaki has been so fun. It allows our remote team of imagineers to build together in one place. It is a magic collaboration portal!"
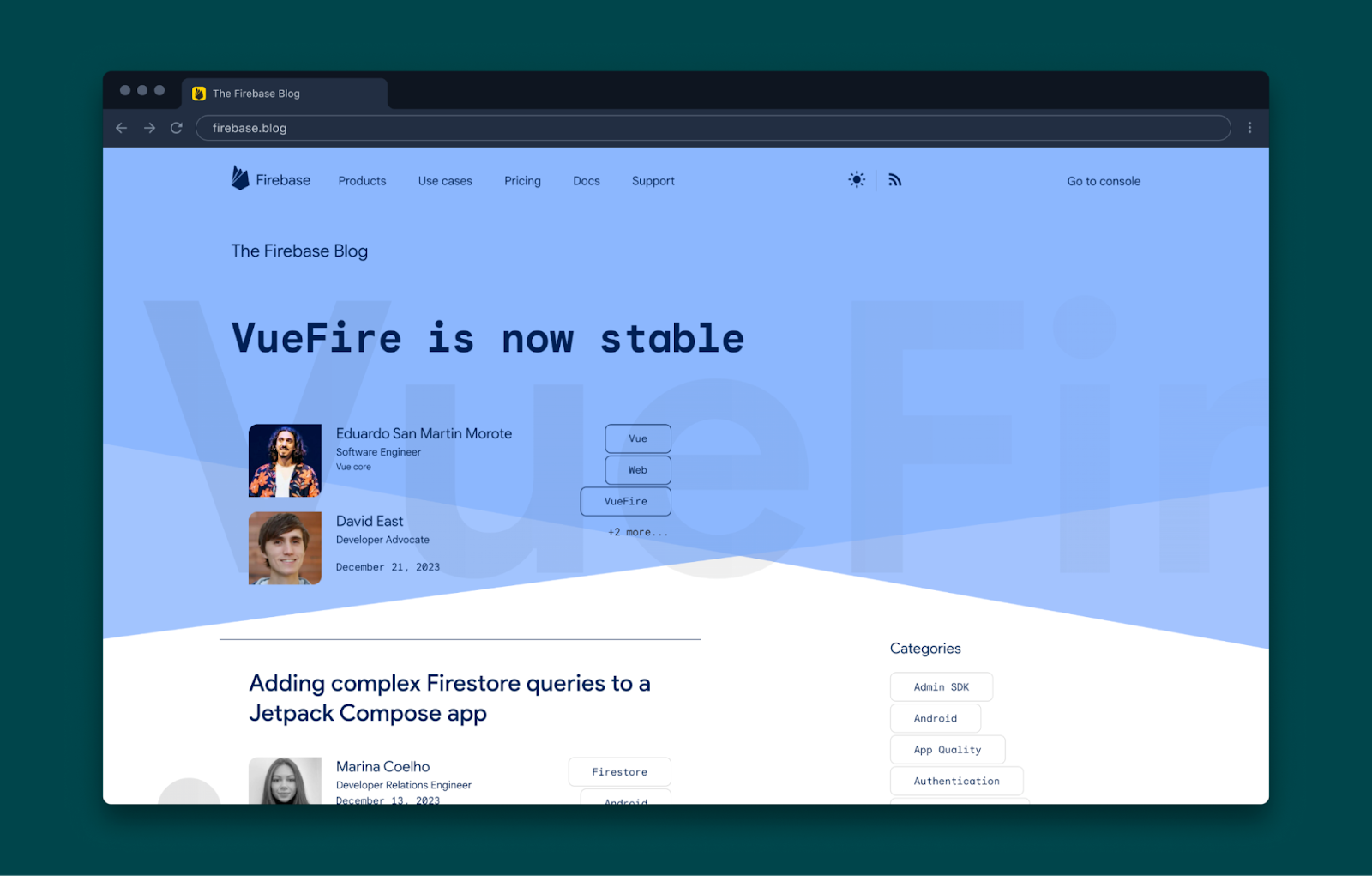
Developers at Google have also been using IDX internally to help speed up development across various projects. One example is the the Firebase Blog, where the full authoring, development, and deployment of the Astro-powered project is handled using IDX:
 |
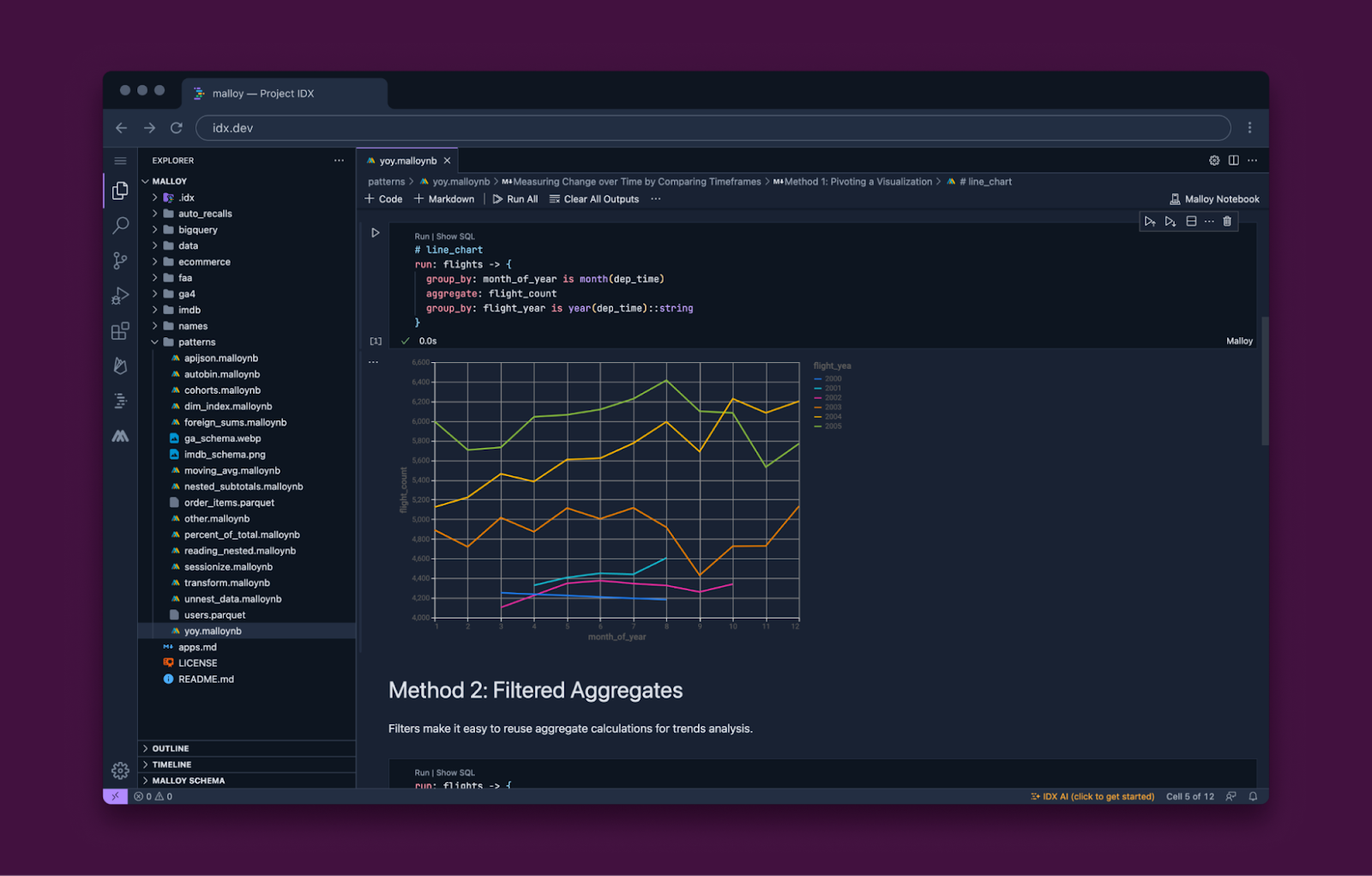
Another interesting project leveraging IDX’s extensibility model is Malloy, a new open-source data language available as a VS Code extension that operates against databases like BigQuery:
 |
Lloyd Tabb, a Distinguished Software Engineer at Google, told us:
“I use IDX with the Malloy project. I often have several different data projects going simultaneously and IDX lets me quickly spin up an instance to solve a problem and it is trivial to configure."
If you want to share what IDX has helped you build, use the #ProjectIDX tag on X.
What’s new in IDX?
In addition to seeing how you’re using IDX, a key part of building Project IDX is your feedback, so we’ve continued to roll out features for you to test. We're excited to share the latest updates we've implemented to expedite and streamline multiplatform app development, so you can deliver with speed, ease and quality.
Preview your app directly in IDX with our iOS simulator and Android emulator
We’re bringing the iOS Simulator and Android Emulator to the browser. Whether you’re building a Flutter or web app, Project IDX now allows you to preview your applications without having to leave your workspace. When you use a Flutter or web template, Project IDX intelligently loads the right preview environment for your application — Safari mobile and Chrome for web templates, or Android, iOS, and Chrome for Flutter templates.
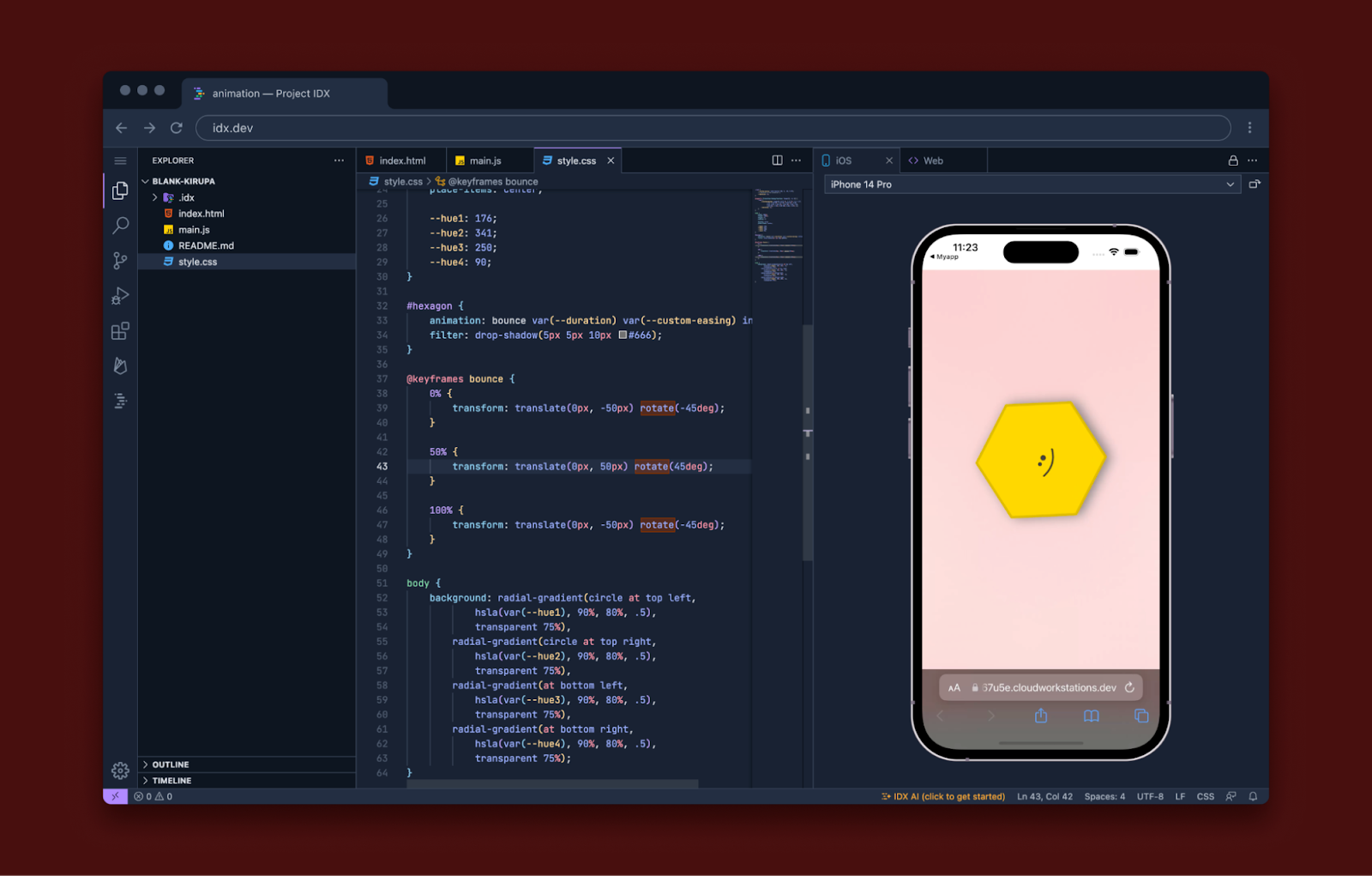 |
IDX’s web and Android emulators allow you to develop, test, and debug directly from your workspace, consolidating your multi-step, multiplatform process into one place. With iOS simulation you can spot-check your app's layout and behavior while you work. This feature is still experimental, so be sure to test it out and send us feedback.
Get started fast with a rich library of project templates
Four of our top ten feature requests have been to support more templates, so we’re pleased to share that we’ve added new templates for Astro, Go, Python/Flask, Qwik, Lit, Preact, Solid.js, and Node.js. Use these templates to jump right into your project so you can spend less time setting up and more time creating.
 |
| Check out our new and improved template gallery |
Of course you can still import your own repo from GitHub, directly from your local files, or you can choose your own setup using a custom Nix environment.
Quickly build and customize your IDX workspace with improvements to Nix
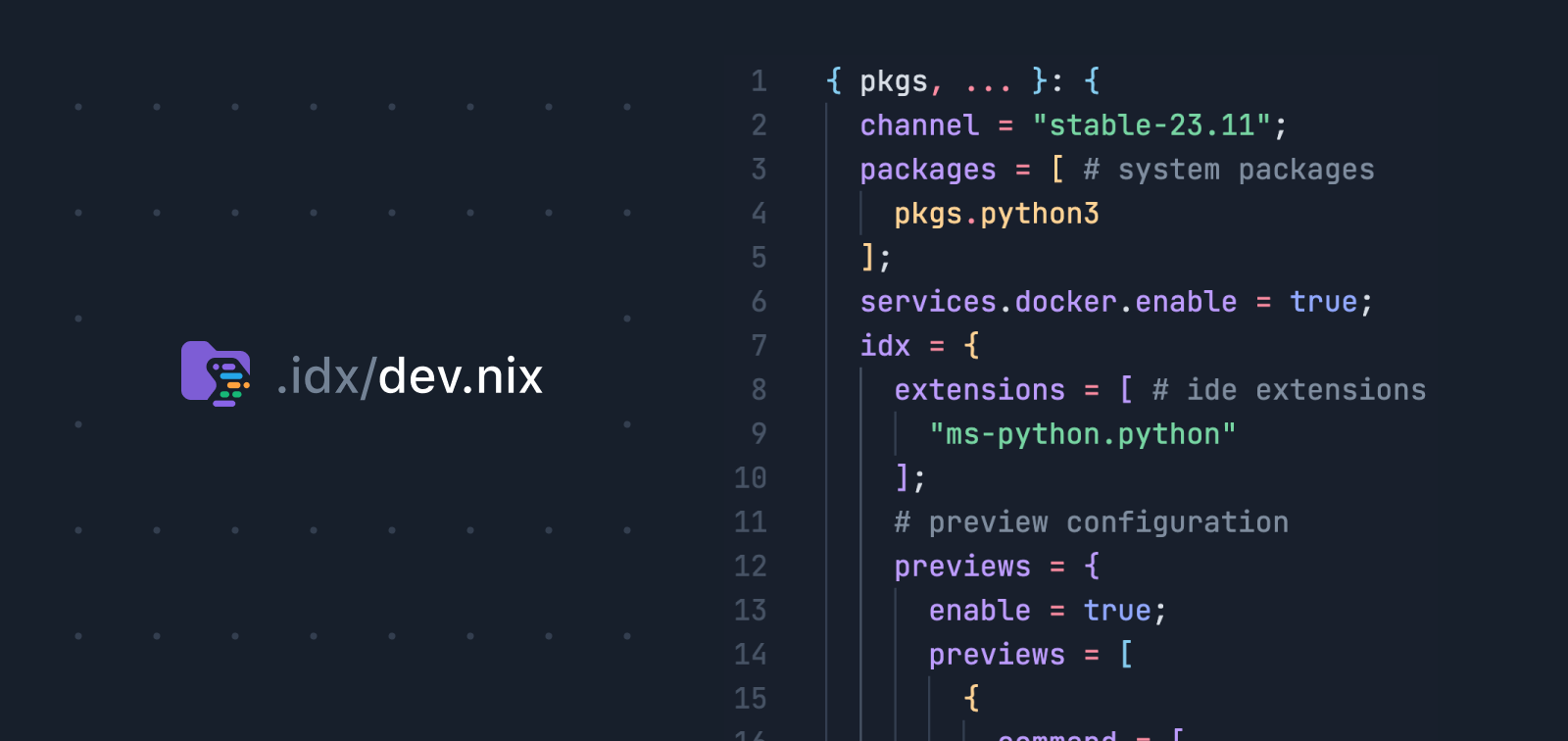 |
IDX uses Nix to define the environment configuration for each workspace to give you flexibility and extensibility in IDX – even our templates and previews are configured using Nix to ensure they’re working correctly inside IDX. We’re continuously working on Nix improvements to help boost your productivity, so now you can:
- Customize IDX starter templates easily by leveraging Nix extensibility.
- Reduce the likelihood of errors and write code more efficiently with Nix file editing, including support for syntax highlighting, error detection, and suggested code completions.
- Recover from broken configurations quickly and avoid unnecessary rebuild attempts with major improvements to our environment customization workflow, including seamless environment rebuilds and troubleshooting.
Easily build, test, and deploy apps with additional new IDX features and resources
 |
- Auto-detect network ports needed for applications or services and adjust the firewall settings to permit ingress and egress without any additional configuration on your end.
- Instantly run command-line tools, scripts, and utilities directly within workspace without the need to install them locally on your machine.
- Simplify the process of working with Docker containers and images directly from the development environment by enabling Docker in your dev.nix file.
AI launched in 15 new regions
 |
We’ve launched our AI capabilities in the following 15 countries: India, Australia, Israel, Brazil, Mexico, Colombia, Argentina, Peru, Chile, Singapore, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Canada, Japan, and South Korea. More countries will be enabled with AI access soon – indicate your interest for AI expansion in this feature tracking post and stay tuned for more AI updates.
Improving together
We're constantly working on adding new capabilities to help you do higher quality work, more efficiently, with less friction. We’ve addressed dozens of your feature requests and fixed a multitude of bugs you flagged for us, so thank you for your continued support and engagement – please keep the feedback coming by filing bugs and feature requests.
For walkthroughs and more information on all the features mentioned above, check out our documentation page. If you haven’t already, visit our website to sign up to try Project IDX and join us on our journey. Also, be sure to check out our new Project IDX Blog for the latest product announcements and updates from the team.
We can’t wait to see what you create with Project IDX!
 Posted by the IDX team
Posted by the IDX team
 A new color for Pixel 8 and 8 Pro, plus new features for the Pixel portfolio have arrived.
A new color for Pixel 8 and 8 Pro, plus new features for the Pixel portfolio have arrived.
 Posted by
Posted by