As the effects of the coronavirus grow, we've seen businesses around the world looking for ways to pause their activities online. With the outlook of coming back and being present for your customers, here's an overview of our recommendations of how to pause your business online and minimize impacts with Google Search. These recommendations are applicable to any business with an online presence, but particularly for those who have paused the selling of their products or services online. For more detailed information, also check our developer documentation.
Recommended: limit site functionality
If your situation is temporary and you plan to reopen your online business, we recommend keeping your site online and limiting the functionality. For example, you might mark items as out of stock, or restrict the cart and checkout process. This is the recommended approach since it minimizes any negative effects on your site's presence in Search. People can still find your products, read reviews, or add wishlists so they can purchase at a later time.
It's also a good practice to:
- Disable the cart functionality: Disabling the cart functionality is the simplest approach, and doesn't change anything for your site's visibility in Search.
- Tell your customers what's going on: Display a banner or popup div with appropriate information for your users, so that they're aware of the business's status. Mention any known and unusual delays, shipping times, pick-up or delivery options, etc. upfront, so that users continue with the right expectations. Make sure to follow our guidelines on popups and banners.
- Update your structured data: If your site uses structured data (such as Products, Books, Events), make sure to adjust it appropriately (reflecting the current product availability, or changing events to cancelled). If your business has a physical storefront, update Local Business structured data to reflect current opening hours.
- Check your Merchant Center feed: If you use Merchant Center, follow the best practices for the availability attribute.
- Tell Google about your updates: To ask Google to recrawl a limited number of pages (for example, the homepage), use Search Console. For a larger number of pages (for example, all of your product pages), use sitemaps.
For more information, check our developers documentation.
Not recommended: disabling the whole website
As a last resort, you may decide to disable the whole website. This is an extreme measure that should only be taken for a very short period of time (a few days at most), as it will otherwise have significant effects on the website in Search, even when implemented properly. That’s why it’s highly recommended to only limit your site's functionality instead. Keep in mind that your customers may also want to find information about your products, your services, and your company, even if you're not selling anything right now.
If you decide that you need to do this (again, which we don't recommend), here are some options:
- If you need to urgently disable the site for 1-2 days, then return an informational error page with a 503 HTTP result code instead of all content. Make sure to follow the best practices for disabling a site.
- If you need to disable the site for a longer time, then provide an indexable homepage as a placeholder for users to find in Search by using the 200 HTTP status code.
- If you quickly need to hide your site in Search while you consider the options, you can temporarily remove it from Search.
For more information, check our developers documentation.
Proceed with caution: To elaborate why we don't recommend disabling the whole website, here are some of the side effects:
- Your customers won't know what's happening with your business if they can't find your business online at all.
- Your customers can't find or read first-hand information about your business and its products & services. For example, reviews, specs, past orders, repair guides, or manuals won't be findable. Third-party information may not be as correct or comprehensive as what you can provide. This often also affects future purchase decisions.
- Knowledge Panels may lose information, like contact phone numbers and your site's logo.
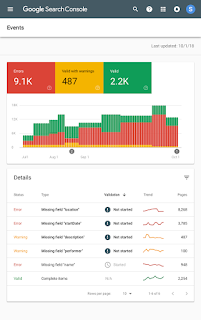
- Search Console verification will fail, and you will lose all access to information about your business in Search. Aggregate reports in Search Console will lose data as pages are dropped from the index.
- Ramping back up after a prolonged period of time will be significantly harder if your website needs to be reindexed first. Additionally, it's uncertain how long this would take, and whether the site would appear similarly in Search afterwards.
Other things to consider
Beyond the operation of your web site, there are other actions you might want to take to pause your online business in Google Search:
- If you hold events, look over the new properties for making them virtual, postponed or canceled.
- Review the guidance from Google My Business on how to change your business hours or indicate temporary closures.
- Review the resources from Google for Small Business on how to communicate with customers and employees, for working remotely and modifying advertising campaigns.
- Understand how to recommend changes to your Google knowledge panel (or how to claim it, if you haven’t already).
Also be sure to keep up with the latest by following updates on Twitter from Google Webmasters at @GoogleWMC and Google My Business at @GoogleMyBiz.
FAQs
What if I only close the site for a few weeks?
Completely closing a site even for just a few weeks can have negative consequences on Google's indexing of your site. We recommend limiting the site functionality instead. Keep in mind that users may also want to find information about your products, your services, and your company, even if you're currently not selling anything.
What if I want to exclude all non-essential products?
That's fine. Make sure that people can't buy the non-essential products by limiting the site functionality.
Can I ask Google to crawl less during this time?
Yes, you can limit crawling with Search Console, though it's not recommended for most cases. This may have some impact on the freshness of your results in Search. For example, it may take longer for Search to reflect that all of your products are currently not available. On the other hand, if Googlebot's crawling causes critical server resource issues, this is a valid approach. We recommend setting a reminder for yourself to reset the crawl rate once you start planning to go back in business.
How do I get a page indexed or updated quickly?
To ask Google to recrawl a limited number of pages (for example, the homepage), use Search Console. For a larger number of pages (for example, all of your product pages), use sitemaps.
What if I block a specific region from accessing my site?
Google generally crawls from the US, so if you block the US, Google Search generally won't be able to access your site at all. We don't recommend that you block an entire region from temporarily accessing your site; instead, we recommend limiting your site's functionality for that region.
Should I use the Removals Tool to remove out-of-stock products?
No. People won't be able to find first-hand information about your products on Search, and there might still be third-party information for the product that may be incorrect or incomplete. It's better to still allow that page, and mark it out of stock. That way people can still understand what's going on, even if they can't purchase the item. If you remove the product from Search, people don't know why it's not there.
--------
We realize that any business closure is a big and stressful step, and not everyone will know what to do. If you notice afterwards that you could have done something differently, everything's not lost: we try to make our systems robust so that your site will be back in Search as quickly as possible. Like you, we're hoping that this crisis finds an end as soon as possible. We hope that with this information, you're able to have your online business up & running quickly when that time comes. Should you run into any problems or questions along the way, please don't hesitate to use our public channels to get help.