Most of the time, our search engine runs properly. Our teams work hard to prevent technical issues that could affect our users who are searching the web, or webmasters whose sites we index and serve to users. Similarly, the underlying systems that we use to power the search engine also run as intended most of the time. When small disruptions happen, they are largely not visible to anyone except our teams who ensure that our products are up and running. However, like all complex systems, sometimes larger outages can occur, which may lead to disruptions for both users and website creators.
In the last few months, such a situation occurred with our indexing systems, which had a ripple effect on some other parts of our infrastructure. While we worked as quickly as possible to remedy the situation, we apologize for the disruption, as our goal is to continuously provide high-quality products to our users and to the web ecosystem.
Since then, we took a closer, careful look into the situation. In the process, we learned a few lessons that we'd like to share with you today. In this blog post, we will go into more details about what happened, clarify how we plan to communicate better if such things happen in the future, and remind website owners of the channels they can use to communicate with us.
So, what happened a few months ago?
In April, we had several issues related to our index. The Search index is the database that holds the hundreds of billions of web pages that we crawled on the web and that we think could answer some of our users’ queries. When a user enters a query in the Google search engine, our ranking algorithms sort through those pages in our Search index to find the most relevant, useful results in a fraction of a second. Here is more information on what happened.
1. The indexing issue
To start it off, we temporarily lost part of the Search index.
Wait... What? What do you mean “lost part of the index?” Is that even possible?
Basically, when serving search results to users, to accelerate the speed of the service, the query of the user only “travels” as far as the closest of our data centers supporting the Google Search product, from which the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is generated. So when there are modifications to the composition of the index (some pages added and removed, documents are merged, or other types of data modification), those modifications need to be reflected in all of those data centers. The consequence is that users all over the world are consistently served pages from the most recent version of the index.

Google owns and operates data centers (like the one pictured above) around the world, to keep our products running 24 hours a day, 7 days a week - source
Keeping the index unified across all those data centers is a non trivial task. For large user-facing services, we may deploy updates by starting in one data center and expand until all relevant data centers are updated. For sensitive pieces of infrastructure, we may extend a rollout over several days, interleaving them across instances in different geographic regions. source
So, as we pushed some planned changes to the Search index, on April 5th parts of the deployment system broke, on a Friday no-less! More specifically: as we were updating the index over some of our data centers, a small number of documents ended up being dropped from the index accidentally. Hence: “we lost part of the index.”
Luckily, our on-call engineers caught the issue pretty quickly, at the same time as we started picking up chatter on social media (thanks to everyone who notified us over that weekend!). As a result, we were able to start reverting the Search index to its previous stable state in all data centers only a few hours after the issue was uncovered (we keep back-ups of our indexes just in case such events happen).
We communicated on Sunday, April 7th that we were aware of the issue, and that things were starting to get back to normal. As data centers were progressively reverting back to a stable index, we continued updating on Twitter (on April 8th, on April 9th), until we were confident that all data centers were fully back to a complete version of the index on April 11th.
2. The Search Console issue
Search Console is the set of tools and reports any webmaster can use to access data about their website’s performance in Search. For example, it shows how many impressions and clicks a website gets in the organic search results every day, or information on what pages of a website are included and excluded from the Search index.
As a consequence of the Search index having the issues we described above, Search Console started to also show inconsistencies. This is because some of the data that surfaces in Search Console originates from the Search index itself:
- the Index Coverage report depends on the Search index being consistent across data centers.
- when we store a page in the Search index, we can annotate the entry with key signals about the page, like the fact that the page contains rich results markup for example. Therefore, an issue with the Search index can have an impact on the Rich Results reports in Search Console.
Basically, many Search Console individual reports read data from a dedicated database. That database is partially built by using information that comes from the Search index. As we had to revert back to a previous version of the Search index, we also had to pause the updating of the Search Console database. This resulted in plateau-ing data for some reports (and flakiness in others, like the URL inspection tool).
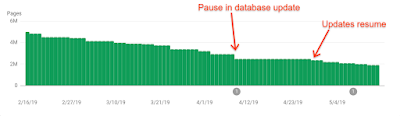
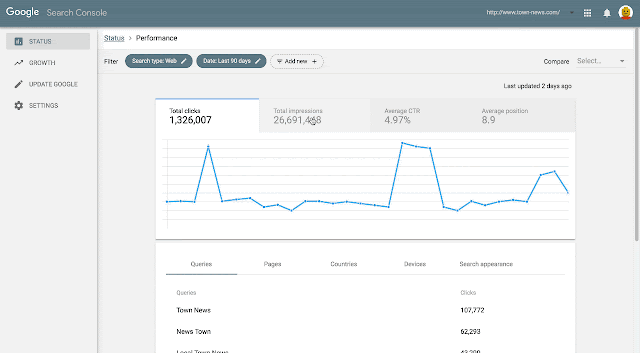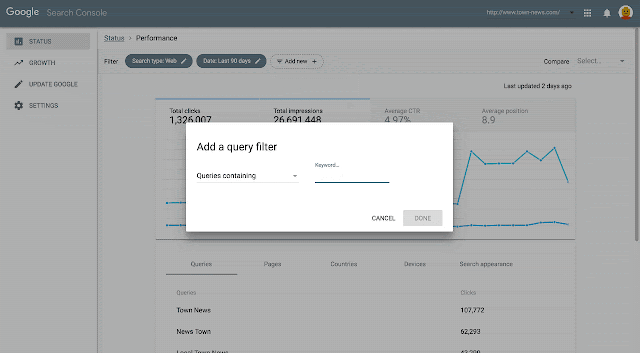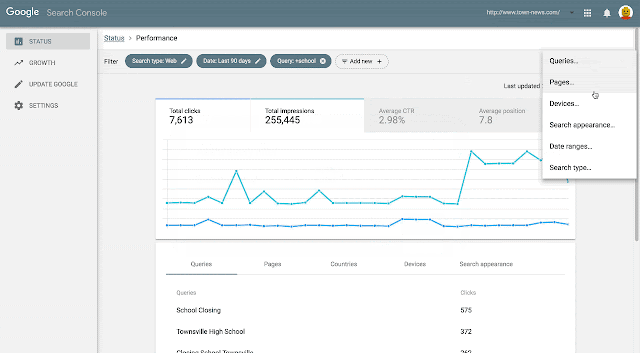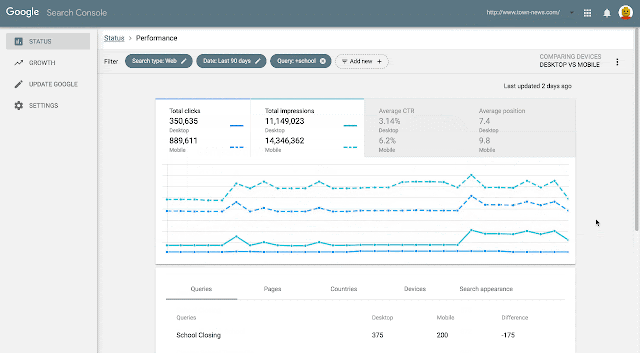
Index coverage report for indexed pages, which shows an example of the data freshness issues in Search Console in April 2019, with a longer time between 2 updates than what is usually observed.
Because the whole Search index issue took several days to roll back (see explanation above), we were delayed focusing on fixing the Search Console database until a few days later, only after the indexing issues were fixed. We communicated on April 15th - tweet - that the Search Console was having troubles and that we were working on fixing it, and we completed our fixes on April 28th (day on which the reports started gathering fresh data again, see graph above). We communicated on Twitter on April 30th that the issue was resolved- tweet.
3. Other issues unrelated to the main indexing bug
Google Search relies on a number of systems that work together. While some of those systems can be tightly linked to one another, in some cases different parts of the system experience unrelated problems around the same time.
In the present case for example, around the same time as the main indexing bug explained above, we also had brief problems gathering fresh Google News content. Additionally, while rendering pages, certain URLs started to redirect Googlebot to other unrelated pages. These issues were entirely unrelated to the indexing bug, and were quickly resolved (tweet 1 & tweet 2).
Our communication and how we intend on doing better
In addition to communicating on social media (as highlighted above) during those few weeks, we also gave webmasters more details in 2 other channels: Search Console, as well as the Search Console Help Center.
In the Search Console Help Center
We updated our “Data anomalies in Search Console” help page after the issue was fully identified. This page is used to communicate information about data disruptions to our Search Console service when the impact affects a large number of website owners.
In Search Console
Because we know that not all our users read social media or the external Help Center page, we also added annotations on Search Console reports, to notify users that the data might not be accurate (see image below). We added this information after the resolution of the bugs. Clicking on “see here for more details” sends users to the “Data Anomalies” page in the Help Center.
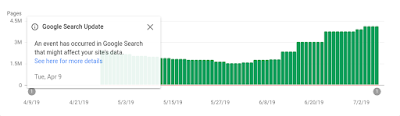
Index coverage report for indexed pages, which shows an example of the data annotations that we can include to notify users of specific issues.
Communications going forward
When things break at Google, we have a strong “postmortem” culture: creating a document to debrief on the breakage, and try to avoid it happening next time. The whole process is described in more detail at the Google Site Reliability Engineering website.
In the wake of the April indexing issues, we included in the postmortem how to better communicate with webmasters in case of large system failures. Our key decisions were:
- Explore ways to more quickly share information within Search Console itself about widespread bugs, and have that information serve as the main point of reference for webmasters to check, in case they are suspecting outages.
- More promptly post to the Search Console data anomalies page, when relevant (if the disturbance is going to be seen over the long term in Search Console data).
- Continue tweeting as quickly as we can about such issues to quickly reassure webmasters we’re aware and that the issue is on our end.
Those commitments should make potential future similar situations more transparent for webmasters as a whole.
Putting our resolutions into action: the “new URLs not indexed” case study
On May 22nd, we tested our new communications strategy, as we experienced another issue. Here’s what happened: while processing certain URLs, our duplicate management system ran out of memory after a planned infrastructure upgrade, which caused all incoming URLs to stop processing.
Here is a timeline of how we thought about communications, following the 3 points highlighted just above:
- We noticed the issue (around 5.30am California time, May 22nd)
We tweeted about the ongoing issue (around 6.40am California time, May 22nd)
We tweeted about the resolution (around 10pm California time, May 22nd) - We evaluated updating the “Data Anomalies” page in the Help Center, but decided against it since we did not expect any long-term impact for the majority of webmasters' Search Console data in the long run.
- The confusion that this issue created for many confirmed our earlier conclusions that we need a way to signal more clearly in the Search Console itself that there might be a disruption to one of our systems which could impact webmasters. Such a solution might take longer to implement. We will communicate on this topic in the future, as we have more news.
Last week, we also had another indexing issue. As with May 22, we tweeted to let people know there was an issue, that we were working to fix it and when the issue was resolved.
How to debug and communicate with us
We hope that this post will bring more clarity to how our systems are complex and can sometimes break, and will also help you understand how we communicate about these matters. But while this post focuses on a widespread breakage of our systems, it’s important to keep in mind that most website indexing issues are caused by an individual website’s configuration, which can create difficulties for Google Search to index that website properly. For those cases, all webmasters can debug issues using Search Console and our Help center. After doing so, if you still think that an issue is not coming from your site or don’t know how to resolve it, come talk to us and our community, we always want to take feedback from our users. Here is how to signal an issue to us:
- Check our Webmaster Community, sometimes other webmasters have highlighted an issue that also impacts your site.
- In person! We love contact, come and talk to us at events. Calendar.
- Within our products! The Search Console feedback tool is very useful to our teams.
- Twitter and YouTube!
Posted by Vincent Courson, Google Search Outreach