 Posted by Nari Yoon, Bitnoori Keum, Hee Jung, DevRel Community Manager / Soonson Kwon, DevRel Program Manager
Posted by Nari Yoon, Bitnoori Keum, Hee Jung, DevRel Community Manager / Soonson Kwon, DevRel Program Manager

Let’s explore highlights and accomplishments of vast Google Machine Learning communities over the second quarter of 2023. We are enthusiastic and grateful about all the activities by the global network of ML communities. Here are the highlights!
ML Training Campaigns Summary
More than 35 communities around the world have hosted ML Campaigns distributed by the ML Developer Programs team during the first half of the year. Thank you all for your training efforts for the entire ML community!
- ML Study Jams: TFUG Bauchi, GDSC Uninter, TFUG Abidjan, MLAct, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, National Institute of Technology (Kosen), Kumamoto College, GDG Assiut, GDG Bassam, GDG Cloud Abidjan, GDG Antananarivo, Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology - Gorakhpur, Université d'Abomey-Calavi (UAC), ABES Engineering College - Ghaziabad, ABV-IIITM, Vishwakarma University - Pune, Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering and Research - Pune, GDG Cloud Edmonton, GDG Cocody, GDG Cloud Wilmington, University of Lay Adventist of Kigali
- ML Paper Reading Clubs: GalsenAI, TFUG Dhaka, Pseudo Lab, TFUG Durg, TFUG Ibadan, Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería, GDG Karaganda, Western University, GDG Raipur, University College Dublin
- ML Math Clubs: TFUG Dhaka, TFUG Hajipur, GDG Yangon, GalsenAI
Community Highlights
Keras
Image Segmentation using Composable Fully-Convolutional Networks by ML GDE Suvaditya Mukherjee (India) is a Kears.io example explaining how to implement a fully-convolutional network with a VGG-16 backend and how to use it for performing image segmentation. His presentation, KerasCV for the Young and Restless (slides | video) at TFUG Malaysia and TFUG Kolkata was an introduction to KerasCV. He discussed how basic computer vision components work, why Keras is an important tool, and how KerasCV builds on top of the established TFX and Keras ecosystem.
[ML Story] My Keras Chronicles by ML GDE Aritra Roy Gosthipaty (India) summarized his story of getting into deep learning with Keras. He included pointers as to how one could get into the open source community. Plus, his Kaggle notebook, [0.11] keras starter: unet + tf data pipeline is a starter guide for Vesuvius Challenge. He and Subvaditya also shared Keras implementation of Temporal Latent Bottleneck Networks, proposed in the paper.
KerasFuse by ML GDE Ayse Ayyuce Demirbas (Portugal) is a Python library that combines the power of TensorFlow and Keras with various computer vision techniques for medical image analysis tasks. It provides a collection of modules and functions to facilitate the development of deep learning models in TensorFlow & Keras for tasks such as image segmentation, classification, and more.
TensorFlow at Google I/O 23: A Preview of the New Features and Tools by TFUG Ibadan explored the preview of the latest features and tools in TensorFlow. They covered a wide range of topics including Dtensor, KerasCV & KerasNLP, TF quantization API, and JAX2TF.
StableDiffusion - Textual-Inversion implementation app by ML GDE Dimitre Oliveira (Brazil) is an example of how to implement code from research and fine-tunes it using the Textual Inversion process. It also provides relevant use cases for valuable tools and frameworks such as HuggingFace, Gradio, TensorFlow serving, and KerasCV.
In Understanding Gradient Descent and Building an Image Classifier in TF From Scratch, ML GDE Tanmay Bakshi (Canada) talked about how to develop a solid intuition for the fundamentals backing ML tech, and actually built a real image classification system for dogs and cats, from scratch in TF.Keras.
TensorFlow and Keras Implementation of the CVPR 2023 paper by Usha Rengaraju (India) is a research paper implementation of BiFormer: Vision Transformer with Bi-Level Routing Attention.
Smile Detection with Python, OpenCV, and Deep Learning by Rouizi Yacine is a tutorial explaining how to use deep learning to build a more robust smile detector using TensorFlow, Keras, and OpenCV.
Kaggle
ML Olympiad for Students by GDSC UNINTER was for students and aspiring ML practitioners who want to improve their ML skills. It consisted of a challenge of predicting US working visa applications. 320+ attendees registered for the opening event, 700+ views on YouTube, 66 teams competed, and the winner got a 71% F1-score.
ICR | EDA & Baseline by ML GDE Ertuğrul Demir (Turkey) is a starter notebook for newcomers interested in the latest featured code competition on Kaggle. It got 200+ Upvotes and 490+ forks.
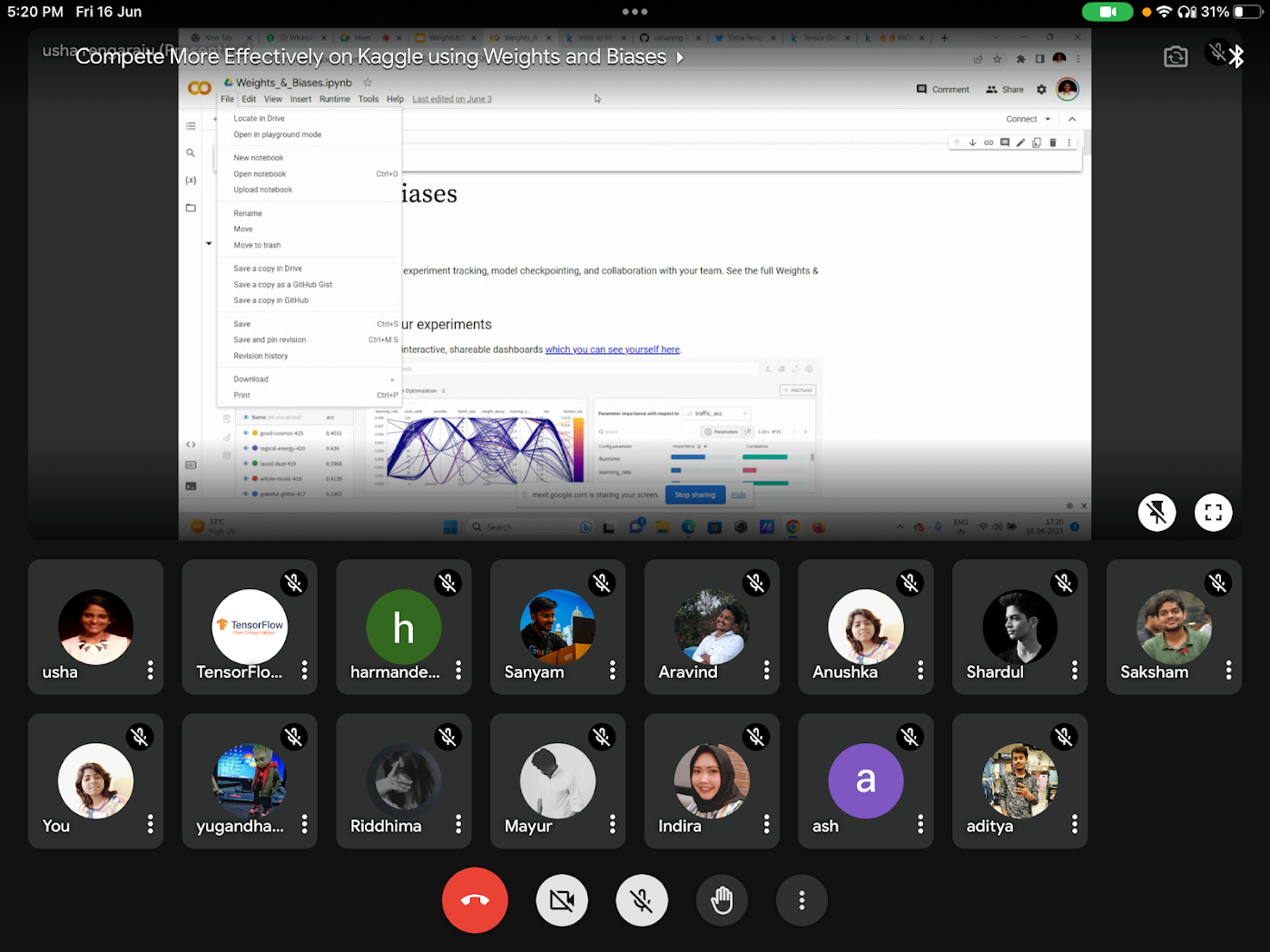
Compete More Effectively on Kaggle using Weights and Biases by TFUG Hajipur was a meetup to explore techniques using Weights and Biases to improve model performance in Kaggle competitions. Usha Rengaraju (India) joined as a speaker and delivered her insights on Kaggle and strategies to win competitions. She shared tips and tricks and demonstrated how to set up a W&B account and how to integrate with Google Colab and Kaggle.
Skeleton Based Action Recognition: A failed attempt by ML GDE Ayush Thakur (India) is a discussion post about documenting his learnings from competing in the Kaggle competition, Google - Isolated Sign Language Recognition. He shared his repository, training logs, and ideas he approached in the competition. Plus, his article Keras Dense Layer: How to Use It Correctly) explored what the dense layer in Keras is and how it works in practice.
On-device ML
Add Machine Learning to your Android App by ML GDE Pankaj Rai (India) at Tech Talks for Educators was a session on on-device ML and how to add ML capabilities to Android apps such as object detection and gesture detection. He explained capabilities of ML Kit, MediaPipe, TF Lite and how to use these tools. 700+ people registered for his talk.
In MediaPipe with a bit of Bard at I/O Extended Singapore 2023, ML GDE Martin Andrews (Singapore) shared how MediaPipe fits into the ecosystem, and showed 4 different demonstrations of MediaPipe functionality: audio classification, facial landmarks, interactive segmentation, and text classification.
Adding ML to our apps with Google ML Kit and MediaPipe by ML GDE Juan Guillermo Gomez Torres (Bolivia) introduced ML Kit & MediaPipe, and the benefits of on-device ML. In Startup Academy México (Google for Startups), he shared how to increase the value for clients with ML and MediaPipe.
LLM
Introduction to Google's PaLM 2 API by ML GDE Hannes Hapke (United States) introduced how to use PaLM2 and summarized major advantages of it. His another article The role of ML Engineering in the time of GPT-4 & PaLM 2 explains the role of ML experts in finding the right balance and alignment among stakeholders to optimally navigate the opportunities and challenges posed by this emerging technology. He did presentations under the same title at North America Connect 2023 and the GDG Portland event.
ChatBard : An Intelligent Customer Service Center App by ML GDE Ruqiya Bin Safi (Saudi Arabia) is an intelligent customer service center app powered by generative AI and LLMs using PaLM2 APIs.
Bard can now code and put that code in Colab for you by ML GDE Sam Witteveen (Singapore) showed how Bard makes code. He runs a Youtube channel exploring ML and AI, with playlists such as Generative AI, Paper Reviews, LLMs, and LangChain.
Google’s Bard Can Write Code by ML GDE Bhavesh Bhatt (India) shows the coding capabilities of Bard, how to create a 2048 game with it, and how to add some basic features to the game. He also uploaded videos about LangChain in a playlist and introduced Google Cloud’s new course on Generative AI in this video.
Attention Mechanisms and Transformers by GDG Cloud Saudi talked about Attention and Transformer in NLP and ML GDE Ruqiya Bin Safi (Saudi Arabia) participated as a speaker. Another event, Hands-on with the PaLM2 API to create smart apps(Jeddah) explored what LLMs, PaLM2, and Bard are, how to use PaLM2 API, and how to create smart apps using PaLM2 API.
Hands-on with Generative AI: Google I/O Extended [Virtual] by ML GDE Henry Ruiz (United States) and Web GDE Rabimba Karanjai (United States) was a workshop on generative AI showing hands-on demons of how to get started using tools such as PaLM API, Hugging Face Transformers, and LangChain framework.
Generative AI with Google PaLM and MakerSuite by ML GDE Kuan Hoong (Malaysia) at Google I/O Extended George Town 2023 was a talk about LLMs with Google PaLM and MakerSuite. The event hosted by GDG George Town and also included ML topics such as LLMs, responsible AI, and MLOps.
Intro to Gen AI with PaLM API and MakerSuite by TFUG São Paulo was for people who want to learn generative AI and how Google tools can help with adoption and value creation. They covered how to start prototyping Gen AI ideas with MakerSuite and how to access advanced features of PaLM2 and PaLM API. The group also hosted Opening Pandora's box: Understanding the paper that revolutionized the field of NLP (video) and ML GDE Pedro Gengo (Brazil) and ML GDE Vinicius Caridá (Brazil) shared the secret behind the famous LLM and other Gen AI models.The group members studied Attention Is All You Need paper together and learned the full potential that the technology can offer.
Language models which PaLM can speak, see, move, and understand by GDG Cloud Taipei was for those who want to understand the concept and application of PaLM. ML GED Jerry Wu (Taiwan) shared the PaLM’s main characteristics, functions, and etc.
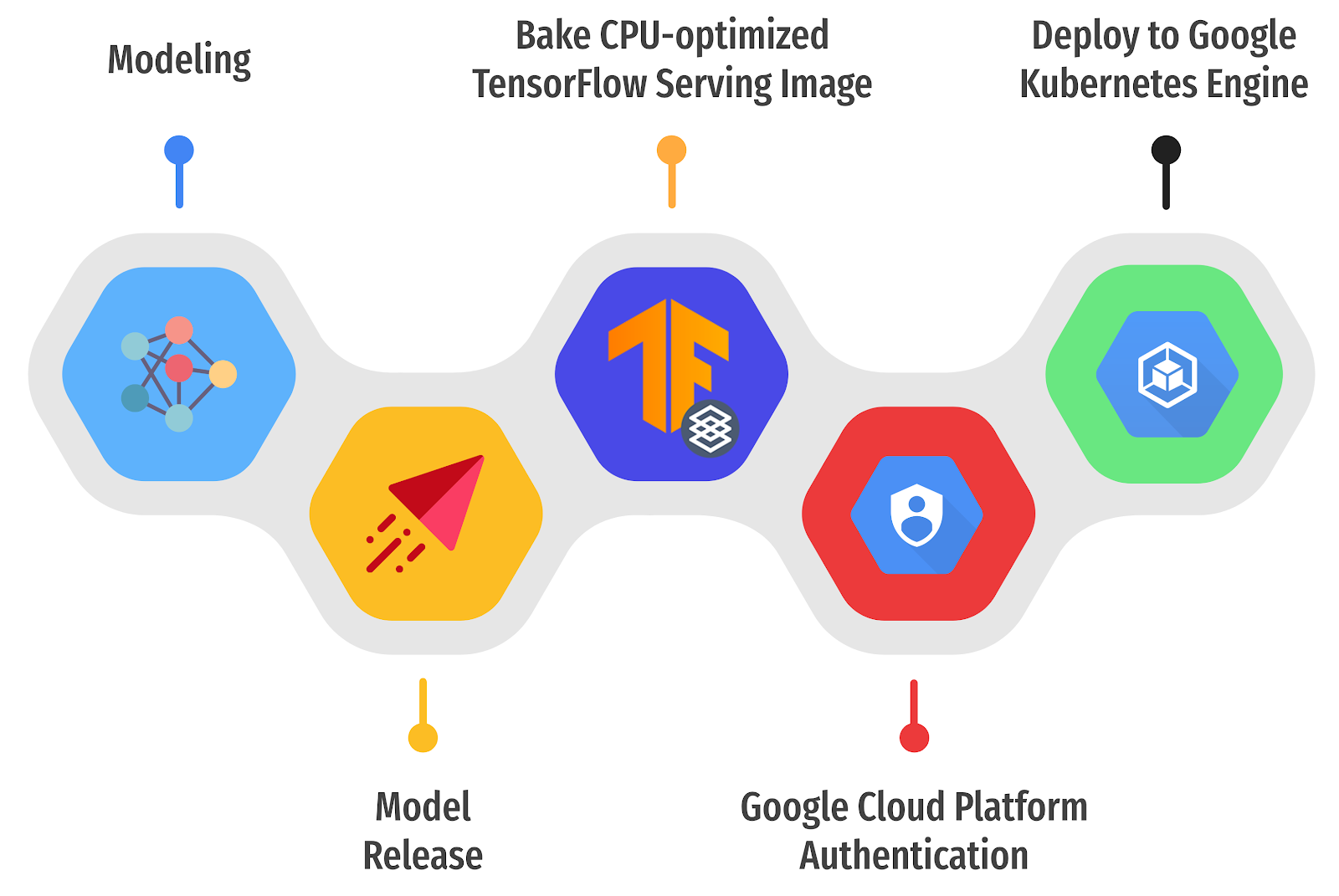
Serving With TF and GKE: Stable Diffusion by ML GDE Chansung Park (Korea) and ML GDE Sayak Paul (India) discusses how TF Serving and Kubernetes Engine can serve a system with online deployment. They broke down Stable Diffusion into main components and how they influence the subsequent consideration for deployment. Then they also covered the deployment-specific bits such as TF Serving deployment and k8s cluster configuration.
TFX + W&B Integration by ML GDE Chansung Park (Korea) shows how KerasTuner can be used with W&B’s experiment tracking feature within the TFX Tuner component. He developed a custom TFX component to push a full-trained model to the W&B Artifact store and publish a working application on Hugging Face Space with the current version of the model. Also, his talk titled, ML Infra and High Level Framework in Google Cloud Platform, delivered what MLOps is, why it is hard, why cloud + TFX is a good starter, and how TFX is seamlessly integrated with Vertex AI and Dataflow. He shared use cases from the past projects that he and ML GDE Sayak Paul (India) have done in the last 2 years.
Open and Collaborative MLOps by ML GDE Sayak Paul (India) was a talk about why openness and collaboration are two important aspects of MLOps. He gave an overview of Hugging Face Hub and how it integrates well with TFX to promote openness and collaboration in MLOps workflows.
ML Research
Paper review: PaLM 2 Technical Report by ML GDE Grigory Sapunov (UK) looked into the details of PaLM2 and the paper. He shares reviews of papers related to Google and DeepMind through his social channels and here are some of them: Model evaluation for extreme risks (paper), Faster sorting algorithms discovered using deep reinforcement learning (paper), Power-seeking can be probable and predictive for trained agents (paper).
Learning JAX in 2023: Part 3 — A Step-by-Step Guide to Training Your First Machine Learning Model with JAX by ML GDE Aritra Roy Gosthipaty (India) and ML GDE Ritwik Raha (India) shows how JAX can train linear and nonlinear regression models and the usage of PyTrees library to train a multilayer perceptron model. In addition, at May 2023 Meetup hosted by TFUG Mumbai, they gave a talk titled Decoding End to End Object Detection with Transformers and covered the architecture of the mode and the various components that led to DETR’s inception.
20 steps to train a deployed version of the GPT model on TPU by ML GDE Jerry Wu (Taiwan) shared how to use JAX and TPU to train and infer Chinese question-answering data.
Multimodal Transformers - Custom LLMs, ViTs & BLIPs by TFUG Singapore looked at what models, systems, and techniques have come out recently related to multimodal tasks. ML GDE Sam Witteveen (Singapore) looked into various multimodal models and systems and how you can build your own with the PaLM2 Model. In June, this group invited Blaise Agüera y Arcas (VP and Fellow at Google Research) and shared the Cerebra project and the research going on at Google DeepMind including the current and future developments in generative AI and emerging trends.
TensorFlow
Training a recommendation model with dynamic embeddings by ML GDE Thushan Ganegedara (Australia) explains how to build a movie recommender model by leveraging TensorFlow Recommenders (TFRS) and TensorFlow Recommenders Addons (TFRA). The primary focus was to show how the dynamic embeddings provided in the TFRA library can be used to dynamically grow and shrink the size of the embedding tables in the recommendation setting.
How I built the most efficient deepfake detector in the world for $100 by ML GDE Mathis Hammel (France) was a talk exploring a method to detect images generated via ThisPersonDoesNotExist.com and even a way to know the exact time the photo was produced. Plus, his Twitter thread, OSINT Investigation on LinkedIn, investigated a network of fake companies on LinkedIn. He used a homemade tool based on a TensorFlow model and hosted it on Google Cloud. Technical explanations of generative neural networks were also included. More than 701K people viewed this thread and it got 1200+ RTs and 3100+ Likes.
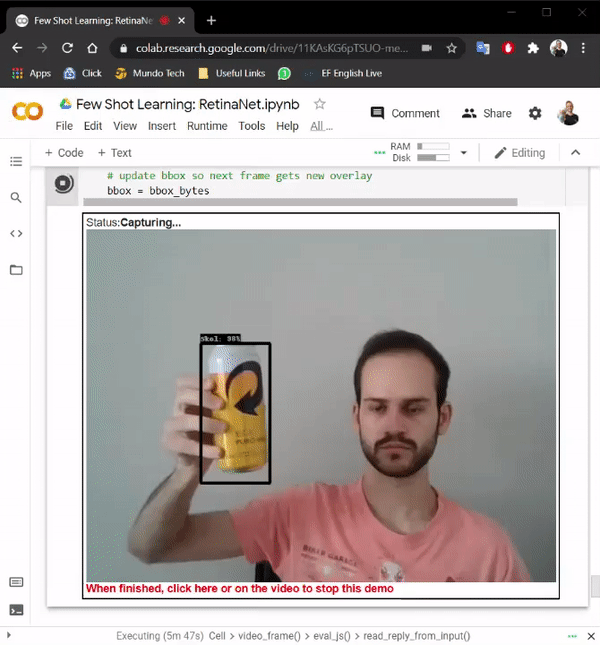
Few-shot learning: Creating a real-time object detection using TensorFlow and Python by ML GDE Hugo Zanini (Brazil) shows how to take pictures of an object using a webcam, label the images, and train a few-shot learning model to run in real-time. Also, his article, Custom YOLOv7 Object Detection with TensorFlow.js explains how he trained a custom YOLOv7 model to run it directly in the browser in real time and offline with TensorFlow.js.
The Lord of the Words : The Return of the experiments with DVC (slides) by ML GDE Gema Parreno Piqueras (Spain) was a talk explaining Transformers in the neural machine learning scenario, and how to use Tensorflow and DVC. In the project, she used Tensorflow Datasets translation catalog to load data from various languages, and TensorFlow Transformers library to train several models.
Accelerate your TensorFlow models with XLA (slides) and Ship faster TensorFlow models with XLA by ML GDE Sayak Paul (India) shared how to accelerate TensorFlow models with XLA in Cloud Community Days Kolkata 2023 and Cloud Community Days Pune 2023.
Setup of NVIDIA Merlin and Tensorflow for Recommendation Models by ML GDE Rubens Zimbres (Brazil) presented a review of recommendation algorithms as well as the Two Towers algorithm, and setup of NVIDIA Merlin on premises and on Vertex AI.
Cloud
AutoML pipeline for tabular data on VertexAI in Go by ML GDE Paolo Galeone (Italy) delved into the development and deployment of tabular models using VertexAI and AutoML with Go, showcasing the actual Go code and sharing insights gained through trial & error and extensive Google research to overcome documentation limitations.
Beyond images: searching information in videos using AI (slides) by ML GDE Pedro Gengo (Brazil) and ML GDE Vinicius Caridá (Brazil) showed how to create a search engine where you can search for information in videos. They presented an architecture where they transcribe the audio and caption the frames, convert this text into embeddings, and save them in a vector DB to be able to search given a user query.
The secret sauce to creating amazing ML experiences for developers by ML GDE Gant Laborde (United States) was a podcast sharing his “aha” moment, 20 years of experience in ML, and the secret to creating enjoyable and meaningful experiences for developers.
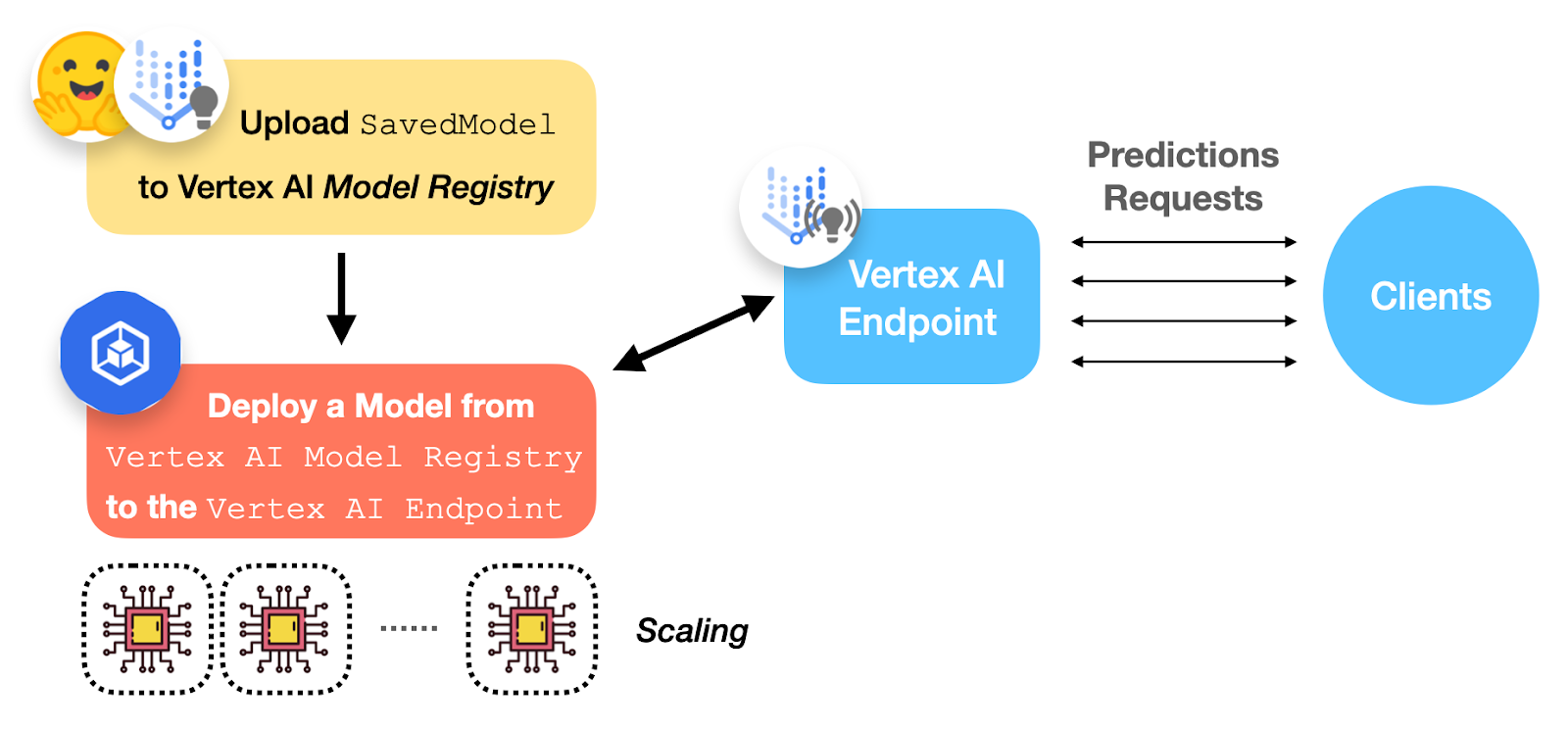
What's inside Google’s Generative AI Studio? by ML GDE Gad Benram (Portugal) shared the preview of the new features and what you can expect from it. Additionally, in How to pitch Vertex AI in 2023, he shared the six simple and honest sales pitch points for Google Cloud representatives on how to convince customers that Vertex AI is the right platform.
In How to build a conversational AI Augmented Reality Experience with Sachin Kumar, ML GDE Sachin Kumar (Qatar) talked about how to build an AR app combining multiple technologies like Google Cloud AI, Unity, and etc. The session walked through the step-by-step process of building the app from scratch.
Machine Learning on Google Cloud Platform by ML GDE Nitin Tiwari (India) was a mentoring aiming to provide students with an in-depth understanding of the processes involved in training an ML model and deploying it using GCP. In Building robust ML solutions with TensorFlow and GCP, he shared how to leverage the capabilities of GCP and TensorFlow for ML solutions and deploy custom ML models.
Data to AI on Google cloud: Auto ML, Gen AI, and more by TFUG Prayagraj educated students on how to leverage Google Cloud’s advanced AI technologies, including AutoML and generative AI.

 Posted by Bitnoori Keum – DevRel Community Manager
Posted by Bitnoori Keum – DevRel Community Manager







 Posted by Nari Yoon, Bitnoori Keum, Hee Jung, DevRel Community Manager / Soonson Kwon, DevRel Program Manager
Posted by Nari Yoon, Bitnoori Keum, Hee Jung, DevRel Community Manager / Soonson Kwon, DevRel Program Manager






















































.jpg)
.jpg)