Tag Archives: identity
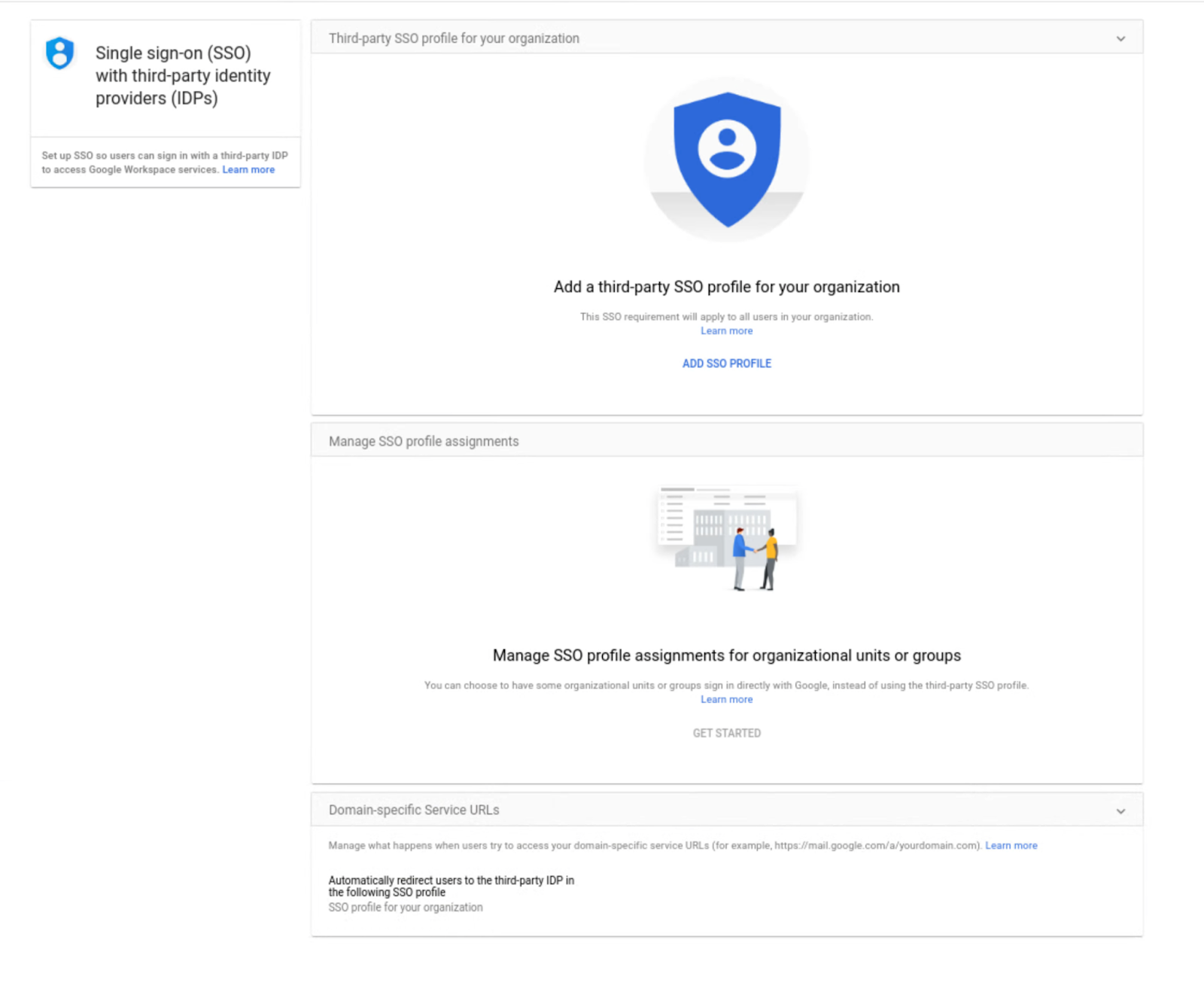
Set up SSO profiles for multiple third-party identity providers with the Multi-IdP SSO beta launch
What’s changing
You can now set up SSO profiles for multiple third-party identity providers
Who’s impacted
Why you’d use it
Getting started
- Admins: In the Admin console, navigate to Security > Settings > Set up single sign-on (SSO) with a third party IdP > Manage SSO Profile assignments. Visit the Help Center to learn more about setting up SSO for your organization.
Go to the Security settings to set up SSO profiles for third-party identity providers
- End users: There is no end user setting for this feature.
Rollout pace
- This feature is available now for all users.
Availability
- Available to Google Workspace Business Starter, Business Standard, Business Plus, Enterprise Essentials, Enterprise Standard, Enterprise Plus, Education Fundamentals, Education Plus, Frontline, and Nonprofits, as well as legacy G Suite Basic and Business customers
- Available to all Cloud Identity customers
- Not available to Google Workspace Essentials customers
- Not available to users with personal Google Accounts
Resources
Source: Google Workspace Updates
Discontinuing authorization support for the Google Sign-In JavaScript Platform Library
Posted by Brian Daugherty, Product Solutions Engineer
Last year, we announced our plan to deprecate the Google Sign-In JavaScript Platform Library for web applications.
On March 31, 2023 we will fully retire the Google Sign-In JavaScript Platform Library and would like to remind you to check if this affects your web application, and if necessary, to plan for a migration.
Beginning April 30th, 2022 new applications must use the Google Identity Services library, existing apps may continue using the Platform Library until the deprecation date.
What does this mean for you?
- Evaluate if you are affected by the deprecation and your need to Migrate to Google Identity Services.
- Complete your migration prior to March 31, 2023, after which the Platform Library will no longer be available for download and web apps relying upon deprecated authorization features to obtain access tokens for calling Google APIs will no longer work as intended.
Are you affected?
To protect users' personal information across the web, Google continues to make signing into apps and services secure by default. Delivering on this promise, we announced Google Identity Services, our family of Identity APIs that consolidate multiple identity offerings under one software development kit (SDK). Recently, we released an update to the Google Identity Services library, adding user authorization and data sharing features based on OAuth 2.0. Due to numerous security and privacy improvements, the new Identity Services library is not fully backward compatible with all features and functionality found in the older Platform Library, and so a migration to the new library and code changes are necessary.
The deprecation applies to web apps loading the Google Sign-In JavaScript Platform Library and apps using the Google API Client Library for JavaScript with access tokens.
If your web pages use the apis.google.com/js/api.js or apis.google.com/js/client.js JavaScript modules to load the Platform Library, you are affected and need to update your existing implementation to use the new Identity Services client library.
Web applications using gapi.client from the Google API Client Library implicitly load and use the Platform Library’s soon to be deprecated gapi.auth2 module when working with access tokens to call Google APIs. Updates to your web app to explicitly include the new Identity Services library, manage access token requests, and replace auth2 module references with newer equivalent methods are necessary.
Your full suite of apps and platforms may be using different methods of authentication and authorization from Google. The following are NOT affected by this deprecation announcement:
- Android or iOS native app SDKs,
- Backend platforms directly calling Google’s OAuth 2.0 or OpenID services.
Migration
Authorization and authentication functionalities are clearly separated in the new Identity Services library.
There are two guides to help you with migration:
(1) migrate to Google Identity Services for user authorization and obtaining access tokens for use with Google APIs, and
(2) migrating from Google Sign-In for user authentication and sign-in.
Your web application may use both authorization (to call Google APIs), and authentication (to manage user sign-in to your app). If this is the case, you’ll need to follow both migration guides to ensure separation of user authorization and authentication flows in your web application.
The migration guides are written to help you understand how the new Identity Services library differs from prior libraries, what these changes are, how to separate authentication from authorization, and how these changes affect both your users and your codebase.
Changes and benefits
Migration to our new Identity Services library includes a number of changes and benefits:
- Pop-ups provide a more secure, reduced UX friction way to authorize your web app without having to use redirects or require users to leave your site.
- Increased privacy and control by default: users approve individual scopes, and only when they are needed, improving how much, and when, sensitive data may be shared with your web app.
- Separate ID token and access token credentials clearly distinguish user identity from application capabilities. Individual credentials are easier to separate, manage, or store based upon their level of risk. An identity may convey only who you are and offer a lower level of risk when compared to an access token with capabilities to read/write sensitive user data.
- Forward compatibility with Chromium Privacy sandbox changes.
This is a brief summary of privacy, security, and usability changes found in the new Identity Services library, additional detail is available in the migration guides.
How to get help
Visit our developer site for more information and check out the google-oauth tag on Stack Overflow for technical assistance. You can also offer your suggestions and feedback by sending an email to [email protected].
Source: Google Developers Blog
Making Google OAuth interactions safer by using more secure OAuth flows
At Google, we constantly strive to provide safer ways for users to sign-in and share their Google account data with third-party applications. In the spirit of that work, we will be rolling out a set of protections against phishing and app impersonation attacks during the OAuth interactions.
The Google sign-in and authorization flows are powered by the Google OAuth platform and over the years we have developed and supported a number of ways for app developers to integrate with supported OAuth flows. With the goal of keeping users safer online, we will end support for two legacy flows and will require developers to migrate to alternative implementation methods that offer greater protections.
To ensure a smooth transition and avoid any service interruption we will give ample time to implement and meet the compliance dates which are specified below. We will share further updates on this rollout via email so please make sure your support email address is up to date in project settings on the Google API console.
Loopback IP address flow will be disallowed for native iOS, Android and Chrome OAuth client types
The Loopback IP address flow is vulnerable to man in the middle attack where a malicious app, accessing the same loopback interface on some operating systems, may intercept the OAuth response and gain access to the authorization code. We intend to remove this threat vector by disallowing this flow for iOS, Android and Chrome app OAuth client types. The existing clients will be able to migrate to more secure implementation methods. New clients will be unable to use this flow starting on March 14, 2022.
What do I need to do
Determine if your app is using the Loopback IP address flow
You can inspect your app code or the outgoing network call (in case your app is using an OAuth library) to determine if the Google OAuth authorization request your app is making has the following values for “redirect_uri” parameter.
redirect_uri=http://127.0.0.1:port or http://[::1]:port">http://[::1]:port or
http://localhost:port
Migrate to an alternative flow
If your app is using the Loopback IP address method you need to migrate to another method which is more secure by default. Please consider the following alternative methods for migration.
- iOS clients: Google Sign-In for iOS SDK
- Android clients: Google Sign-In for Android SDK
- Chrome clients: Chrome Identity API
Key dates for compliance
- Mar 14, 2022 - new OAuth usage will be blocked for the Loopback IP address flow
- Aug 1, 2022 - a user-facing warning message may be displayed to non-compliant OAuth requests one month before the compliance date
- Aug 31, 2022 - the Loopback IP address flow is blocked for existing clients
OAuth out-of-band (oob) flow will be deprecated
OAuth out-of-band (OOB) is a legacy flow developed to support native clients which do not have a redirect URI like web apps to accept the credentials after a user approves an OAuth consent request. The OOB flow poses a remote phishing risk and clients must migrate to an alternative method to protect against this vulnerability. New clients will be unable to use this flow starting on Feb 28, 2022.
What do I need to do
Determine if your app is using the OOB flow
You can inspect your app code or the outgoing network call (in case your app is using an OAuth library) to determine if the Google OAuth authorization request your app is making has the following values for “redirect_uri” parameter.
redirect_uri=urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob or urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob:auto or oob
Migrate to an alternative flow
If your app is using the OOB method you need to migrate to another method which is more secure by default. Please consider the following alternative methods for migration.
- iOS clients: Google Sign-In for iOS SDK
- Android clients: Google Sign-In for Android SDK
- Chrome clients: Chrome Identity API
- Desktop clients: OAuth 2.0 for Desktop apps
Key dates for compliance
- Feb 28, 2022 - new OAuth usage will be blocked for the OOB flow
- Sep 5, 2022 - a user-facing warning message may be displayed to non-compliant OAuth requests
- Oct 3, 2022 - the OOB flow is deprecated for existing clients
User-facing warning message
A user-facing warning message may be displayed for non-compliant requests one month before the aforementioned OAuth methods are due to be blocked. The message will convey to the users that the app may be blocked soon while displaying the support email that you have registered in the OAuth consent screen in Google API Console.
[Sample user-facing warning]
The developers can acknowledge the user-facing warning message and suppress it by passing a query parameter in the authorization call as shown below.
- Go to the code in your app where you send requests to Google's OAuth 2.0 Authorization Endpoint.
- Add a parameter with a value of the enforcement date
- For OOB: Add an
ack_oob_shutdownparameter with a value of the enforcement date: 2022-10-03. Example:ack_oob_shutdown=2022-10-03- For Loopback IP address: Add an
ack_loopback_shutdownparameter with a value of the enforcement date: 2022-08-31. Example:ack_loopback_shutdown=2022-08-31
User-facing error message
If an app is not updated to meet compliance by the required date the authorization requests will be blocked and users may encounter an invalid request error screen (sample shown below).
[Sample user-facing error]
Source: Google Developers Blog
Making Google OAuth interactions safer by using more secure OAuth flows
At Google, we constantly strive to provide safer ways for users to sign-in and share their Google account data with third-party applications. In the spirit of that work, we will be rolling out a set of protections against phishing and app impersonation attacks during the OAuth interactions.
The Google sign-in and authorization flows are powered by the Google OAuth platform and over the years we have developed and supported a number of ways for app developers to integrate with supported OAuth flows. With the goal of keeping users safer online, we will end support for two legacy flows and will require developers to migrate to alternative implementation methods that offer greater protections.
To ensure a smooth transition and avoid any service interruption we will give ample time to implement and meet the compliance dates which are specified below. We will share further updates on this rollout via email so please make sure your support email address is up to date in project settings on the Google API console.
Loopback IP address flow will be disallowed for native iOS, Android and Chrome OAuth client types
The Loopback IP address flow is vulnerable to man in the middle attack where a malicious app, accessing the same loopback interface on some operating systems, may intercept the OAuth response and gain access to the authorization code. We intend to remove this threat vector by disallowing this flow for iOS, Android and Chrome app OAuth client types. The existing clients will be able to migrate to more secure implementation methods. New clients will be unable to use this flow starting on March 14, 2022.
What do I need to do
Determine if your app is using the Loopback IP address flow
You can inspect your app code or the outgoing network call (in case your app is using an OAuth library) to determine if the Google OAuth authorization request your app is making has the following values for “redirect_uri” parameter.
redirect_uri=http://127.0.0.1:port or http://[::1]:port">http://[::1]:port or
http://localhost:port
Migrate to an alternative flow
If your app is using the Loopback IP address method you need to migrate to another method which is more secure by default. Please consider the following alternative methods for migration.
- iOS clients: Google Sign-In for iOS SDK
- Android clients: Google Sign-In for Android SDK
- Chrome clients: Chrome Identity API
Key dates for compliance
- Mar 14, 2022 - new OAuth usage will be blocked for the Loopback IP address flow
- Aug 1, 2022 - a user-facing warning message may be displayed to non-compliant OAuth requests one month before the compliance date
- Aug 31, 2022 - the Loopback IP address flow is blocked for existing clients
OAuth out-of-band (oob) flow will be deprecated
OAuth out-of-band (OOB) is a legacy flow developed to support native clients which do not have a redirect URI like web apps to accept the credentials after a user approves an OAuth consent request. The OOB flow poses a remote phishing risk and clients must migrate to an alternative method to protect against this vulnerability. New clients will be unable to use this flow starting on Feb 28, 2022.
What do I need to do
Determine if your app is using the OOB flow
You can inspect your app code or the outgoing network call (in case your app is using an OAuth library) to determine if the Google OAuth authorization request your app is making has the following values for “redirect_uri” parameter.
redirect_uri=urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob or urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob:auto or oob
Migrate to an alternative flow
If your app is using the OOB method you need to migrate to another method which is more secure by default. Please consider the following alternative methods for migration.
- iOS clients: Google Sign-In for iOS SDK
- Android clients: Google Sign-In for Android SDK
- Chrome clients: Chrome Identity API
- Desktop clients: OAuth 2.0 for Desktop apps
Key dates for compliance
- Feb 28, 2022 - new OAuth usage will be blocked for the OOB flow
- Sep 5, 2022 - a user-facing warning message may be displayed to non-compliant OAuth requests
- Oct 3, 2022 - the OOB flow is deprecated for existing clients
User-facing warning message
A user-facing warning message may be displayed for non-compliant requests one month before the aforementioned OAuth methods are due to be blocked. The message will convey to the users that the app may be blocked soon while displaying the support email that you have registered in the OAuth consent screen in Google API Console.
[Sample user-facing warning]
The developers can acknowledge the user-facing warning message and suppress it by passing a query parameter in the authorization call as shown below.
- Go to the code in your app where you send requests to Google's OAuth 2.0 Authorization Endpoint.
- Add a parameter with a value of the enforcement date
- For OOB: Add an
ack_oob_shutdownparameter with a value of the enforcement date: 2022-10-03. Example:ack_oob_shutdown=2022-10-03- For Loopback IP address: Add an
ack_loopback_shutdownparameter with a value of the enforcement date: 2022-08-31. Example:ack_loopback_shutdown=2022-08-31
User-facing error message
If an app is not updated to meet compliance by the required date the authorization requests will be blocked and users may encounter an invalid request error screen (sample shown below).
[Sample user-facing error]
Source: Google Developers Blog
Google Workspace Updates Weekly Recap – January 7, 2022
New updates
Previous announcements
Source: Google Workspace Updates
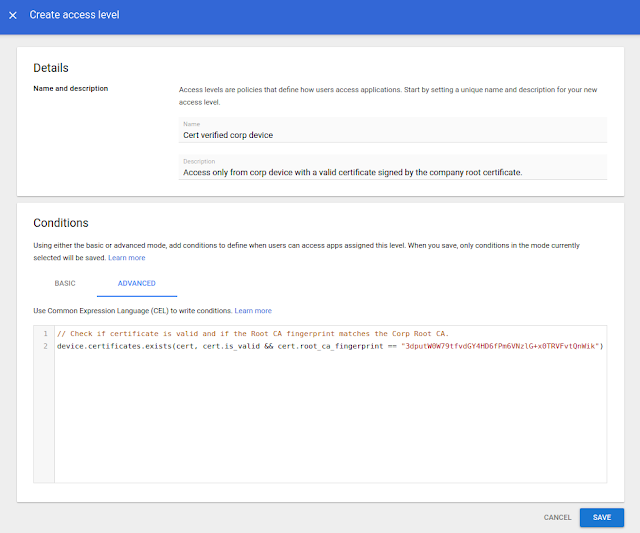
Use a new enterprise certificate condition to set context-aware access rules for company-managed devices
Quick launch summary
Getting started
- Admins: The feature is available by default, but needs to be configured before use. Use our Help Center to learn more about configuring enterprise certificates and configuring context-aware access rules.
- End users: No end user impact.
Rollout pace
- This feature is now available for all eligible users.
Availability
- Available to Google Workspace Enterprise Standard, Enterprise Plus, Education Standard, Education Plus, and Cloud Identity Premium customers
- Not available to Google Workspace Essentials, Business Starter, Business Standard, Business Plus, Enterprise Essentials, Education Fundamentals, Frontline, and Nonprofits, as well as G Suite Basic and Business, and Cloud Identity Free customers
Resources
Source: Google Workspace Updates
Making dynamic groups more powerful with custom user attributes and OrgUnit queries
What’s changing
- First, dynamic groups can now be defined by querying custom user attributes. This functionality is available as an open beta (no sign up required).
- Second, dynamic groups can also be defined based on users’ membership in Organizational Units (OUs). This feature is now generally available.
Who’s impacted
Why you’d use it
- Create a dynamic group for all users of a subsidiary (an organizational unit) based in a particular city or state.
- Create a dynamic group with all users with a custom attribute of a “job_skill” or “speciality”.
Getting started
- Admins: To take advantage of this new dynamic group functionality, you will need to have already defined custom user fields or organizational units.
- Once this is in place you can test membership queries and then create / update dynamic groups to take advantage of them.
- To query a customer attribute “EmployeeNumber” (based on this sample schema):
user.custom_schemas.employmentData.EmployeeNumber == '123456789' - To query all direct members of an organizational unit:
user.org_unit_id==orgUnitId('03ph8a2z1enx4lx') - To query all direct and indirect members of an organizational unit:
user.org_units.exists(org_unit, org_unit.org_unit_id==orgUnitId('03ph8a2z1khexns')) - End users: Not available to end users.
Rollout pace
- Custom user attribute queries are available now for all users in open beta (no sign up required)
- Organizational unit based dynamic group queries are now generally available for all users.
Availability
- Available to Google Workspace Enterprise Standard, Enterprise Plus, and Education Plus customers
- Not available to Google Workspace Essentials, Business Starter, Business Standard, Business Plus, Enterprise Essentials, Education Fundamentals, Frontline, and Nonprofits, as well as G Suite Basic and Business customers
Resources
Source: Google Workspace Updates
Set user language programmatically with the Directory API
Quick launch summary
Getting started
- Admins and developers: No action required. This function is available by default. Use our API documentation to learn more about using the Directory API to update the ULS.
- End users: No end user impact.
Rollout pace
- Rapid Release and Scheduled Release domains: Full rollout (1–3 days for feature visibility) starting on December 9, 2021.
Availability
- Available to all Google Workspace customers, as well as G Suite Basic and Business customers
Resources
Source: Google Workspace Updates
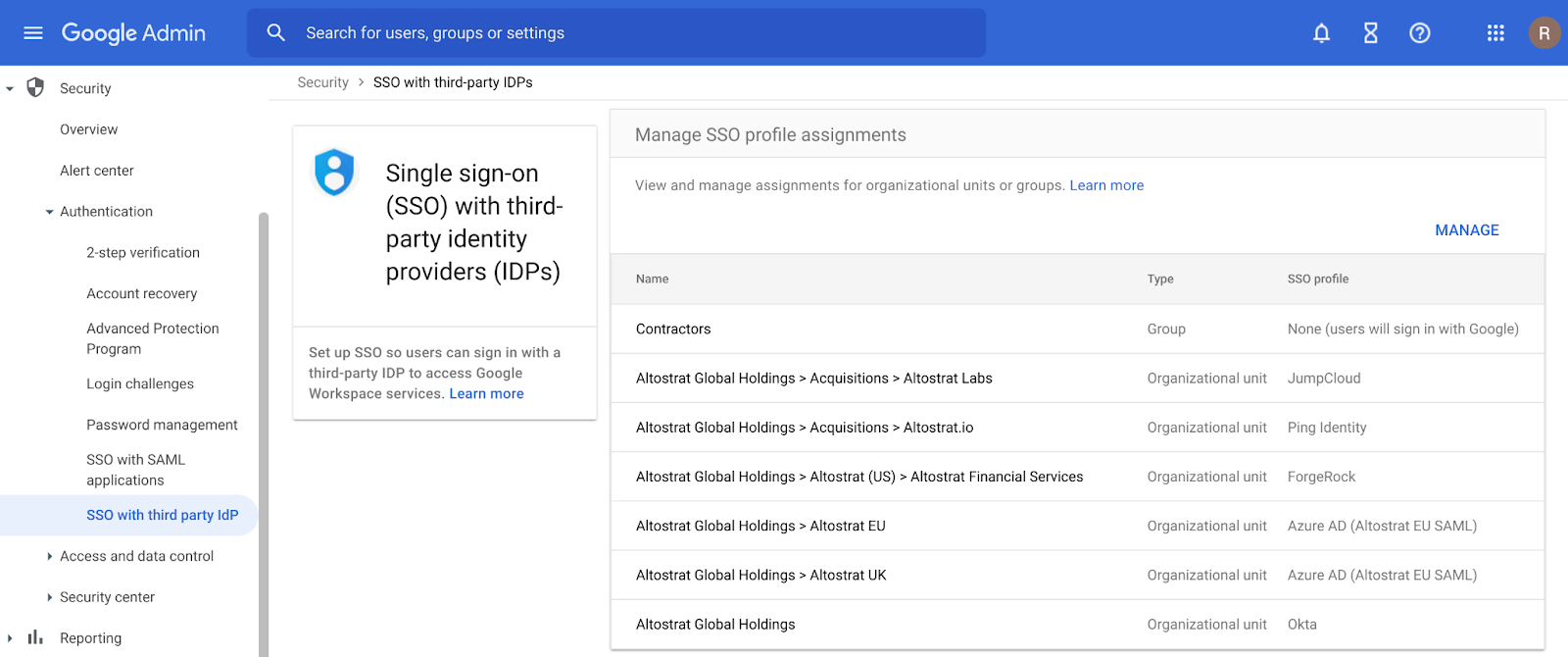
Assign SSO profile to organizational units or groups with the SAML Partial SSO feature, now generally available
What’s changing
Earlier this year, we announced a beta for assigning SSO profiles to organizational units or groups. This feature is now generally available and allows admins to specify groups or organizational units (OUs) to authenticate a subset of your users using Google.
Who’s impacted
Admins
Why it’s important
Currently, when you configure SSO with a third-party identity provider, the setting applies to your entire domain. However, there are some instances where you may want a subset of your users, such as vendors or contractors, to authenticate with Google instead. The Partial SSO feature gives you the flexibility to specify the authentication method for various users in your organization as needed.
Getting started
- Admins: In the Admin console, navigate to Security > Settings > Set up single sign-on (SSO) with a third party IdP > Manage SSO Profile assignments. Visit the Help Center to learn more about assigning SSO profiles to organizational units or groups.
- End users: No action required.
Rollout pace
- Rapid Release and Scheduled Release domains: Full rollout (1–3 days for feature visibility) starting on November 19, 2021
Availability
- Available to Google Workspace Business Starter, Business Standard, Business Plus, Enterprise Essentials, Enterprise Standard, Enterprise Plus, Education Fundamentals, Education Plus, Frontline, and Nonprofits, as well as G Suite Basic and Business customers
- Available to all Cloud Identity customers
- Not available to Google Workspace Essentials customers

.png)
.png)
 Posted by Vikrant Rana, Product Manager and Badi Azad, Group Product Manager, Google
Posted by Vikrant Rana, Product Manager and Badi Azad, Group Product Manager, Google