Google Cloud Platform (GCP) employs several security measures to help ensure authenticity, privacy and integrity of your data in transit. As enterprise users turn to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) as their preferred deployment model, they too require the same levels of privacy for their data.
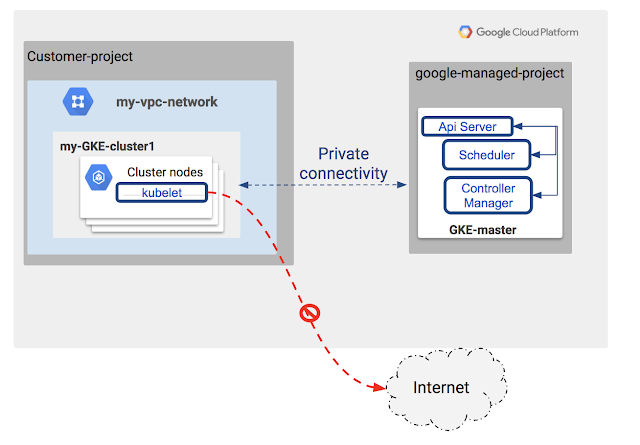
Today, we're excited to announce the beta launch of Kubernetes Engine Private Clusters. Now, Kubernetes Engine allows you to deploy clusters privately as part of the Google Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), which provides an isolated boundary where you can securely deploy your applications. With Kubernetes Engine Private Clusters, your cluster’s nodes can only be accessed from within the trusted VPC. In addition, private clusters protect the master node from unwanted access, as the master is completely blocked from access from the internet by default.
In the Kubernetes Engine Private Cluster model, your nodes have access to the rest of your VPC private deployments, including private access to Google managed services such as gcr.io, Google Cloud Storage and Google BigQuery. Access to the internet isn’t possible unless you set up additional mechanisms such as a NAT gateway.
Kubernetes Engine Private Clusters greatly simplify PCI-DSS compliance of your deployments, by limiting how a cluster can be reached from outside of a private network.
Let's take a closer look at how Kubernetes Engine Private Clusters fit into GCP’s private VPC model.
Get started with Private Clusters on Kubernetes Engine
The following tutorial highlights how you can enable Private Clusters for your deployments. In this private cluster model, the Kubernetes Engine cluster nodes are allocated private IP addresses and the master is protected from internet access. As you can see in the example below, you enable a Kubernetes Engine Private Cluster at cluster creation time, selecting the private IP range within your RFC 1918 IP space to use for your master, nodes, pods and services.
Note that you must deploy Kubernetes Engine Private Clusters with IP Aliases enabled. It also requires cluster version 1.8.5 or later.
The following diagram displays the internals of private clusters:
The fastest way to get started is to use the UI during cluster creation:
Alternatively, you can also create your private cluster with the GCP gcloud CLI:
# Create a Private Cluster with IP Alias auto-subnetwork)
gcloud beta container clusters create --project=<project_id>>
--zone= --private-cluster --master-ipv4-cidr=
--enable-ip-alias --create-subnetwork=""</master_cidr_block></zone></project_id></cluster></code> The Master Authorized Network firewall protects access to the Kubernetes Engine master. When Kubernetes Engine Private Clusters is enabled, it's set to “default deny,” making your master inaccessible from the public internet at creation time.
Try it out today!
Create a Kubernetes Engine Private Cluster today. Stay tuned for more updates in this space as we continue to invest in Kubernetes Engine to ensure customers get defense-in-depth security features. Interested in optimal load balancing?
Do you want to get access to a more container-native load balancing approach in Kubernetes Engine? Sign up here!